| Battle of Daugavpils | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of Polish-Soviet War and Latvian War of Independence | |||||||
 Renault FT tanks of the Polish 2nd Tank Regiment preparing for the battle | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
22,000 Latvians 20,000 Poles | Around 26,700 soldiers | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| Unknown | Unknown | ||||||
| Polish–Soviet War | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
| Latvian War of Independence | |
|---|---|
|
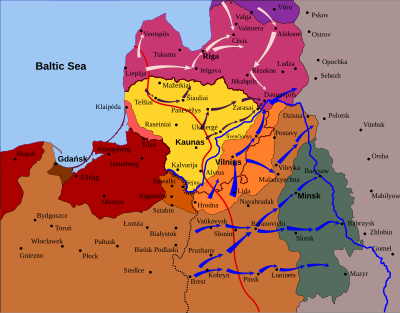
The Battle of Daugavpils, or Battle of Dyneburg, or Operation Winter was the final battle during the Polish-Soviet War of 1919. A joint Polish and Latvian force, operating under Polish Staff orders known as "Operation Winter", attacked the Red Army garrison in Dunaburg, or Daugavpils, from 3 to 5 January 1920.
From the Polish perspective, the battle was part of the Polish-Soviet War. In Latvia, it is considered to be part of Latvian War of Independence.
Background
The Polish commander of the 1st Legions Infantry Division and 3rd Legions Infantry Division, General (later Marshal) Edward Rydz-Śmigły had been occupying the left bank of the Dvina since August. The Latvian Foreign Minister had met with Pilsudski in Vilnius (then Wilno in Polish) in October 1919 and asked for assistance at Dunaburg. The Poles wanted to prevent the Soviet XVth and XVIth armies from consolidating at that juncture and readily agreed. A final agreement was reached on 30 December 1919, and a military alliance was signed between the governments of Poland and Latvia.
Battle
General Rydz-Śmigły was given the command over a small Operational Group composed of his 1st Legions Infantry Division, the 3rd Legions Infantry Division and several minor Latvian auxiliary forces. In addition, the force included Renault FT tanks of the 2nd company, 1st Tank Regiment, which was commanded by the French Captain Jean Dufour.
The battle for the city and its surroundings took place under harsh weather conditions. The area was covered with more than 1 metre (3.3 ft) of snow and the temperature dropped below −25 °C (−13 °F), which permitted the Poles to cross the frozen Dvina. The Polish 3rd Legionary Division stormed the Daugavpils fortress, and the 1st Infantry Division attacked from the north. The Red Army garrison retreated to the west, where it surrendered to the Latvians. On 5 January 1920, Dunaburg was turned over to the Latvian Republic.
Aftermath
Interwar relations between Poland and Latvia were mostly good because of the battle although Latvia refused to join Poland in its continued struggle against Soviet Russia. Other problems that precluded the Polish and Latvian governments from expanding their relationship were opposition from Lithuania, which was hostile towards Poland after the Polish-Lithuanian War, and a dispute about six Latvian rural municipalities and the city of Grīva that had many Poles south of the Daugava River.
Several forms of alliance were proposed by Poland, such as Latvia joining the Międzymorze, a federation led by Poland. However, Latvia chose instead to join the Baltic Entente.
See also
References
- ^ Davies, N., 1972, White Eagle, Red Star, London: Orbis Books, ISBN 9780712606943
- Daniel Kochan (2006). "Łotewski sojusznik" [Latvian ally]. Polska Zbrojna (in Polish). ISSN 0867-4523. OCLC 22656693. Retrieved 25 October 2006.
Categories:
- 1919 in Poland
- 1920 in Poland
- Battles of the Latvian War of Independence
- Battles of the Polish–Soviet War
- Latvian Socialist Soviet Republic
- 1919 in Latvia
- 1920 in Latvia
- History of Daugavpils
- January 1920 events
- Battles of the Russian Civil War in 1919
- Battles of the Russian Civil War in 1920
- Tank battles involving Poland
- Tank battles involving the Soviet Union
- Latvia–Poland relations