| This article relies excessively on references to primary sources. Please improve this article by adding secondary or tertiary sources. Find sources: "West Japan Railway Company" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| [REDACTED] | |
 The company headquarters in Kita-ku, Osaka The company headquarters in Kita-ku, Osaka | |
| Native name | 西日本旅客鉄道株式会社 |
|---|---|
| Romanized name | Nishi-nihon Ryokaku Tetsudō Kabushiki-gaisha lit. "West Japan Passenger Railway Stock Company" |
| Company type | Public KK |
| Traded as |
|
| Industry | Rail transport |
| Predecessor | Japanese National Railways (JNR) |
| Founded | Osaka, Japan (1 April 1987; 37 years ago (1987-04-01), privatization of JNR) |
| Headquarters | 4-24 Shibata 2-chome, Kita-ku, Osaka, 530-8341, Japan |
| Area served | |
| Key people | Takayuki Sasaki (Executive Chairman of the Board) Seiji Manabe (Representative Director and President) |
| Products | ICOCA (a rechargeable contactless smart card) |
| Services |
|
| Revenue | |
| Operating income | |
| Net income | |
| Total assets | |
| Total equity | |
| Owners | Investment trusts (TMTBJ 5.52%, JTSB 4.74%) SMBC (3.33%) MUFG Bank (3.27%) Nippon Life (2.08%) As of 31 March 2018 |
| Number of employees |
|
| Divisions |
|
| Subsidiaries |
|
| Website | westjr.co.jp |
| West Japan Railway Company | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operation | |||||
| National railway | Japan Railways Group | ||||
| Infrastructure company | Japan Railway Construction, Transport and Technology Agency | ||||
| Statistics | |||||
| Ridership | 1.778 billion per year | ||||
| Passenger km | 52.614 billion per year | ||||
| System length | |||||
| Total | 5,012.7 km (3,114.7 mi) | ||||
| Double track | 2,253.2 km (1,400.1 mi) (44.9%) | ||||
| Electrified | 3,385.7 km (2,103.8 mi) (67.5%) | ||||
| High-speed | 644.0 km (400.2 mi) (12.8%) | ||||
| Track gauge | |||||
| Main | 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) | ||||
| High-speed | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) | ||||
| Electrification | |||||
| Main | 1,500 V DC overhead catenary 2,447 km (1,520 mi) | ||||
| 20 kV AC 60 Hz overhead | 278.0 km (172.7 mi) Hokuriku Main Line (Tsuruga - Itoigawa) | ||||
| 25 kV AC 60 Hz overhead | 644.0 km (400.2 mi) Sanyo Shinkansen | ||||
| Features | |||||
| No. tunnels | 1,016 | ||||
| Tunnel length | 667 km (414 mi) | ||||
| Longest tunnel | The Shin-Kanmon Tunnel 18,713 metres (61,394 ft) Sanyo Shinkansen (Shin-Shimonoseki - Kokura) | ||||
| No. bridges | 28,568 | ||||
| Longest bridge | The Yoshii River Bridge 669 m (2,195 ft) Sanyo Shinkansen (Okayama - Aioi) | ||||
| No. stations | 1,222 | ||||
| |||||
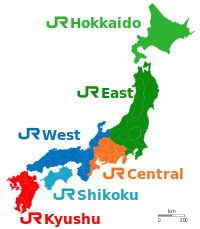
The West Japan Railway Company, also referred to as JR West (JR西日本, Jeiāru Nishi-Nihon), is one of the Japan Railways Group (JR Group) companies and operates in western Honshu. It has its headquarters in Kita-ku, Osaka. It is listed in the Tokyo Stock Exchange, is a constituent of the TOPIX Large70 index, and is also one of only three Japan Railways Group constituents of the Nikkei 225 index: the others are JR East and JR Central. It was also listed in the Nagoya and Fukuoka stock exchanges until late 2020.
Lines
Shinkansen
- Officially not a Shinkansen
JR-West's highest-grossing line is the Sanyo Shinkansen high-speed rail line between Osaka and Fukuoka. The Sanyo Shinkansen alone accounts for about 40% of JR-West's passenger revenues. The company also operates Hakata Minami Line, a short commuter line with Shinkansen trains in Fukuoka.
Urban Network
The "Urban Network" is JR-West's name for its commuter rail lines in the Osaka-Kobe-Kyoto metropolitan area. These lines together comprise 610 km of track, have 245 stations and account for about 43% of JR-West's passenger revenues. Urban Network stations are equipped to handle ICOCA fare cards. Train control on these lines is highly automated, and during peak hours trains run as often as every two minutes.
JR-West's Urban Network competes with a number of private commuter rail operators around Osaka, the "Big 4" being Hankyu Railway/Hanshin Railway (Hankyu bought Hanshin in April 2005), Keihan Railway, Kintetsu, and Nankai Railway. JR-West's market share in the region is roughly equal to that of the Big 4 put together, largely due to its comprehensive network and high-speed commuter trains (Special Rapid Service trains on the Kobe and Kyoto lines operate at up to 130 km/h).
Those in italics are announcement names.
- Officially Tōkaidō Main Line, Hokuriku Main Line
- Officially Katamachi Line
- Officially Tōkaidō Main Line, San'yō Main Line
- Officially Tōkaidō Main Line
- Officially San'in Main Line
- Officially Sakurai Line
- Officially Fukuchiyama Line
- Officially Kansai Main Line
- Officially Sakurajima Line
Intercity and regional lines
A number of other lines account for more than half of JR-West's track mileage. These lines mainly handle business and leisure travel between smaller cities and rural areas in western Japan. They account for about 20% of the company's passenger revenues.
Intercity lines
- Includes JR Takarazuka Line.
- Includes Biwako Line.
 Seto-Ōhashi Line, Chayamachi — Kojima
Seto-Ōhashi Line, Chayamachi — Kojima
- Officially Seto-Ōhashi Line
 Kansai Main Line, Kameyama — JR Namba
Kansai Main Line, Kameyama — JR Namba
- Includes Yamatoji Line.
 Kisei Main Line, Shingū — Wakayamashi
Kisei Main Line, Shingū — Wakayamashi
- Includes Kinokuni Line.
- Includes Sagano Line.




 San'yō Main Line, Kobe — Shimonoseki, Hyōgo — Wadamisaki.
San'yō Main Line, Kobe — Shimonoseki, Hyōgo — Wadamisaki.
- Includes JR Kobe Line.
- ■ Takayama Main Line, Inotani — Toyama
 Tōkaidō Main Line, Maibara — Kobe
Tōkaidō Main Line, Maibara — Kobe
- Includes Biwako Line, JR Kyoto Line, and JR Kobe Line.
Regional lines
- Nicknamed Kuzuryū Line
 Fukuen Line
Fukuen Line- ■ Gantoku Line
 Geibi Line
Geibi Line- ■ Himi Line
 Inbi Line
Inbi Line- ■ Jōhana Line
 Kabe Line
Kabe Line Kakogawa Line
Kakogawa Line Momotarō Line
Momotarō Line
- Officially Kibi Line
- Includes Setouchi Sazanami Line
 Kusatsu Line
Kusatsu Line Maizuru Line
Maizuru Line- Mine Line
- ■ Nanao Line
- ■ Obama Line
- ■ Ōito Line, Minami-Otari — Itoigawa
- ■ Onoda Line
 Sakai Line
Sakai Line Tsuyama Line
Tsuyama Line- ■ Ube Line
 Uno-Port Line
Uno-Port Line
- Officially Uno Line
Other businesses
JR-West subsidiaries include the following.
- West Japan Railway Hotel Development Company - Owns Hotel Granvia Kyoto, Hotel Granvia Osaka, Hotel Granvia Wakayama, Hotel Granvia Okayama, Hotel Granvia Hiroshima, Nara Hotel, Sannomiya Terminal Hotel and Hotel Hopinn Aming
- West Japan Railway Isetan - A joint venture with Isetan Mitsukoshi Holdings Ltd; operates the Isetan department store in Kyoto Station
- West JR Bus Company - Intercity bus operator
- Chūgoku JR Bus Company - Intercity bus operator
- Japan Railway West Trading Co.
- Nippon Travel Agency Co., Ltd
- Sagano Scenic Railway
- JR-West Miyajima Ferry Company - operator of JR Miyajima Ferry service to the island of Miyajima
History
JR-West was incorporated as a business corporation (kabushiki kaisha) on April 1, 1987, as part of the breakup of the state-owned Japanese National Railways (JNR). Initially, it was a wholly owned subsidiary of the JNR Settlement Corporation (JNRSC), a special company created to hold the assets of the former JNR while they were shuffled among the new JR companies.
For the first four years of its existence, JR-West leased its highest-revenue line, the Sanyō Shinkansen, from the separate Shinkansen Holding Corporation. JR-West purchased the line in October 1991 at a cost of 974.1 billion JPY (about US$7.2 billion) in long-term debt.
JNRSC sold 68.3% of JR-West in an initial public offering on the Tokyo Stock Exchange in October 1996. After JNRSC was dissolved in October 1998, its shares of JR-West were transferred to the government-owned Japan Railway Construction Public Corporation (JRCC), which merged into the Japan Railway Construction, Transport and Technology Agency (JRTT) as part of a bureaucratic reform package in October 2003. JRTT offered all of its shares in JR-West to the public in an international IPO in 2004, ending the era of government ownership of JR-West. JR-West is now listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange, Nagoya Stock Exchange, Osaka Securities Exchange and Fukuoka Stock Exchange.
Accidents and incidents
- Shigaraki train disaster: A collision between a JR West and a Shigaraki Kōgen Railway train in Shigaraki (now Koka), Shiga Prefecture on 14 May 1991, killed 42 people.
- Amagasaki derailment: A train derailment in Amagasaki, Hyōgo Prefecture on 25 April 2005, killed 107 people.
References
- ^ West Japan Railway Company. "JR West 2013 Annual Business Report (Japanese)" (PDF). Retrieved 25 June 2013.
- ^ West Japan Railway Company. "2011 Annual Report" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 April 2012. Retrieved 3 May 2012.
- ^ West Japan Railway Company. "JR West 2013 Earnings Summary (Japanese)" (PDF). Retrieved 25 June 2013.
- West Japan Railway Company (27 April 2012). "Supplemental Data Fiscal Year ended March 31, 2011" (PDF). Retrieved 3 May 2012.
- ^ West Japan Railway Company. "Company Profile 2007-2008 ebook". Archived from the original on 16 June 2009. Retrieved 6 July 2009.
- 西日本旅客鉄道株式会社, Nishi-Nihon Ryokaku Tetsudō kabushiki gaisha, lit. "West Japan Passenger Railway Share Company"
External links
| Shinkansen | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lines |
|     | ||||||||||||||||||
| Service names |
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Train types |
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Operators |
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Builders and owners |
| |||||||||||||||||||
| People | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Transit in Keihanshin | |
|---|---|
| Shinkansen | |
| [REDACTED] JR West |
|
| [REDACTED] Osaka Metro | |
| [REDACTED] Hanshin | |
| |
| [REDACTED] Nankai |
|
| [REDACTED] Shintetsu | |
| Other commuter rail lines |
|
| Monorails and Trams | |
| Hinterland |
|
| Cable car and aerial tramways | |
| Public ferries |
|
| Major terminals | |
| Miscellaneous |
|
|
| TOPIX 100 companies of Japan | |
|---|---|
| Core 30 | |
| Large 70 |
|
- TOPIX 100
- West Japan Railway Company
- Companies based in Osaka Prefecture
- Railway companies established in 1987
- Companies listed on the Osaka Exchange
- Companies listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange
- Companies listed on the Fukuoka Stock Exchange
- Companies in the Nikkei 225
- Japanese companies established in 1987
- Japan Railway companies
