| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
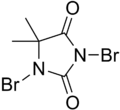
| Preferred IUPAC name 1,3-Dibromo-5,5-dimethylimidazolidine-2,4-dione | |||
| Other names DBDMH, Dibromantin, Dibromodimethylhydantoin | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.938 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| PubChem CID | |||
| UNII | |||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Chemical formula | C5H6Br2N2O2 | ||
| Molar mass | 285.923 g·mol | ||
| Appearance | White solid | ||
| Density | 1.36 g/cm | ||
| Melting point | 197 to 203 °C (387 to 397 °F; 470 to 476 K) | ||
| Solubility in water | 0.1 g/100 mL (20 °C) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
| Pictograms |    
| ||
| Signal word | Danger | ||
| Hazard statements | H301, H302, H314, H317, H319, H410 | ||
| Precautionary statements | P260, P261, P264, P270, P272, P273, P280, P301+P310, P301+P312, P301+P330+P331, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P330, P333+P313, P337+P313, P363, P391, P405, P501 | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |||
DBDMH (also known as 1,3-Dibromo-5,5-Dimethylhydantoin) is an organic compound derived from the heterocycle called dimethylhydantoin. This white crystalline compound with a slight bromine odor is widely used as a disinfectant used for drinking water purification, recreational water treatment, as a bleaching agent in pulp and paper mills, and for treating industrial/commercial water cooling systems. Its action does not involve the use of hypochlorous acid.
Mechanism of action
1,3-Dibromo-5,5-Dimethylhydantoin is a source of bromine, which is equivalent to hypobromous acid (HOBr).
- Br2X + 2 H2O → 2 HOBr + H2X
(Where H2X is 5,5-dimethylhydantoin)
With a pKa of 8.6, hypobromous acid partially dissociates in water:
- HOBr ⇌ H + BrO
Hypobromous acid serves as a source of "Br," which produces bromide ions in the process of disinfection:
- HOBr + live pathogens → Br + dead pathogens
The resulting bromide ions can then undergo oxidation to hypobromous acid in the presence of an oxidizer of sufficient strength e.g. ozone, hypochlorous acid, potassium monopersulfate. This reoxidation process is commonly called "activation" of the bromide ion:
- Br + HOCl → HOBr + Cl
References
- David Ioffe, Arieh Kampf "Bromine, Organic Compounds" in Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, 2002, by John Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/0471238961.0218151325150606.a01