 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
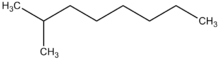
| Preferred IUPAC name 2-Methyloctane | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Beilstein Reference | 1696917 |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.019.771 |
| EC Number |
|
| Gmelin Reference | 240576 |
| MeSH | nonane |
| PubChem CID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1920 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C9H20 |
| Molar mass | 128.259 g·mol |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Gasoline-like |
| Density | 0.718 g/mL |
| Melting point | −54.1 to −53.1 °C; −65.5 to −63.7 °F; 219.0 to 220.0 K |
| Boiling point | 150.4 to 151.0 °C; 302.6 to 303.7 °F; 423.5 to 424.1 K |
| log P | 5.293 |
| Vapor pressure | 0.59 kPa (at 25.0 °C) |
| Henry's law constant (kH) |
1.7 nmol Pa kg |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | −108.13×10 cm/mol |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.405 |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Heat capacity (C) | 284.34 J K mol |
| Std molar entropy (S298) |
393.67 J K mol |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH298) |
−275.7 – −273.7 kJ mol |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH298) |
−6125.75 – −6124.67 kJ mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |   
|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H226, H304, H315, H319, H332, H336 |
| Precautionary statements | P261, P301+P310, P305+P351+P338, P331 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 |
| Flash point | 31.0 °C (87.8 °F; 304.1 K) |
| Autoignition temperature |
205.0 °C (401.0 °F; 478.1 K) |
| Explosive limits | 0.87–2.9% |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
| PEL (Permissible) | none |
| REL (Recommended) | TWA 200 ppm (1050 mg/m) |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) | N.D. |
| Related compounds | |
| Related alkanes | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
2-Methyloctane is a branched alkane hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C9H20. It is a colorless, flammable liquid
Combustion reactions
2-Methyloctane burns in the same way as other alkanes. Where there is enough oxygen, nonane burns to form water and carbon dioxide, so 2-methyloctane would do the same.
When insufficient oxygen is present for complete combustion, carbon monoxide is produced.
- 2 C9H20 + 19 O2 → 18 CO + 20 H2O
See also
References
- "nonane - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 16 September 2004. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 6 January 2012.
- ^ NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0466". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- "NFPA Hazard Rating Information for Common Chemicals". Archived from the original on 2015-02-17. Retrieved 2015-03-13.
| Hydrocarbons | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saturated aliphatic hydrocarbons |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aromatic hydrocarbons |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||