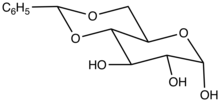
In organic chemistry, a benzylidene acetal is the functional group with the structural formula C6H5CH(OR)2 (R = alkyl, aryl). Benzylidene acetals are used as protecting groups in glycochemistry. These compounds can also be oxidized to carboxylic acids in order to open important biological molecules, such as glycosaminoglycans, to other routes of synthesis. They arise from the reaction of a 1,2- or 1,3-diols with benzaldehyde. Other aromatic aldehydes are also used.
References
- David Crich (2010). "Mechanism of a Chemical Glycosylation Reaction". Acc. Chem. Res. 43 (8): 1144–1153. doi:10.1021/ar100035r. PMID 20496888.
- S. Hanessian (1987). "6-Bromo-6-deoxy Hexose Derivatives By Ring Opening Of Benzylidene Acetals With N-bromosuccinimide: Methyl 4-o-benzoyl-6-bromo-6-deoxy-α-d-glucopyranoside". Org. Synth. 65: 243. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.065.0243.
- Banerjee, Amit; Senthilkumar, Soundararasu; Baskaran, Sundarababu (2015-12-07). "Benzylidene Acetal Protecting Group as Carboxylic Acid Surrogate: Synthesis of Functionalized Uronic Acids and Sugar Amino Acids". Chemistry - A European Journal. 22 (3): 902–906. doi:10.1002/chem.201503998. ISSN 0947-6539. PMID 26572799.
- Hiroyuki Osajima; Hideto Fujiwara; Kentaro Okano; Hidetoshi Tokuyama; Tohru Fukuyama (2009). "Protection Of Diols With 4-(Tert-butyldimethylsilyloxy)benzylidene Acetal And Its Deprotection". Org. Synth. 86: 130. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.086.0130.