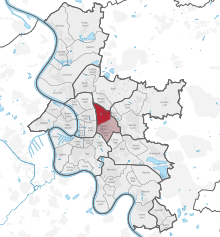
Düsseltal is a quarter of Düsseldorf within Borough 2, it is known for its relatively well-off population and developed around an old convent. It is also known as Düsseldorf-Zoo (after Düsseltal's S-Bahn station), because, until 1943, there was a zoological garden in Düsseltal. The word Düsseltal is German for the valley of the river Düssel.

Geography
Düsseltal's neighboring quarters are, clockwise from the north: Rath, Grafenberg, Flingern, and Derendorf. It is also bordered by the Cologne–Duisburg railway and the Grafenberg forest.
Düsseltal has an area of 2.88 km (1.11 sq mi), and 28,032 inhabitants (2020).
History

There was a low population density in the region between Düsseldorf (proper) and Grafenberg until the end of the 19th century.
In the Middle Ages, the knights Hayc von Flingern ruled the town. The oldest buildings of Düsseltal are the Speckerhöfe and the Buscher Mühle, first mentioned in the 14th century.
Jan Wellem, Elector Palantine, donated the Speckerhöfe to the Cistercian monks of Orval who founded a priory in 1701. The monks were henceforth also called the Specker monks. Later on, the monastery took on the name Düsselthal which then became the name of the borough.
Count Adalbert von Recke-Volmerstein founded the orphanage Düsseltal in 1822. According to legend it was financed in part by the sale of "original" Eau de Cologne made with water taken from the Düssel. In 1835, he founded the first ever deaconess institute in Düsseltal.
During the Industrial Revolution, the factory of Haniel & Lueg was built in Düsseltal, and the town hosted an international industrial exhibition in 1880, with more than 3,000 companies exhibiting in more than 100 halls. It was opened by Emperor William II.
The zoological garden was initiated by the zoologist Alfred Brehm and founded in 1876. It opened officially on May 31, 1876. During World War II, in 1943, it was completely destroyed. After World War II, Düsseltal became a more exclusive borough of Düsseldorf.
Attractions
Düsseltal is home to the Düsseldorfer EG, today known as DEG Metro Stars, an ice hockey club that won six German championships. The Zoopark surrounds the Ice Stadium on Brehmstraße where they played until 2006. Since DEL-Season 06/07 they play in the multi-use indoor arena ISS Dome. Another building of interest is the Catholic Paulus Church, built in neoclassicist style.
Düsseltal today
Today, Düsseltal is one of the most exclusive boroughs of Düsseldorf. Many Japanese live there (but not as many as in Oberkassel). The Rethelstraße is a well-known shopping district.
References
- "Stadtgebietsprofile - Stadtbezirke und Stadtteile 03 Geografie" (PDF). Landeshauptstadt Düsseldorf. Retrieved 4 November 2022.
- "Stadtgebietsprofile - Stadtbezirke und Stadtteile 05 Bevölkerung" (PDF). Landeshauptstadt Düsseldorf. Retrieved 4 November 2022.
- Communal Administration, District Mayor (German)
- Communal Administration (German)
- Websites from Düsseldorf-Düsseltal on Duesselgo.de
| Boroughs of Düsseldorf | ||
|---|---|---|
 | ||
| ||
51°14′27″N 6°48′12″E / 51.24083°N 6.80333°E / 51.24083; 6.80333
Category: