| This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (April 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

An articulated locomotive is a steam locomotive (rarely, an electric locomotive) with one or more engine units that can move independently of the main frame. Articulation allows the operation of locomotives that would otherwise be too large to negotiate a railroad's curves, whether mainlines or special lines with extreme curvature such as logging, industrial, or mountain railways.
Articulated locomotives saw service in many nations, but were very popular on narrow-gauge railways in Europe. The largest examples were developed in the United States, where the Union Pacific Big Boy 4-8-8-4s and the Allegheny H-8 2-6-6-6s were some of the largest steam locomotives ever built, with Big Boy 4014 remaining as the largest, and last of its kind, to still operate.
Many schemes for articulation were developed over the years. Of these, the Mallet locomotive and its simple-expansion derivative were the most popular, followed by the Garratt type (mostly built in the United Kingdom, popular throughout Europe, Africa and European colonies), and the various geared steam locomotive types, the latter largely used in logging, mining and industry. Most other types saw only limited success.
As distinct from articulated locomotives, a non-articulated locomotive is referred to as a straight or rigid locomotive.
Articulated steam locomotive types
Major types
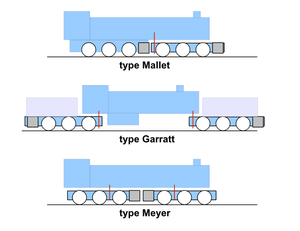
The major types of articulated locomotive are:
- The Fairlie, with two powered trucks under a double boiler, or its Single Fairlie single-boiler derivative with one powered and one unpowered truck (known as a Mason Bogie in the United States).
- The Garratt locomotive, with an engine unit at each end carrying coal and water supplies, and a boiler unit articulated between them.
- The Mallet locomotive, with one fixed engine under the rear of the locomotive and a radially swinging engine unit in front.
- The Meyer locomotive, with two powered engine trucks under the locomotive (generally with the cylinders inward). Also, the Kitson-Meyer variant with the trucks spread apart to allow a deeper firebox between them.
Simple expansion
Simple expansion, or simple, articulated steam engines had two sets of equally sized cylinders. High-pressure steam was supplied to all cylinders and exhausted out of the stack once it had been used. The American simple-expansion articulated, thanks largely to the smaller mass of the forward cylinders when compared to the compound-expansion Mallets allowing for higher piston speed, were generally better suited for high speed than their compound cousins. Examples of the "simple mallet" design include the Union Pacific Big Boys and Challengers, the Chesapeake and Ohio class H-8, the 2-8-8-4 "Yellowstones", the majority of Southern Pacific's Cab-forwards, and the Norfolk & Western A-class.
Compound expansion
Compound expansion, or compound, articulated steam engines like Anatole Mallet's original idea, consist of two sets of unequally sized cylinders. The smaller pair of cylinders near the cab was fed with high pressure steam directly from the boiler and then the steam was passed into a pair of low-pressure cylinders at the front, with larger diameter to offset the lower pressure, before exhausting through the smokestack. While the thermal efficiency was greatly improved through the compound use of steam in Mallet designs, the large low-pressure cylinders posed unique limitations, both in terms of loading gauge (the cylinders could only be as large as the track and track-side infrastructure allowed) and in terms of performance at speed. The large and consequently heavier pistons caused stability issues at higher speed, which generally limited compound expansion articulated locomotives to below 30 or 40 miles per hour. A notable exception to this was to be found in later iterations of Norfolk & Western Y-class 2-8-8-2s, which could and did often exceed 50 miles per hour in service as well as being one of the hardest-pulling steam locomotives ever built.
The first Garratt locomotives constructed, the Tasmanian Government Railways K class were also compound locomotives, but were complicated as a result. All subsequent Garratts were simple engines only.
Geared types
There were various types of articulated geared steam locomotive, including:
Other types
- du Bousquet locomotive
- Engerth locomotive
- Gölsdorf axle
- Golwé locomotive
- Hagans locomotive, such as the Prussian T 13 (Hagans variant)
- Klien-Lindner locomotive
- Krauss-Helmholtz bogie
- Luttermöller axle
Electric locomotives
There are several classes of articulated electric locomotives of generally two types:
- Three sections, where the middle part sits on the two outer parts (similar to the Garratt design), e.g.
- Two sections which share a central or Jacobs bogie, e.g.
- FS Class E.636 in Italy, first built in 1940
- HŽ series 1061, a derivative of E.636 operating in Croatia - also known as SŽ series 362 in Slovenia and as JŽ series 362 in Yugoslavia
- FS Class E.646 in Italy, first built in 1958
- FS Class E.656 operating in Italy since 1975
- Rhaetian Railway Ge 6/6 II in Switzerland
- New Zealand EW class, built by English Electric in 1952.
The conventional electric and diesel locomotive dual bogie design uses the same general configuration as the Meyer design but is not considered to be articulated.
References
- Wiener, Lionel, Articulated Locomotives, 1930, reprinted 1970 by Kalmbach Publishing Company as ISBN 0-89024-019-1
External links
| Steam locomotive wheel arrangements (Whyte notation) | |
|---|---|
| Single engine types |
|
| Divided drive and Duplex engine types | |
| Articulated locomotives Fairlie, Meyer and Garratt types | |
| Articulated locomotives Mallet types | |
| Articulated locomotives Triplex and other Multiplex types | |
| Articulated locomotives Engerth types | |
| Geared locomotives | |