This is an old revision of this page, as edited by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) at 23:04, 16 October 2011 (Updating {{chembox}} (changes to verified fields - updated 'DrugBank_Ref', 'UNII_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report errors or bugs)). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 23:04, 16 October 2011 by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) (Updating {{chembox}} (changes to verified fields - updated 'DrugBank_Ref', 'UNII_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report errors or bugs))(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)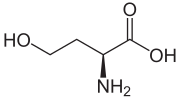 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name (S)-2-Amino-4-hydroxybutanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.538 |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C4H9NO3 |
| Molar mass | 119.12 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Homoserine (also called isothreonine) is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCH(NH2)CH2CH2OH. L-Homoserine is not one of the common amino acids encoded by DNA. It differs from the proteinogenic amino acid serine by insertion of an additional methylene group. Homoserine, or its lactone form, is the product of a cyanogen bromide cleavage of a peptide by degradation of methionine.
Homoserine is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of three essential amino acids: methionine, threonine (an isomer of homoserine), and isoleucine. It forms by two reductions of aspartic acid via the intermediacy of aspartate semialdehyde.
References
- Berg, J. M.; Stryer, L. et al. (2002), Biochemistry. W.H. Freeman. ISBN 0-7167-4684-0
This biochemistry article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |