 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 2-Methylpropyl acetate | |
| Other names
Isobutyl acetate Isobutyl ester | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.406 |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C6H12O2 |
| Molar mass | 116.16 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colourless liquid |
| Odor | Fruity, floral |
| Density | 0.875 g/cm, liquid |
| Melting point | −99 °C (−146 °F; 174 K) |
| Boiling point | 118 °C (244 °F; 391 K) |
| Solubility in water | Slightly soluble 0.63–0.7 g/100g at 20 °C |
| Vapor pressure | 13 mmHg (20 °C) |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | −78.52·10 cm/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 18 °C; 64 °F; 291 K |
| Explosive limits | 1.3–10.5% |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) | 4673 mg/kg (rabbit, oral) 13,400 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
| PEL (Permissible) | TWA 150 ppm (700 mg/m) |
| REL (Recommended) | TWA 150 ppm (700 mg/m) |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) | 1300 ppm |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
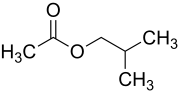
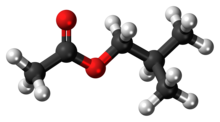
The chemical compound isobutyl acetate, also known as 2-methylpropyl ethanoate (IUPAC name) or β-methylpropyl acetate, is a common solvent. It is produced from the esterification of isobutanol with acetic acid. It is used as a solvent for lacquer and nitrocellulose. Like many esters it has a fruity or floral smell at low concentrations and occurs naturally in raspberries, pears and other plants. At higher concentrations the odor can be unpleasant and may cause symptoms of central nervous system depression such as nausea, dizziness and headache.
A common method for preparing isobutyl acetate is Fischer esterification, where precursors isobutyl alcohol and acetic acid are heated in the presence of a strong acid.
Isobutyl acetate has three isomers: n-butyl acetate, tert-butyl acetate, and sec-butyl acetate, which are also common solvents.
References
- Isobutyl acetate Chemical Profile, Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety
- Isobutyl acetate at chemicalland21.com
- ^ NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0351". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- "Isobutyl acetate". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
| Esters | |
|---|---|
| Methyl esters | |
| Ethyl esters | |
| Propyl esters | |
| Butyl esters | |
| Amyl esters | |
| Hexyl esters | |
| Phenyl esters | |
| Heptyl esters | |
| Benzyl esters | |