This is an old revision of this page, as edited by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) at 02:47, 21 October 2011 (Updating {{drugbox}} (changes to verified and watched fields - updated 'ChEBI_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref', 'CAS_number_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report errors or bugs)). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 02:47, 21 October 2011 by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) (Updating {{drugbox}} (changes to verified and watched fields - updated 'ChEBI_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref', 'CAS_number_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report errors or bugs))(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Pharmaceutical compound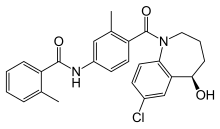 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | N-{4-undeca-8,10,12-triene-2-carbonyl]-3-methyl-phenyl}-2-methyl-benzamide |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a609033 |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Unknown (40% absorbed) |
| Protein binding | 99% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP3A4-mediated) |
| Elimination half-life | 12 hours (terminal) |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.219.212 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C26H25ClN2O3 |
| Molar mass | 448.941 g/mol g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Tolvaptan (INN), also known as OPC-41061, is a selective, competitive vasopressin receptor 2 antagonist used to treat hyponatremia (low blood sodium levels) associated with congestive heart failure, cirrhosis, and the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH). Tolvaptan was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on May 19, 2009, and is sold by Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co. under the trade name Samsca.
Tolvaptan is also in fast-track clinical trials for polycystic kidney disease. In a 2004 trial, tolvaptan, when administered with traditional diuretics, was noted to increase excretion of excess fluids and improve blood sodium levels in patients with heart failure without producing side effects such as hypotension (low blood pressure) or hypokalemia (decreased blood levels of potassium) and without having an adverse effect on kidney function.
Chemistry
Chemical synthesis:
References
- WHO International Working Group for Drug Statistics Methodology (August 27, 2008). "ATC/DDD Classification (FINAL): New ATC 5th level codes". WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. Retrieved 2008-09-05.
- "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 Oct 2023.
- Shoaf S, Elizari M, Wang Z; et al. (2005). "Tolvaptan administration does not affect steady state amiodarone concentrations in patients with cardiac arrhythmias". J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 10 (3): 165–71. doi:10.1177/107424840501000304. PMID 16211205.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Otsuka Maryland Research Institute, Inc.
- Gheorghiade M, Gattis W, O'Connor C; et al. (2004). "Effects of tolvaptan, a vasopressin antagonist, in patients hospitalized with worsening heart failure: a randomized controlled trial". JAMA. 291 (16): 1963–71. doi:10.1001/jama.291.16.1963. PMID 15113814.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Kondo, K.; Ogawa, H.; Yamashita, H.; Miyamoto, H.; Tanaka, M.; Nakaya, K.; Kitano, K.; Yamamura, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Onogawa, T.; et al.; Bioor. Med. Chem. 1999, 7, 1743.
- Gheorghiade M, Niazi I, Ouyang J; et al. (2003). "Vasopressin V2-receptor blockade with tolvaptan in patients with chronic heart failure: results from a double-blind, randomized trial". Circulation. 107 (21): 2690–6. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000070422.41439.04. PMID 12742979.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
| Diuretics (C03) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfonamides (and etacrynic acid) |
| ||||||||
| Potassium-sparing (at CD) |
| ||||||||
| Osmotic diuretics (PT, DL) | |||||||||
| Vasopressin receptor inhibitors (DCT and CD) | |||||||||
| Other | |||||||||
| Combination products | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Hypothalamic-pituitary hormones and analogues (H01) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothalamus |
| ||||||
| Anterior pituitary |
| ||||||
| Posterior pituitary |
| ||||||
Template:Neuropeptide agonists and antagonists
This hormonal preparation article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |
This drug article relating to the cardiovascular system is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |
