
Caption: 0.800 – 1.000 (very high HDI) 0.700 – 0.799 (high HDI) 0.600 – 0.699 (medium HDI)
Introduced by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in 1990, the Human Development Index (HDI) is a composite statistic of education, income and longevity indices, calculated in order to measure social and economic development within countries. It consists of a number between 0 and 1, comprising five tiers of human development—very low, low, medium, high, or very high—wherein the development is considered higher when closer to 1. According to the latest Human Development Report, published in 2015 and reflecting data from 2014, Brazil placed 75th among 188 countries with an HDI value of 0.755. The UNDP highlighted the "rapid advance" of Brazil in two decades, leaving a situation of low human development (0.590) in 1990, reaching medium development (0.669) in 2000 and, finally, achieving high human development (0.726) in 2010.
In order to bring a human development perspective to the national level, the UNDP also created, in 1998, the Human Development Atlas in Brazil, which calculates the HDI of all the Brazilian administrative divisions, based on data provided by the decennial censuses conducted by the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE). Released in 2013, in partnership with the Institute of Applied Economic Research (IPEA) and the João Pinheiro Foundation (FJP), the latest edition of the Human Development Atlas in Brazil shows that the average HDI of the Brazilian federative units grew by 47.5% from 1991 to 2010.
Since the beginning of the statistical series in 1991, the Federal District, which contains the national capital—Brasília—, has the highest HDI among the 27 federative units of Brazil, being the only one to fall in the category of very high human development according to 2010 figures. It also topped every subindex composing the HDI, except for longevity, when, in 1991, it was surpassed by Santa Catarina. Meanwhile, Alagoas set out the lowest HDI since 2000, especially due to a poor performance in education. Tocantins put forward the fastest progress in HDI value (0.330) from 1991 to 2010, while Rio de Janeiro had the smallest increase (0.188). According to the UNDP report, the states of the North and Northeast regions have the lowest indicators, with most municipalities registering low or medium human development, while in the South, more than 65% of municipalities have achieved high human development. The South and Southeast regions and the Federal District have the highest indicators and human development indices.
Human Development Atlas
The methodology used by the UNDP to measure the HDI of all 5,565 Brazilian municipalities and 27 federative units differs from that used for countries. Although it has the same three dimensions of the global HDI—education, income and longevity—it adapts the global methodology to the Brazilian context and the availability of national indicators. Therefore, a comparison between Brazilian federative units and countries is discouraged and the numbers cannot be used as a parameter. The global report uses mean years of schooling and expected years of schooling to evaluate education, while the local report utilizes schooling of the adult population and school flow of young people. In the case of income, while the global report uses GNI per capita (PPP USD), the local report makes use of the Municipal Income per capita (BRL). As for longevity, both use life expectancy at birth as indicator.
|
|
| 2021 | 2010 | 2000 | 1991 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Federative unit | HDI | E | I | L | HDI | E | I | L | HDI | E | I | L | HDI | E | I | L |
| 1 | |
0.814 | 0.817 | 0.821 | 0.803 | 0.824 | 0.742 | 0.863 | 0.873 | 0.725 | 0.582 | 0.805 | 0.814 | 0.616 | 0.419 | 0.762 | 0.731 |
| 2 | |
0.806 | 0.839 | 0.771 | 0.810 | 0.783 | 0.719 | 0.789 | 0.845 | 0.702 | 0.581 | 0.756 | 0.786 | 0.578 | 0.363 | 0.729 | 0.730 |
| 3 | |
0.792 | 0.790 | 0.759 | 0.827 | 0.774 | 0.697 | 0.773 | 0.860 | 0.674 | 0.526 | 0.717 | 0.812 | 0.543 | 0.329 | 0.648 | 0.753 |
| 4 | |
0.774 | 0.762 | 0.718 | 0.846 | 0.731 | 0.638 | 0.730 | 0.838 | 0.624 | 0.470 | 0.680 | 0.759 | 0.478 | 0.257 | 0.618 | 0.689 |
| 5 | |
0.771 | 0.750 | 0.767 | 0.797 | 0.761 | 0.675 | 0.782 | 0.835 | 0.664 | 0.530 | 0.745 | 0.740 | 0.573 | 0.392 | 0.696 | 0.690 |
| |
0.742 | 0.715 | 0.864 | 0.740 | 0.653 | 0.743 | 0.835 | 0.640 | 0.491 | 0.687 | 0.777 | 0.505 | 0.304 | 0.619 | 0.686 | ||
| 7 | |
0.769 | 0.780 | 0.744 | 0.785 | 0.746 | 0.642 | 0.769 | 0.840 | 0.664 | 0.505 | 0.720 | 0.804 | 0.542 | 0.328 | 0.667 | 0.729 |
| 8 | |
0.762 | 0.758 | 0.759 | 0.769 | 0.749 | 0.668 | 0.757 | 0.830 | 0.650 | 0.522 | 0.704 | 0.747 | 0.507 | 0.298 | 0.644 | 0.679 |
| 9 | |
0.742 | 0.741 | 0.733 | 0.751 | 0.729 | 0.629 | 0.740 | 0.833 | 0.613 | 0.445 | 0.687 | 0.752 | 0.488 | 0.259 | 0.641 | 0.699 |
| 10 | |
0.737 | 0.778 | 0.714 | 0.721 | 0.735 | 0.646 | 0.742 | 0.827 | 0.615 | 0.439 | 0.686 | 0.773 | 0.487 | 0.273 | 0.633 | 0.668 |
| 11 | |
0.736 | 0.758 | 0.720 | 0.730 | 0.725 | 0.635 | 0.732 | 0.821 | 0.601 | 0.426 | 0.689 | 0.740 | 0.449 | 0.221 | 0.627 | 0.654 |
| 12 | |
0.734 | 0.766 | 0.658 | 0.784 | 0.682 | 0.615 | 0.651 | 0.793 | 0.541 | 0.377 | 0.588 | 0.713 | 0.405 | 0.204 | 0.532 | 0.613 |
| 13 | |
0.731 | 0.732 | 0.684 | 0.779 | 0.699 | 0.624 | 0.690 | 0.793 | 0.525 | 0.348 | 0.605 | 0.688 | 0.369 | 0.155 | 0.549 | 0.589 |
| 14 | |
0.728 | 0.680 | 0.692 | 0.819 | 0.684 | 0.597 | 0.678 | 0.792 | 0.552 | 0.396 | 0.608 | 0.700 | 0.428 | 0.242 | 0.547 | 0.591 |
| 15 | |
0.719 | 0.721 | 0.647 | 0.797 | 0.673 | 0.574 | 0.673 | 0.789 | 0.544 | 0.372 | 0.615 | 0.705 | 0.440 | 0.232 | 0.569 | 0.617 |
| 16 | |
0.710 | 0.692 | 0.655 | 0.788 | 0.663 | 0.559 | 0.671 | 0.777 | 0.517 | 0.325 | 0.612 | 0.694 | 0.402 | 0.176 | 0.574 | 0.645 |
| 17 | |
0.702 | 0.684 | 0.662 | 0.764 | 0.665 | 0.560 | 0.672 | 0.781 | 0.518 | 0.343 | 0.596 | 0.678 | 0.413 | 0.211 | 0.552 | 0.581 |
| 18 | |
0.700 | 0.720 | 0.641 | 0.744 | 0.674 | 0.561 | 0.677 | 0.805 | 0.515 | 0.324 | 0.608 | 0.692 | 0.430 | 0.204 | 0.605 | 0.645 |
| |
0.694 | 0.677 | 0.731 | 0.690 | 0.577 | 0.712 | 0.800 | 0.537 | 0.345 | 0.654 | 0.688 | 0.407 | 0.181 | 0.585 | 0.635 | ||
| 20 | |
0.699 | 0.673 | 0.680 | 0.745 | 0.707 | 0.628 | 0.695 | 0.809 | 0.598 | 0.457 | 0.652 | 0.717 | 0.459 | 0.240 | 0.643 | 0.628 |
| 21 | |
0.698 | 0.669 | 0.653 | 0.779 | 0.658 | 0.555 | 0.656 | 0.783 | 0.506 | 0.331 | 0.582 | 0.672 | 0.382 | 0.191 | 0.515 | 0.565 |
| 22 | |
0.691 | 0.659 | 0.648 | 0.772 | 0.660 | 0.555 | 0.663 | 0.783 | 0.512 | 0.332 | 0.594 | 0.680 | 0.386 | 0.182 | 0.543 | 0.582 |
| 23 | |
0.690 | 0.698 | 0.649 | 0.726 | 0.646 | 0.547 | 0.635 | 0.777 | 0.484 | 0.301 | 0.556 | 0.676 | 0.362 | 0.164 | 0.488 | 0.595 |
| |
0.686 | 0.645 | 0.744 | 0.646 | 0.528 | 0.646 | 0.789 | 0.518 | 0.319 | 0.601 | 0.725 | 0.413 | 0.194 | 0.567 | 0.640 | ||
| 25 | |
0.688 | 0.647 | 0.648 | 0.778 | 0.708 | 0.629 | 0.694 | 0.813 | 0.577 | 0.424 | 0.638 | 0.711 | 0.472 | 0.254 | 0.620 | 0.668 |
| 26 | |
0.684 | 0.679 | 0.630 | 0.748 | 0.631 | 0.520 | 0.641 | 0.755 | 0.471 | 0.282 | 0.574 | 0.647 | 0.370 | 0.174 | 0.527 | 0.552 |
| 27 | |
0.676 | 0.716 | 0.603 | 0.715 | 0.639 | 0.562 | 0.612 | 0.757 | 0.476 | 0.312 | 0.531 | 0.649 | 0.357 | 0.173 | 0.478 | 0.551 |
- Maps
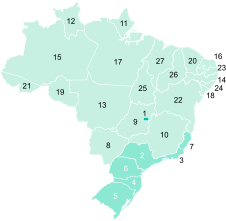 1991
1991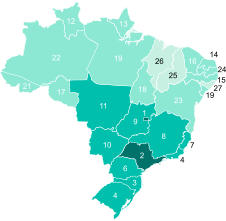 2000
2000 2010
2010 2021Every region of Brazil has significantly increased its Human Development Index in the span of two decades, with no federative unit under low human development by 2010. South, Southeast and Central-West are the most advanced regions, while the North and Northeast still presented states with a medium human development.
2021Every region of Brazil has significantly increased its Human Development Index in the span of two decades, with no federative unit under low human development by 2010. South, Southeast and Central-West are the most advanced regions, while the North and Northeast still presented states with a medium human development.
See also
- Federative units of Brazil
- List of municipalities in Amazonas by HDI
- List of municipalities in Mato Grosso do Sul by HDI
- List of municipalities in Rio Grande do Sul by HDI
- List of municipalities in Roraima by HDI
- List of municipalities in São Paulo by HDI
References
- Specific
- "Human Development Index (HDI)". United Nations Development Programme. Retrieved August 5, 2013.
- Human Development Atlas in Brazil 2013, p. 24.
- Human Development Atlas in Brazil 2013, p. 27.
- Human Development Report 2013, p. 145.
- "Brazil" (PDF). Human Development Report (2013 ed.). United Nations Development Programme. March 14, 2013. Retrieved August 5, 2013.
- Human Development Report 2013, p. 1.
- "UNDP report highlights Brazil's social progress" (Press release). Brazilian Ministry of Social Development and Fight against Hunger. March 15, 2013. Archived from the original on August 5, 2013. Retrieved August 5, 2013.
- "Brazil". Country Profile: Human Development Indicators. United Nations Development Programme. Archived from the original on June 6, 2013. Retrieved August 5, 2013.
- "1998 Human Development Atlas" (in Portuguese). United Nations Development Programme. Retrieved August 5, 2013.
- Human Development Atlas in Brazil 2013, p. 13.
- Richard, Ivan (July 29, 2013). "Brazil's Human Development Index nearly doubled in 20 years". Brasília: EBC. Retrieved August 5, 2013.
- Acayaba, Cíntia; Oliveira, Mariana (July 29, 2013). "Municipal HDI of Brazil grows 47,5% in 20 years, appoints UNDP" (in Portuguese). Brasília: G1. Retrieved August 5, 2013.
- Human Development Atlas in Brazil 2013, p. 45.
- "Brazil's Human Development Improves". Rio de Janeiro: Bernama. July 30, 2013. Retrieved August 5, 2013.
- ^ Human Development Atlas in Brazil 2013, pp. 24–29.
- ^ "Atlas do Desenvolvimento Humano no Brasil. Pnud Brasil, Ipea e FJP, 2022". www.atlasbrasil.org.br. Retrieved 2023-06-11.
- "2013 Human Development Atlas in Brazil". Database (in Portuguese). United Nations Development Programme. Retrieved August 5, 2013.
- Human Development Report 2013, pp. 148–151.
- PNUD Brasil. "Radar IDHM: evolução do IDHM e de seus índices componentes no período de 2012 a 2017" (PDF).
- General
-
- Human Development Atlas in Brazil (PDF) (in Portuguese) (2013 ed.). Brasília: United Nations Development Programme. July 29, 2013. ISBN 978-85-7811-171-7.
- Human Development Report (PDF) (2013 ed.). Mexico City: United Nations Development Programme. March 14, 2013. ISBN 978-92-1-126340-4.
| Lists of Brazilian federative units | |
|---|---|
| Geography | |
| Politics | |
| Economy | |
| Demographics | |
| Miscellaneous | |
| Economy of Brazil | |
|---|---|
| History | |
| Agriculture | |
| Welfare | |
| Energy | |
| Other sectors | |
| Misc. | |