| Part of a series on |
| Spacetime |
|---|
 |
| Spacetime concepts |
| General relativity |
| Classical gravity |
| Relevant mathematics |
In physics, the Lorentz transformations are a six-parameter family of linear transformations from a coordinate frame in spacetime to another frame that moves at a constant velocity relative to the former. The respective inverse transformation is then parameterized by the negative of this velocity. The transformations are named after the Dutch physicist Hendrik Lorentz.
The most common form of the transformation, parametrized by the real constant representing a velocity confined to the x-direction, is expressed as where (t, x, y, z) and (t′, x′, y′, z′) are the coordinates of an event in two frames with the spatial origins coinciding at t=t′=0, where the primed frame is seen from the unprimed frame as moving with speed v along the x-axis, where c is the speed of light, and is the Lorentz factor. When speed v is much smaller than c, the Lorentz factor is negligibly different from 1, but as v approaches c, grows without bound. The value of v must be smaller than c for the transformation to make sense.
Expressing the speed as an equivalent form of the transformation is
Frames of reference can be divided into two groups: inertial (relative motion with constant velocity) and non-inertial (accelerating, moving in curved paths, rotational motion with constant angular velocity, etc.). The term "Lorentz transformations" only refers to transformations between inertial frames, usually in the context of special relativity.
In each reference frame, an observer can use a local coordinate system (usually Cartesian coordinates in this context) to measure lengths, and a clock to measure time intervals. An event is something that happens at a point in space at an instant of time, or more formally a point in spacetime. The transformations connect the space and time coordinates of an event as measured by an observer in each frame.
They supersede the Galilean transformation of Newtonian physics, which assumes an absolute space and time (see Galilean relativity). The Galilean transformation is a good approximation only at relative speeds much less than the speed of light. Lorentz transformations have a number of unintuitive features that do not appear in Galilean transformations. For example, they reflect the fact that observers moving at different velocities may measure different distances, elapsed times, and even different orderings of events, but always such that the speed of light is the same in all inertial reference frames. The invariance of light speed is one of the postulates of special relativity.
Historically, the transformations were the result of attempts by Lorentz and others to explain how the speed of light was observed to be independent of the reference frame, and to understand the symmetries of the laws of electromagnetism. The transformations later became a cornerstone for special relativity.
The Lorentz transformation is a linear transformation. It may include a rotation of space; a rotation-free Lorentz transformation is called a Lorentz boost. In Minkowski space—the mathematical model of spacetime in special relativity—the Lorentz transformations preserve the spacetime interval between any two events. This property is the defining property of a Lorentz transformation. They describe only the transformations in which the spacetime event at the origin is left fixed. They can be considered as a hyperbolic rotation of Minkowski space. The more general set of transformations that also includes translations is known as the Poincaré group.
History
Main article: History of Lorentz transformationsMany physicists—including Woldemar Voigt, George FitzGerald, Joseph Larmor, and Hendrik Lorentz himself—had been discussing the physics implied by these equations since 1887. Early in 1889, Oliver Heaviside had shown from Maxwell's equations that the electric field surrounding a spherical distribution of charge should cease to have spherical symmetry once the charge is in motion relative to the luminiferous aether. FitzGerald then conjectured that Heaviside's distortion result might be applied to a theory of intermolecular forces. Some months later, FitzGerald published the conjecture that bodies in motion are being contracted, in order to explain the baffling outcome of the 1887 aether-wind experiment of Michelson and Morley. In 1892, Lorentz independently presented the same idea in a more detailed manner, which was subsequently called FitzGerald–Lorentz contraction hypothesis. Their explanation was widely known before 1905.
Lorentz (1892–1904) and Larmor (1897–1900), who believed the luminiferous aether hypothesis, also looked for the transformation under which Maxwell's equations are invariant when transformed from the aether to a moving frame. They extended the FitzGerald–Lorentz contraction hypothesis and found out that the time coordinate has to be modified as well ("local time"). Henri Poincaré gave a physical interpretation to local time (to first order in v/c, the relative velocity of the two reference frames normalized to the speed of light) as the consequence of clock synchronization, under the assumption that the speed of light is constant in moving frames. Larmor is credited to have been the first to understand the crucial time dilation property inherent in his equations.
In 1905, Poincaré was the first to recognize that the transformation has the properties of a mathematical group, and he named it after Lorentz. Later in the same year Albert Einstein published what is now called special relativity, by deriving the Lorentz transformation under the assumptions of the principle of relativity and the constancy of the speed of light in any inertial reference frame, and by abandoning the mechanistic aether as unnecessary.
Derivation of the group of Lorentz transformations
Main articles: Derivations of the Lorentz transformations and Lorentz groupAn event is something that happens at a certain point in spacetime, or more generally, the point in spacetime itself. In any inertial frame an event is specified by a time coordinate ct and a set of Cartesian coordinates x, y, z to specify position in space in that frame. Subscripts label individual events.
From Einstein's second postulate of relativity (invariance of c) it follows that:
| D1 |
in all inertial frames for events connected by light signals. The quantity on the left is called the spacetime interval between events a1 = (t1, x1, y1, z1) and a2 = (t2, x2, y2, z2). The interval between any two events, not necessarily separated by light signals, is in fact invariant, i.e., independent of the state of relative motion of observers in different inertial frames, as is shown using homogeneity and isotropy of space. The transformation sought after thus must possess the property that:
| D2 |
where (t, x, y, z) are the spacetime coordinates used to define events in one frame, and (t′, x′, y′, z′) are the coordinates in another frame. First one observes that (D2) is satisfied if an arbitrary 4-tuple b of numbers are added to events a1 and a2. Such transformations are called spacetime translations and are not dealt with further here. Then one observes that a linear solution preserving the origin of the simpler problem solves the general problem too:
| D3 |
(a solution satisfying the first formula automatically satisfies the second one as well; see polarization identity). Finding the solution to the simpler problem is just a matter of look-up in the theory of classical groups that preserve bilinear forms of various signature. First equation in (D3) can be written more compactly as:
| D4 |
where (·, ·) refers to the bilinear form of signature (1, 3) on R exposed by the right hand side formula in (D3). The alternative notation defined on the right is referred to as the relativistic dot product. Spacetime mathematically viewed as R endowed with this bilinear form is known as Minkowski space M. The Lorentz transformation is thus an element of the group O(1, 3), the Lorentz group or, for those that prefer the other metric signature, O(3, 1) (also called the Lorentz group). One has:
| D5 |
which is precisely preservation of the bilinear form (D3) which implies (by linearity of Λ and bilinearity of the form) that (D2) is satisfied. The elements of the Lorentz group are rotations and boosts and mixes thereof. If the spacetime translations are included, then one obtains the inhomogeneous Lorentz group or the Poincaré group.
Generalities
The relations between the primed and unprimed spacetime coordinates are the Lorentz transformations, each coordinate in one frame is a linear function of all the coordinates in the other frame, and the inverse functions are the inverse transformation. Depending on how the frames move relative to each other, and how they are oriented in space relative to each other, other parameters that describe direction, speed, and orientation enter the transformation equations.
Transformations describing relative motion with constant (uniform) velocity and without rotation of the space coordinate axes are called Lorentz boosts or simply boosts, and the relative velocity between the frames is the parameter of the transformation. The other basic type of Lorentz transformation is rotation in the spatial coordinates only, these like boosts are inertial transformations since there is no relative motion, the frames are simply tilted (and not continuously rotating), and in this case quantities defining the rotation are the parameters of the transformation (e.g., axis–angle representation, or Euler angles, etc.). A combination of a rotation and boost is a homogeneous transformation, which transforms the origin back to the origin.
The full Lorentz group O(3, 1) also contains special transformations that are neither rotations nor boosts, but rather reflections in a plane through the origin. Two of these can be singled out; spatial inversion in which the spatial coordinates of all events are reversed in sign and temporal inversion in which the time coordinate for each event gets its sign reversed.
Boosts should not be conflated with mere displacements in spacetime; in this case, the coordinate systems are simply shifted and there is no relative motion. However, these also count as symmetries forced by special relativity since they leave the spacetime interval invariant. A combination of a rotation with a boost, followed by a shift in spacetime, is an inhomogeneous Lorentz transformation, an element of the Poincaré group, which is also called the inhomogeneous Lorentz group.
Physical formulation of Lorentz boosts
Further information: Derivations of the Lorentz transformationsCoordinate transformation

Top: frame F′ moves at velocity v along the x-axis of frame F.
Bottom: frame F moves at velocity −v along the x′-axis of frame F′.
A "stationary" observer in frame F defines events with coordinates t, x, y, z. Another frame F′ moves with velocity v relative to F, and an observer in this "moving" frame F′ defines events using the coordinates t′, x′, y′, z′.
The coordinate axes in each frame are parallel (the x and x′ axes are parallel, the y and y′ axes are parallel, and the z and z′ axes are parallel), remain mutually perpendicular, and relative motion is along the coincident xx′ axes. At t = t′ = 0, the origins of both coordinate systems are the same, (x, y, z) = (x′, y′, z′) = (0, 0, 0). In other words, the times and positions are coincident at this event. If all these hold, then the coordinate systems are said to be in standard configuration, or synchronized.
If an observer in F records an event t, x, y, z, then an observer in F′ records the same event with coordinates
Lorentz boost (x direction)
where v is the relative velocity between frames in the x-direction, c is the speed of light, and (lowercase gamma) is the Lorentz factor.
Here, v is the parameter of the transformation, for a given boost it is a constant number, but can take a continuous range of values. In the setup used here, positive relative velocity v > 0 is motion along the positive directions of the xx′ axes, zero relative velocity v = 0 is no relative motion, while negative relative velocity v < 0 is relative motion along the negative directions of the xx′ axes. The magnitude of relative velocity v cannot equal or exceed c, so only subluminal speeds −c < v < c are allowed. The corresponding range of γ is 1 ≤ γ < ∞.
The transformations are not defined if v is outside these limits. At the speed of light (v = c) γ is infinite, and faster than light (v > c) γ is a complex number, each of which make the transformations unphysical. The space and time coordinates are measurable quantities and numerically must be real numbers.
As an active transformation, an observer in F′ notices the coordinates of the event to be "boosted" in the negative directions of the xx′ axes, because of the −v in the transformations. This has the equivalent effect of the coordinate system F′ boosted in the positive directions of the xx′ axes, while the event does not change and is simply represented in another coordinate system, a passive transformation.
The inverse relations (t, x, y, z in terms of t′, x′, y′, z′) can be found by algebraically solving the original set of equations. A more efficient way is to use physical principles. Here F′ is the "stationary" frame while F is the "moving" frame. According to the principle of relativity, there is no privileged frame of reference, so the transformations from F′ to F must take exactly the same form as the transformations from F to F′. The only difference is F moves with velocity −v relative to F′ (i.e., the relative velocity has the same magnitude but is oppositely directed). Thus if an observer in F′ notes an event t′, x′, y′, z′, then an observer in F notes the same event with coordinates
Inverse Lorentz boost (x direction)
and the value of γ remains unchanged. This "trick" of simply reversing the direction of relative velocity while preserving its magnitude, and exchanging primed and unprimed variables, always applies to finding the inverse transformation of every boost in any direction.
Sometimes it is more convenient to use β = v/c (lowercase beta) instead of v, so that which shows much more clearly the symmetry in the transformation. From the allowed ranges of v and the definition of β, it follows −1 < β < 1. The use of β and γ is standard throughout the literature.
When the boost velocity is in an arbitrary vector direction with the boost vector , then the transformation from an unprimed spacetime coordinate system to a primed coordinate system is given by,
where the Lorentz factor is . The determinant of the transformation matrix is +1 and its trace is . The inverse of the transformation is given by reversing the sign of . The quantity is invariant under the transformation.
The Lorentz transformations can also be derived in a way that resembles circular rotations in 3d space using the hyperbolic functions. For the boost in the x direction, the results are
Lorentz boost (x direction with rapidity ζ)
where ζ (lowercase zeta) is a parameter called rapidity (many other symbols are used, including θ, ϕ, φ, η, ψ, ξ). Given the strong resemblance to rotations of spatial coordinates in 3d space in the Cartesian xy, yz, and zx planes, a Lorentz boost can be thought of as a hyperbolic rotation of spacetime coordinates in the xt, yt, and zt Cartesian-time planes of 4d Minkowski space. The parameter ζ is the hyperbolic angle of rotation, analogous to the ordinary angle for circular rotations. This transformation can be illustrated with a Minkowski diagram.
The hyperbolic functions arise from the difference between the squares of the time and spatial coordinates in the spacetime interval, rather than a sum. The geometric significance of the hyperbolic functions can be visualized by taking x = 0 or ct = 0 in the transformations. Squaring and subtracting the results, one can derive hyperbolic curves of constant coordinate values but varying ζ, which parametrizes the curves according to the identity
Conversely the ct and x axes can be constructed for varying coordinates but constant ζ. The definition provides the link between a constant value of rapidity, and the slope of the ct axis in spacetime. A consequence these two hyperbolic formulae is an identity that matches the Lorentz factor
Comparing the Lorentz transformations in terms of the relative velocity and rapidity, or using the above formulae, the connections between β, γ, and ζ are
Taking the inverse hyperbolic tangent gives the rapidity
Since −1 < β < 1, it follows −∞ < ζ < ∞. From the relation between ζ and β, positive rapidity ζ > 0 is motion along the positive directions of the xx′ axes, zero rapidity ζ = 0 is no relative motion, while negative rapidity ζ < 0 is relative motion along the negative directions of the xx′ axes.
The inverse transformations are obtained by exchanging primed and unprimed quantities to switch the coordinate frames, and negating rapidity ζ → −ζ since this is equivalent to negating the relative velocity. Therefore,
Inverse Lorentz boost (x direction with rapidity ζ)
The inverse transformations can be similarly visualized by considering the cases when x′ = 0 and ct′ = 0.
So far the Lorentz transformations have been applied to one event. If there are two events, there is a spatial separation and time interval between them. It follows from the linearity of the Lorentz transformations that two values of space and time coordinates can be chosen, the Lorentz transformations can be applied to each, then subtracted to get the Lorentz transformations of the differences;
with inverse relations
where Δ (uppercase delta) indicates a difference of quantities; e.g., Δx = x2 − x1 for two values of x coordinates, and so on.
These transformations on differences rather than spatial points or instants of time are useful for a number of reasons:
- in calculations and experiments, it is lengths between two points or time intervals that are measured or of interest (e.g., the length of a moving vehicle, or time duration it takes to travel from one place to another),
- the transformations of velocity can be readily derived by making the difference infinitesimally small and dividing the equations, and the process repeated for the transformation of acceleration,
- if the coordinate systems are never coincident (i.e., not in standard configuration), and if both observers can agree on an event t0, x0, y0, z0 in F and t0′, x0′, y0′, z0′ in F′, then they can use that event as the origin, and the spacetime coordinate differences are the differences between their coordinates and this origin, e.g., Δx = x − x0, Δx′ = x′ − x0′, etc.
Physical implications
A critical requirement of the Lorentz transformations is the invariance of the speed of light, a fact used in their derivation, and contained in the transformations themselves. If in F the equation for a pulse of light along the x direction is x = ct, then in F′ the Lorentz transformations give x′ = ct′, and vice versa, for any −c < v < c.
For relative speeds much less than the speed of light, the Lorentz transformations reduce to the Galilean transformation: in accordance with the correspondence principle. It is sometimes said that nonrelativistic physics is a physics of "instantaneous action at a distance".
Three counterintuitive, but correct, predictions of the transformations are:
- Relativity of simultaneity
- Suppose two events occur along the x axis simultaneously (Δt = 0) in F, but separated by a nonzero displacement Δx. Then in F′, we find that , so the events are no longer simultaneous according to a moving observer.
- Time dilation
- Suppose there is a clock at rest in F. If a time interval is measured at the same point in that frame, so that Δx = 0, then the transformations give this interval in F′ by Δt′ = γΔt. Conversely, suppose there is a clock at rest in F′. If an interval is measured at the same point in that frame, so that Δx′ = 0, then the transformations give this interval in F by Δt = γΔt′. Either way, each observer measures the time interval between ticks of a moving clock to be longer by a factor γ than the time interval between ticks of his own clock.
- Length contraction
- Suppose there is a rod at rest in F aligned along the x axis, with length Δx. In F′, the rod moves with velocity -v, so its length must be measured by taking two simultaneous (Δt′ = 0) measurements at opposite ends. Under these conditions, the inverse Lorentz transform shows that Δx = γΔx′. In F the two measurements are no longer simultaneous, but this does not matter because the rod is at rest in F. So each observer measures the distance between the end points of a moving rod to be shorter by a factor 1/γ than the end points of an identical rod at rest in his own frame. Length contraction affects any geometric quantity related to lengths, so from the perspective of a moving observer, areas and volumes will also appear to shrink along the direction of motion.
Vector transformations
Further information: Euclidean vector and vector projection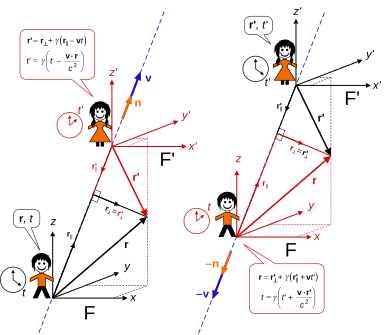
Left: Standard configuration. Right: Inverse configuration.
The use of vectors allows positions and velocities to be expressed in arbitrary directions compactly. A single boost in any direction depends on the full relative velocity vector v with a magnitude |v| = v that cannot equal or exceed c, so that 0 ≤ v < c.
Only time and the coordinates parallel to the direction of relative motion change, while those coordinates perpendicular do not. With this in mind, split the spatial position vector r as measured in F, and r′ as measured in F′, each into components perpendicular (⊥) and parallel ( ‖ ) to v, then the transformations are where · is the dot product. The Lorentz factor γ retains its definition for a boost in any direction, since it depends only on the magnitude of the relative velocity. The definition β = v/c with magnitude 0 ≤ β < 1 is also used by some authors.
Introducing a unit vector n = v/v = β/β in the direction of relative motion, the relative velocity is v = vn with magnitude v and direction n, and vector projection and rejection give respectively
Accumulating the results gives the full transformations,
Lorentz boost (in direction n with magnitude v)
The projection and rejection also applies to r′. For the inverse transformations, exchange r and r′ to switch observed coordinates, and negate the relative velocity v → −v (or simply the unit vector n → −n since the magnitude v is always positive) to obtain
Inverse Lorentz boost (in direction n with magnitude v)
The unit vector has the advantage of simplifying equations for a single boost, allows either v or β to be reinstated when convenient, and the rapidity parametrization is immediately obtained by replacing β and βγ. It is not convenient for multiple boosts.
The vectorial relation between relative velocity and rapidity is and the "rapidity vector" can be defined as each of which serves as a useful abbreviation in some contexts. The magnitude of ζ is the absolute value of the rapidity scalar confined to 0 ≤ ζ < ∞, which agrees with the range 0 ≤ β < 1.
Transformation of velocities
Further information: differential of a function and velocity addition formula
Defining the coordinate velocities and Lorentz factor by
taking the differentials in the coordinates and time of the vector transformations, then dividing equations, leads to
The velocities u and u′ are the velocity of some massive object. They can also be for a third inertial frame (say F′′), in which case they must be constant. Denote either entity by X. Then X moves with velocity u relative to F, or equivalently with velocity u′ relative to F′, in turn F′ moves with velocity v relative to F. The inverse transformations can be obtained in a similar way, or as with position coordinates exchange u and u′, and change v to −v.
The transformation of velocity is useful in stellar aberration, the Fizeau experiment, and the relativistic Doppler effect.
The Lorentz transformations of acceleration can be similarly obtained by taking differentials in the velocity vectors, and dividing these by the time differential.
Transformation of other quantities
In general, given four quantities A and Z = (Zx, Zy, Zz) and their Lorentz-boosted counterparts A′ and Z′ = (Z′x, Z′y, Z′z), a relation of the form implies the quantities transform under Lorentz transformations similar to the transformation of spacetime coordinates;
The decomposition of Z (and Z′) into components perpendicular and parallel to v is exactly the same as for the position vector, as is the process of obtaining the inverse transformations (exchange (A, Z) and (A′, Z′) to switch observed quantities, and reverse the direction of relative motion by the substitution n ↦ −n).
The quantities (A, Z) collectively make up a four-vector, where A is the "timelike component", and Z the "spacelike component". Examples of A and Z are the following:
| Four-vector | A | Z |
|---|---|---|
| Position four-vector | Time (multiplied by c), ct | Position vector, r |
| Four-momentum | Energy (divided by c), E/c | Momentum, p |
| Four-wave vector | angular frequency (divided by c), ω/c | wave vector, k |
| Four-spin | (No name), st | Spin, s |
| Four-current | Charge density (multiplied by c), ρc | Current density, j |
| Electromagnetic four-potential | Electric potential (divided by c), φ/c | Magnetic vector potential, A |
For a given object (e.g., particle, fluid, field, material), if A or Z correspond to properties specific to the object like its charge density, mass density, spin, etc., its properties can be fixed in the rest frame of that object. Then the Lorentz transformations give the corresponding properties in a frame moving relative to the object with constant velocity. This breaks some notions taken for granted in non-relativistic physics. For example, the energy E of an object is a scalar in non-relativistic mechanics, but not in relativistic mechanics because energy changes under Lorentz transformations; its value is different for various inertial frames. In the rest frame of an object, it has a rest energy and zero momentum. In a boosted frame its energy is different and it appears to have a momentum. Similarly, in non-relativistic quantum mechanics the spin of a particle is a constant vector, but in relativistic quantum mechanics spin s depends on relative motion. In the rest frame of the particle, the spin pseudovector can be fixed to be its ordinary non-relativistic spin with a zero timelike quantity st, however a boosted observer will perceive a nonzero timelike component and an altered spin.
Not all quantities are invariant in the form as shown above, for example orbital angular momentum L does not have a timelike quantity, and neither does the electric field E nor the magnetic field B. The definition of angular momentum is L = r × p, and in a boosted frame the altered angular momentum is L′ = r′ × p′. Applying this definition using the transformations of coordinates and momentum leads to the transformation of angular momentum. It turns out L transforms with another vector quantity N = (E/c)r − tp related to boosts, see relativistic angular momentum for details. For the case of the E and B fields, the transformations cannot be obtained as directly using vector algebra. The Lorentz force is the definition of these fields, and in F it is F = q(E + v × B) while in F′ it is F′ = q(E′ + v′ × B′). A method of deriving the EM field transformations in an efficient way which also illustrates the unit of the electromagnetic field uses tensor algebra, given below.
Mathematical formulation
Main article: Lorentz group Further information: Matrix (mathematics), matrix product, linear algebra, and rotation formalisms in three dimensionsThroughout, italic non-bold capital letters are 4×4 matrices, while non-italic bold letters are 3×3 matrices.
Homogeneous Lorentz group
Writing the coordinates in column vectors and the Minkowski metric η as a square matrix the spacetime interval takes the form (superscript T denotes transpose) and is invariant under a Lorentz transformation where Λ is a square matrix which can depend on parameters.
The set of all Lorentz transformations in this article is denoted . This set together with matrix multiplication forms a group, in this context known as the Lorentz group. Also, the above expression X·X is a quadratic form of signature (3,1) on spacetime, and the group of transformations which leaves this quadratic form invariant is the indefinite orthogonal group O(3,1), a Lie group. In other words, the Lorentz group is O(3,1). As presented in this article, any Lie groups mentioned are matrix Lie groups. In this context the operation of composition amounts to matrix multiplication.
From the invariance of the spacetime interval it follows and this matrix equation contains the general conditions on the Lorentz transformation to ensure invariance of the spacetime interval. Taking the determinant of the equation using the product rule gives immediately
Writing the Minkowski metric as a block matrix, and the Lorentz transformation in the most general form, carrying out the block matrix multiplications obtains general conditions on Γ, a, b, M to ensure relativistic invariance. Not much information can be directly extracted from all the conditions, however one of the results is useful; bb ≥ 0 always so it follows that
The negative inequality may be unexpected, because Γ multiplies the time coordinate and this has an effect on time symmetry. If the positive equality holds, then Γ is the Lorentz factor.
The determinant and inequality provide four ways to classify Lorentz Transformations (herein LTs for brevity). Any particular LT has only one determinant sign and only one inequality. There are four sets which include every possible pair given by the intersections ("n"-shaped symbol meaning "and") of these classifying sets.
| Intersection, ∩ | Antichronous (or non-orthochronous) LTs
|
Orthochronous LTs
|
|---|---|---|
| Proper LTs
|
Proper antichronous LTs
|
Proper orthochronous LTs
|
| Improper LTs
|
Improper antichronous LTs
|
Improper orthochronous LTs
|
where "+" and "−" indicate the determinant sign, while "↑" for ≥ and "↓" for ≤ denote the inequalities.
The full Lorentz group splits into the union ("u"-shaped symbol meaning "or") of four disjoint sets
A subgroup of a group must be closed under the same operation of the group (here matrix multiplication). In other words, for two Lorentz transformations Λ and L from a particular subgroup, the composite Lorentz transformations ΛL and LΛ must be in the same subgroup as Λ and L. This is not always the case: the composition of two antichronous Lorentz transformations is orthochronous, and the composition of two improper Lorentz transformations is proper. In other words, while the sets , , , and all form subgroups, the sets containing improper and/or antichronous transformations without enough proper orthochronous transformations (e.g. , , ) do not form subgroups.
Proper transformations
If a Lorentz covariant 4-vector is measured in one inertial frame with result , and the same measurement made in another inertial frame (with the same orientation and origin) gives result , the two results will be related by where the boost matrix represents the rotation-free Lorentz transformation between the unprimed and primed frames and is the velocity of the primed frame as seen from the unprimed frame. The matrix is given by
where is the magnitude of the velocity and is the Lorentz factor. This formula represents a passive transformation, as it describes how the coordinates of the measured quantity changes from the unprimed frame to the primed frame. The active transformation is given by .
If a frame F′ is boosted with velocity u relative to frame F, and another frame F′′ is boosted with velocity v relative to F′, the separate boosts are and the composition of the two boosts connects the coordinates in F′′ and F, Successive transformations act on the left. If u and v are collinear (parallel or antiparallel along the same line of relative motion), the boost matrices commute: B(v)B(u) = B(u)B(v). This composite transformation happens to be another boost, B(w), where w is collinear with u and v.
If u and v are not collinear but in different directions, the situation is considerably more complicated. Lorentz boosts along different directions do not commute: B(v)B(u) and B(u)B(v) are not equal. Although each of these compositions is not a single boost, each composition is still a Lorentz transformation as it preserves the spacetime interval. It turns out the composition of any two Lorentz boosts is equivalent to a boost followed or preceded by a rotation on the spatial coordinates, in the form of R(ρ)B(w) or B(w)R(ρ). The w and w are composite velocities, while ρ and ρ are rotation parameters (e.g. axis-angle variables, Euler angles, etc.). The rotation in block matrix form is simply where R(ρ) is a 3d rotation matrix, which rotates any 3d vector in one sense (active transformation), or equivalently the coordinate frame in the opposite sense (passive transformation). It is not simple to connect w and ρ (or w and ρ) to the original boost parameters u and v. In a composition of boosts, the R matrix is named the Wigner rotation, and gives rise to the Thomas precession. These articles give the explicit formulae for the composite transformation matrices, including expressions for w, ρ, w, ρ.
In this article the axis-angle representation is used for ρ. The rotation is about an axis in the direction of a unit vector e, through angle θ (positive anticlockwise, negative clockwise, according to the right-hand rule). The "axis-angle vector" will serve as a useful abbreviation.
Spatial rotations alone are also Lorentz transformations since they leave the spacetime interval invariant. Like boosts, successive rotations about different axes do not commute. Unlike boosts, the composition of any two rotations is equivalent to a single rotation. Some other similarities and differences between the boost and rotation matrices include:
- inverses: B(v) = B(−v) (relative motion in the opposite direction), and R(θ) = R(−θ) (rotation in the opposite sense about the same axis)
- identity transformation for no relative motion/rotation: B(0) = R(0) = I
- unit determinant: det(B) = det(R) = +1. This property makes them proper transformations.
- matrix symmetry: B is symmetric (equals transpose), while R is nonsymmetric but orthogonal (transpose equals inverse, R = R).
The most general proper Lorentz transformation Λ(v, θ) includes a boost and rotation together, and is a nonsymmetric matrix. As special cases, Λ(0, θ) = R(θ) and Λ(v, 0) = B(v). An explicit form of the general Lorentz transformation is cumbersome to write down and will not be given here. Nevertheless, closed form expressions for the transformation matrices will be given below using group theoretical arguments. It will be easier to use the rapidity parametrization for boosts, in which case one writes Λ(ζ, θ) and B(ζ).
The Lie group SO(3,1)
The set of transformations with matrix multiplication as the operation of composition forms a group, called the "restricted Lorentz group", and is the special indefinite orthogonal group SO(3,1). (The plus sign indicates that it preserves the orientation of the temporal dimension).
For simplicity, look at the infinitesimal Lorentz boost in the x direction (examining a boost in any other direction, or rotation about any axis, follows an identical procedure). The infinitesimal boost is a small boost away from the identity, obtained by the Taylor expansion of the boost matrix to first order about ζ = 0, where the higher order terms not shown are negligible because ζ is small, and Bx is simply the boost matrix in the x direction. The derivative of the matrix is the matrix of derivatives (of the entries, with respect to the same variable), and it is understood the derivatives are found first then evaluated at ζ = 0,
For now, Kx is defined by this result (its significance will be explained shortly). In the limit of an infinite number of infinitely small steps, the finite boost transformation in the form of a matrix exponential is obtained where the limit definition of the exponential has been used (see also characterizations of the exponential function). More generally
The axis-angle vector θ and rapidity vector ζ are altogether six continuous variables which make up the group parameters (in this particular representation), and the generators of the group are K = (Kx, Ky, Kz) and J = (Jx, Jy, Jz), each vectors of matrices with the explicit forms
These are all defined in an analogous way to Kx above, although the minus signs in the boost generators are conventional. Physically, the generators of the Lorentz group correspond to important symmetries in spacetime: J are the rotation generators which correspond to angular momentum, and K are the boost generators which correspond to the motion of the system in spacetime. The derivative of any smooth curve C(t) with C(0) = I in the group depending on some group parameter t with respect to that group parameter, evaluated at t = 0, serves as a definition of a corresponding group generator G, and this reflects an infinitesimal transformation away from the identity. The smooth curve can always be taken as an exponential as the exponential will always map G smoothly back into the group via t → exp(tG) for all t; this curve will yield G again when differentiated at t = 0.
Expanding the exponentials in their Taylor series obtains which compactly reproduce the boost and rotation matrices as given in the previous section.
It has been stated that the general proper Lorentz transformation is a product of a boost and rotation. At the infinitesimal level the product is commutative because only linear terms are required (products like (θ·J)(ζ·K) and (ζ·K)(θ·J) count as higher order terms and are negligible). Taking the limit as before leads to the finite transformation in the form of an exponential
The converse is also true, but the decomposition of a finite general Lorentz transformation into such factors is nontrivial. In particular, because the generators do not commute. For a description of how to find the factors of a general Lorentz transformation in terms of a boost and a rotation in principle (this usually does not yield an intelligible expression in terms of generators J and K), see Wigner rotation. If, on the other hand, the decomposition is given in terms of the generators, and one wants to find the product in terms of the generators, then the Baker–Campbell–Hausdorff formula applies.
The Lie algebra so(3,1)
Lorentz generators can be added together, or multiplied by real numbers, to obtain more Lorentz generators. In other words, the set of all Lorentz generators together with the operations of ordinary matrix addition and multiplication of a matrix by a number, forms a vector space over the real numbers. The generators Jx, Jy, Jz, Kx, Ky, Kz form a basis set of V, and the components of the axis-angle and rapidity vectors, θx, θy, θz, ζx, ζy, ζz, are the coordinates of a Lorentz generator with respect to this basis.
Three of the commutation relations of the Lorentz generators are where the bracket = AB − BA is known as the commutator, and the other relations can be found by taking cyclic permutations of x, y, z components (i.e. change x to y, y to z, and z to x, repeat).
These commutation relations, and the vector space of generators, fulfill the definition of the Lie algebra . In summary, a Lie algebra is defined as a vector space V over a field of numbers, and with a binary operation (called a Lie bracket in this context) on the elements of the vector space, satisfying the axioms of bilinearity, alternatization, and the Jacobi identity. Here the operation is the commutator which satisfies all of these axioms, the vector space is the set of Lorentz generators V as given previously, and the field is the set of real numbers.
Linking terminology used in mathematics and physics: A group generator is any element of the Lie algebra. A group parameter is a component of a coordinate vector representing an arbitrary element of the Lie algebra with respect to some basis. A basis, then, is a set of generators being a basis of the Lie algebra in the usual vector space sense.
The exponential map from the Lie algebra to the Lie group, provides a one-to-one correspondence between small enough neighborhoods of the origin of the Lie algebra and neighborhoods of the identity element of the Lie group. In the case of the Lorentz group, the exponential map is just the matrix exponential. Globally, the exponential map is not one-to-one, but in the case of the Lorentz group, it is surjective (onto). Hence any group element in the connected component of the identity can be expressed as an exponential of an element of the Lie algebra.
Improper transformations
Lorentz transformations also include parity inversion which negates all the spatial coordinates only, and time reversal which negates the time coordinate only, because these transformations leave the spacetime interval invariant. Here I is the 3d identity matrix. These are both symmetric, they are their own inverses (see involution (mathematics)), and each have determinant −1. This latter property makes them improper transformations.
If Λ is a proper orthochronous Lorentz transformation, then TΛ is improper antichronous, PΛ is improper orthochronous, and TPΛ = PTΛ is proper antichronous.
Inhomogeneous Lorentz group
Two other spacetime symmetries have not been accounted for. In order for the spacetime interval to be invariant, it can be shown that it is necessary and sufficient for the coordinate transformation to be of the form where C is a constant column containing translations in time and space. If C ≠ 0, this is an inhomogeneous Lorentz transformation or Poincaré transformation. If C = 0, this is a homogeneous Lorentz transformation. Poincaré transformations are not dealt further in this article.
Tensor formulation
Main article: Representation theory of the Lorentz group For the notation used, see Ricci calculus.Contravariant vectors
Writing the general matrix transformation of coordinates as the matrix equation allows the transformation of other physical quantities that cannot be expressed as four-vectors; e.g., tensors or spinors of any order in 4d spacetime, to be defined. In the corresponding tensor index notation, the above matrix expression is
where lower and upper indices label covariant and contravariant components respectively, and the summation convention is applied. It is a standard convention to use Greek indices that take the value 0 for time components, and 1, 2, 3 for space components, while Latin indices simply take the values 1, 2, 3, for spatial components (the opposite for Landau and Lifshitz). Note that the first index (reading left to right) corresponds in the matrix notation to a row index. The second index corresponds to the column index.
The transformation matrix is universal for all four-vectors, not just 4-dimensional spacetime coordinates. If A is any four-vector, then in tensor index notation
Alternatively, one writes in which the primed indices denote the indices of A in the primed frame. For a general n-component object one may write where Π is the appropriate representation of the Lorentz group, an n×n matrix for every Λ. In this case, the indices should not be thought of as spacetime indices (sometimes called Lorentz indices), and they run from 1 to n. E.g., if X is a bispinor, then the indices are called Dirac indices.
Covariant vectors
There are also vector quantities with covariant indices. They are generally obtained from their corresponding objects with contravariant indices by the operation of lowering an index; e.g., where η is the metric tensor. (The linked article also provides more information about what the operation of raising and lowering indices really is mathematically.) The inverse of this transformation is given by where, when viewed as matrices, η is the inverse of ημν. As it happens, η = ημν. This is referred to as raising an index. To transform a covariant vector Aμ, first raise its index, then transform it according to the same rule as for contravariant 4-vectors, then finally lower the index;
But
That is, it is the (μ, ν)-component of the inverse Lorentz transformation. One defines (as a matter of notation), and may in this notation write
Now for a subtlety. The implied summation on the right hand side of is running over a row index of the matrix representing Λ. Thus, in terms of matrices, this transformation should be thought of as the inverse transpose of Λ acting on the column vector Aμ. That is, in pure matrix notation,
This means exactly that covariant vectors (thought of as column matrices) transform according to the dual representation of the standard representation of the Lorentz group. This notion generalizes to general representations, simply replace Λ with Π(Λ).
Tensors
If A and B are linear operators on vector spaces U and V, then a linear operator A ⊗ B may be defined on the tensor product of U and V, denoted U ⊗ V according to
(T1)
From this it is immediately clear that if u and v are a four-vectors in V, then u ⊗ v ∈ T2V ≡ V ⊗ V transforms as
(T2)
The second step uses the bilinearity of the tensor product and the last step defines a 2-tensor on component form, or rather, it just renames the tensor u ⊗ v.
These observations generalize in an obvious way to more factors, and using the fact that a general tensor on a vector space V can be written as a sum of a coefficient (component!) times tensor products of basis vectors and basis covectors, one arrives at the transformation law for any tensor quantity T. It is given by
(T3)
where Λχ′ is defined above. This form can generally be reduced to the form for general n-component objects given above with a single matrix (Π(Λ)) operating on column vectors. This latter form is sometimes preferred; e.g., for the electromagnetic field tensor.
Transformation of the electromagnetic field

Lorentz transformations can also be used to illustrate that the magnetic field B and electric field E are simply different aspects of the same force — the electromagnetic force, as a consequence of relative motion between electric charges and observers. The fact that the electromagnetic field shows relativistic effects becomes clear by carrying out a simple thought experiment.
- An observer measures a charge at rest in frame F. The observer will detect a static electric field. As the charge is stationary in this frame, there is no electric current, so the observer does not observe any magnetic field.
- The other observer in frame F′ moves at velocity v relative to F and the charge. This observer sees a different electric field because the charge moves at velocity −v in their rest frame. The motion of the charge corresponds to an electric current, and thus the observer in frame F′ also sees a magnetic field.
The electric and magnetic fields transform differently from space and time, but exactly the same way as relativistic angular momentum and the boost vector.
The electromagnetic field strength tensor is given by in SI units. In relativity, the Gaussian system of units is often preferred over SI units, even in texts whose main choice of units is SI units, because in it the electric field E and the magnetic induction B have the same units making the appearance of the electromagnetic field tensor more natural. Consider a Lorentz boost in the x-direction. It is given by where the field tensor is displayed side by side for easiest possible reference in the manipulations below.
The general transformation law (T3) becomes
For the magnetic field one obtains
For the electric field results
Here, β = (β, 0, 0) is used. These results can be summarized by and are independent of the metric signature. For SI units, substitute E → E⁄c. Misner, Thorne & Wheeler (1973) refer to this last form as the 3 + 1 view as opposed to the geometric view represented by the tensor expression and make a strong point of the ease with which results that are difficult to achieve using the 3 + 1 view can be obtained and understood. Only objects that have well defined Lorentz transformation properties (in fact under any smooth coordinate transformation) are geometric objects. In the geometric view, the electromagnetic field is a six-dimensional geometric object in spacetime as opposed to two interdependent, but separate, 3-vector fields in space and time. The fields E (alone) and B (alone) do not have well defined Lorentz transformation properties. The mathematical underpinnings are equations (T1) and (T2) that immediately yield (T3). One should note that the primed and unprimed tensors refer to the same event in spacetime. Thus the complete equation with spacetime dependence is
Length contraction has an effect on charge density ρ and current density J, and time dilation has an effect on the rate of flow of charge (current), so charge and current distributions must transform in a related way under a boost. It turns out they transform exactly like the space-time and energy-momentum four-vectors,
or, in the simpler geometric view,
Charge density transforms as the time component of a four-vector. It is a rotational scalar. The current density is a 3-vector.
The Maxwell equations are invariant under Lorentz transformations.
Spinors
Equation (T1) hold unmodified for any representation of the Lorentz group, including the bispinor representation. In (T2) one simply replaces all occurrences of Λ by the bispinor representation Π(Λ),
(T4)
The above equation could, for instance, be the transformation of a state in Fock space describing two free electrons.
Transformation of general fields
A general noninteracting multi-particle state (Fock space state) in quantum field theory transforms according to the rule
| 1 |
where W(Λ, p) is the Wigner's little group and D is the (2j + 1)-dimensional representation of SO(3).
See also
- Ricci calculus
- Electromagnetic field
- Galilean transformation
- Hyperbolic rotation
- Lorentz group
- Representation theory of the Lorentz group
- Principle of relativity
- Velocity-addition formula
- Algebra of physical space
- Relativistic aberration
- Prandtl–Glauert transformation
- Split-complex number
- Gyrovector space
Footnotes
- One can imagine that in each inertial frame there are observers positioned throughout space, each with a synchronized clock and at rest in the particular inertial frame. These observers then report to a central office, where all reports are collected. When one speaks of a particular observer, one refers to someone having, at least in principle, a copy of this report. See, e.g., Sard (1970).
- The separate requirements of the three equations lead to three different groups. The second equation is satisfied for spacetime translations in addition to Lorentz transformations leading to the Poincaré group or the inhomogeneous Lorentz group. The first equation (or the second restricted to lightlike separation) leads to a yet larger group, the conformal group of spacetime.
- The groups O(3, 1) and O(1, 3) are isomorphic. It is widely believed that the choice between the two metric signatures has no physical relevance, even though some objects related to O(3, 1) and O(1, 3) respectively, e.g., the Clifford algebras corresponding to the different signatures of the bilinear form associated to the two groups, are non-isomorphic.
- For two square matrices A and B, det(AB) = det(A)det(B)
- Explicitly,
- In quantum mechanics, relativistic quantum mechanics, and quantum field theory, a different convention is used for these matrices; the right hand sides are all multiplied by a factor of the imaginary unit i = √−1.
- Until now the term "vector" has exclusively referred to "Euclidean vector", examples are position r, velocity v, etc. The term "vector" applies much more broadly than Euclidean vectors, row or column vectors, etc., see linear algebra and vector space for details. The generators of a Lie group also form a vector space over a field of numbers (e.g. real numbers, complex numbers), since a linear combination of the generators is also a generator. They just live in a different space to the position vectors in ordinary 3d space.
- In ordinary 3d position space, the position vector r = xex + yey + zez is expressed as a linear combination of the Cartesian unit vectors ex, ey, ez which form a basis, and the Cartesian coordinates x, y, z are coordinates with respect to this basis.
Notes
- Rao, K. N. Srinivasa (1988). The Rotation and Lorentz Groups and Their Representations for Physicists (illustrated ed.). John Wiley & Sons. p. 213. ISBN 978-0-470-21044-4. Equation 6-3.24, page 210
- Forshaw & Smith 2009
- Cottingham & Greenwood 2007, p. 21
- Lorentz 1904
- O'Connor & Robertson 1996
- Brown 2003
- Rothman 2006, pp. 112f.
- Darrigol 2005, pp. 1–22
- Macrossan 1986, pp. 232–34
- The reference is within the following paper:Poincaré 1905, pp. 1504–1508
- Einstein 1905, pp. 891–921
- Young & Freedman 2008
- Forshaw & Smith 2009
- Moses Fayngold (2008). Special Relativity and How it Works (illustrated ed.). John Wiley & Sons. p. 102. ISBN 978-3-527-40607-4. Extract of page 102
- Mircea S. Rogalski; Stuart B. Palmer (2018). Advanced University Physics (2nd, revised ed.). CRC Press. p. 70. ISBN 978-1-4200-5712-6. Extract of page 70
- Andrew M. Steane (2012). Relativity Made Relatively Easy (illustrated ed.). OUP Oxford. p. 124. ISBN 978-0-19-966286-9. Extract of page 124
- George Arfken (2012). International Edition University Physics. Elsevier. p. 367. ISBN 978-0-323-14203-8. Extract of page 367
- E.R. Dobbs (2013). Basic Electromagnetism (illustrated ed.). Springer Science & Business Media. p. 113. ISBN 978-94-011-2112-5. Extract of page 113
- Einstein 1916
- Barut 1964, p. 18–19
- Chaichian & Hagedorn 1997, p. 239
- Furry, W. H. (1955-11-01). "Lorentz Transformation and the Thomas Precession". American Journal of Physics. 23 (8): 517–525. Bibcode:1955AmJPh..23..517F. doi:10.1119/1.1934085. ISSN 0002-9505.
- Weinberg 1972
- Weinberg 2005, pp. 55–58
- Ohlsson 2011, p. 3–9
- Dennery & Krzywicki 2012, p. 138
- Hall 2003, Chapter 4
- Carroll 2004, p. 22
- Grant & Phillips 2008
- Griffiths 2007
- Jackson 1975, p.
- Misner, Thorne & Wheeler 1973
- Weinberg 2002, Chapter 3
- "INSPIRE". inspirehep.net. Retrieved 2024-09-04.
References
Websites
- O'Connor, John J.; Robertson, Edmund F. (1996), A History of Special Relativity
- Brown, Harvey R. (2003), Michelson, FitzGerald and Lorentz: the Origins of Relativity Revisited
Papers
- Cushing, J. T. (1967). "Vector Lorentz transformations". American Journal of Physics. 35 (9): 858–862. Bibcode:1967AmJPh..35..858C. doi:10.1119/1.1974267.
- Macfarlane, A. J. (1962). "On the Restricted Lorentz Group and Groups Homomorphically Related to It". Journal of Mathematical Physics. 3 (6): 1116–1129. Bibcode:1962JMP.....3.1116M. doi:10.1063/1.1703854. hdl:2027/mdp.39015095220474.
- Rothman, Tony (2006), "Lost in Einstein's Shadow" (PDF), American Scientist, 94 (2): 112f
- Darrigol, Olivier (2005), "The Genesis of the theory of relativity" (PDF), Séminaire Poincaré, 1: 1–22, Bibcode:2006eins.book....1D, doi:10.1007/3-7643-7436-5_1, ISBN 978-3-7643-7435-8
- Macrossan, Michael N. (1986), "A Note on Relativity Before Einstein", Br. J. Philos. Sci., 37 (2): 232–34, CiteSeerX 10.1.1.679.5898, doi:10.1093/bjps/37.2.232, archived from the original on 2013-10-29, retrieved 2007-04-02
- Poincaré, Henri (1905), "On the Dynamics of the Electron" , Comptes Rendus Hebdomadaires des Séances de l'Académie des Sciences, 140: 1504–1508
- Einstein, Albert (1905), "Zur Elektrodynamik bewegter Körper" (PDF), Annalen der Physik, 322 (10): 891–921, Bibcode:1905AnP...322..891E, doi:10.1002/andp.19053221004. See also: English translation.
- Lorentz, Hendrik Antoon (1904). "Electromagnetic phenomena in a system moving with any velocity smaller than that of light" . Proceedings of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences. 6: 809–831.
- Einstein, A. (1916). Relativity: The Special and General Theory. Retrieved 2012-01-23. Einstein, A. (1916). Relativity: The Special and General Theory. New York: Three Rivers Press (published 1995). ISBN 978-0-517-88441-6 – via Albert Einstein Reference Archive.
- Ungar, A. A. (1988). "Thomas rotation and the parameterization of the Lorentz transformation group". Foundations of Physics Letters. 1 (1): 55–89. Bibcode:1988FoPhL...1...57U. doi:10.1007/BF00661317. ISSN 0894-9875. S2CID 121240925. eqn (55).
- Ungar, A. A. (1989). "The relativistic velocity composition paradox and the Thomas rotation". Foundations of Physics. 19 (11): 1385–1396. Bibcode:1989FoPh...19.1385U. doi:10.1007/BF00732759. S2CID 55561589.
- Ungar, A. A. (2000). "The relativistic composite-velocity reciprocity principle". Foundations of Physics. 30 (2): 331–342. Bibcode:2000FoPh...30..331U. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.35.1131. doi:10.1023/A:1003653302643. S2CID 118634052.
- Mocanu, C. I. (1986). "Some difficulties within the framework of relativistic electrodynamics". Archiv für Elektrotechnik. 69 (2): 97–110. doi:10.1007/bf01574845. S2CID 123543303.
- Mocanu, C. I. (1992). "On the relativistic velocity composition paradox and the Thomas rotation". Foundations of Physics. 5 (5): 443–456. Bibcode:1992FoPhL...5..443M. doi:10.1007/bf00690425. S2CID 122472788.
- Weinberg, S. (2002). The Quantum Theory of Fields, vol I. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-55001-7.
Books
- Barut, Asim Orhan (1964). Electrodynamics and Classical Theory of Fields and Particles. Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-486-64038-9.
- Dennery, Philippe; Krzywicki, André (2012). Mathematics for Physicists. Courier Corporation. ISBN 978-0-486-15712-2.
- Cottingham, W. N.; Greenwood, D. A. (2007). An Introduction to the Standard Model of Particle Physics (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-139-46221-1.
- Young, H. D.; Freedman, R. A. (2008). University Physics – With Modern Physics (12th ed.). Pearson Addison-Wesley. ISBN 978-0-321-50130-1.
- Halpern, A. (1988). 3000 Solved Problems in Physics. Schaum Series. Mc Graw Hill. p. 688. ISBN 978-0-07-025734-4.
- Forshaw, J. R.; Smith, A. G. (2009). Dynamics and Relativity. Manchester Physics Series. John Wiley & Sons Ltd. pp. 124–126. ISBN 978-0-470-01460-8.
- Wheeler, J. A.; Taylor, E. F (1971). Spacetime Physics. Freeman. ISBN 978-0-7167-0336-5.
- Wheeler, J. A.; Thorne, K. S.; Misner, C. W. (1973). Gravitation. Freeman. ISBN 978-0-7167-0344-0.
- Carroll, S. M. (2004). Spacetime and Geometry: An Introduction to General Relativity (illustrated ed.). Addison Wesley. p. 22. ISBN 978-0-8053-8732-2.
- Grant, I. S.; Phillips, W. R. (2008). "14". Electromagnetism. Manchester Physics (2nd ed.). John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-471-92712-9.
- Griffiths, D. J. (2007). Introduction to Electrodynamics (3rd ed.). Pearson Education, Dorling Kindersley. ISBN 978-81-7758-293-2.
- Hall, Brian C. (2003). Lie Groups, Lie Algebras, and Representations An Elementary Introduction. Springer. ISBN 978-0-387-40122-5.
- Weinberg, Steven (1972). Gravitation and Cosmology: Principles and Applications of the General Theory of Relativity. Wiley. ISBN 978-0-471-92567-5.
- Weinberg, S. (2008), Cosmology, Wiley, ISBN 978-0-19-852682-7
- Weinberg, S. (2005), The quantum theory of fields (3 vol.), vol. 1, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-67053-1
- Ohlsson, T. (2011), Relativistic Quantum Physics, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-76726-2
- Goldstein, H. (1980) . Classical Mechanics (2nd ed.). Reading MA: Addison-Wesley. ISBN 978-0-201-02918-5.
- Jackson, J. D. (1975) . "Chapter 11". Classical Electrodynamics (2nd ed.). John Wiley & Sons. pp. 542–545. ISBN 978-0-471-43132-9.
- Landau, L. D.; Lifshitz, E. M. (2002) . The Classical Theory of Fields. Course of Theoretical Physics. Vol. 2 (4th ed.). Butterworth–Heinemann. pp. 9–12. ISBN 0-7506-2768-9.
- Feynman, R. P.; Leighton, R. B.; Sands, M. (1977) . "15". The Feynman Lectures on Physics. Vol. 1. Addison Wesley. ISBN 978-0-201-02117-2.
- Feynman, R. P.; Leighton, R. B.; Sands, M. (1977) . "13". The Feynman Lectures on Physics. Vol. 2. Addison Wesley. ISBN 978-0-201-02117-2.
- Misner, Charles W.; Thorne, Kip S.; Wheeler, John Archibald (1973). Gravitation. San Francisco: W. H. Freeman. ISBN 978-0-7167-0344-0.
- Rindler, W. (2006) . "Chapter 9". Relativity Special, General and Cosmological (2nd ed.). Dallas: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-856732-5.
- Ryder, L. H. (1996) . Quantum Field Theory (2nd ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0521478144.
- Sard, R. D. (1970). Relativistic Mechanics - Special Relativity and Classical Particle Dynamics. New York: W. A. Benjamin. ISBN 978-0805384918.
- Sexl, R. U.; Urbantke, H. K. (2001) . Relativity, Groups Particles. Special Relativity and Relativistic Symmetry in Field and Particle Physics. Springer. ISBN 978-3211834435.
- Gourgoulhon, Eric (2013). Special Relativity in General Frames: From Particles to Astrophysics. Springer. p. 213. ISBN 978-3-642-37276-6.
- Chaichian, Masud; Hagedorn, Rolf (1997). Symmetry in quantum mechanics:From angular momentum to supersymmetry. IoP. p. 239. ISBN 978-0-7503-0408-5.
- Landau, L.D.; Lifshitz, E.M. (2002) . The Classical Theory of Fields. Course of Theoretical Physics. Vol. 2 (4th ed.). Butterworth–Heinemann. ISBN 0-7506-2768-9.
Further reading
- Ernst, A.; Hsu, J.-P. (2001), "First proposal of the universal speed of light by Voigt 1887" (PDF), Chinese Journal of Physics, 39 (3): 211–230, Bibcode:2001ChJPh..39..211E, archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-16
- Thornton, Stephen T.; Marion, Jerry B. (2004), Classical dynamics of particles and systems (5th ed.), Belmont, : Brooks/Cole, pp. 546–579, ISBN 978-0-534-40896-1
- Voigt, Woldemar (1887), "Über das Doppler'sche princip", Nachrichten von der Königlicher Gesellschaft den Wissenschaft zu Göttingen, 2: 41–51
External links
- Derivation of the Lorentz transformations. This web page contains a more detailed derivation of the Lorentz transformation with special emphasis on group properties.
- The Paradox of Special Relativity. This webpage poses a problem, the solution of which is the Lorentz transformation, which is presented graphically in its next page.
- Relativity Archived 2011-08-29 at the Wayback Machine – a chapter from an online textbook
- Warp Special Relativity Simulator. A computer program demonstrating the Lorentz transformations on everyday objects.
- Animation clip on YouTube visualizing the Lorentz transformation.
- MinutePhysics video on YouTube explaining and visualizing the Lorentz transformation with a mechanical Minkowski diagram
- Interactive graph on Desmos (graphing) showing Lorentz transformations with a virtual Minkowski diagram
- Interactive graph on Desmos showing Lorentz transformations with points and hyperbolas
- Lorentz Frames Animated from John de Pillis. Online Flash animations of Galilean and Lorentz frames, various paradoxes, EM wave phenomena, etc.
| Relativity | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Special relativity |
| ||||||||||||
| General relativity |
| ||||||||||||
| Scientists | |||||||||||||
 representing a velocity confined to the x-direction, is expressed as
representing a velocity confined to the x-direction, is expressed as
 where (t, x, y, z) and (t′, x′, y′, z′) are the coordinates of an event in two frames with the spatial origins coinciding at t=t′=0, where the primed frame is seen from the unprimed frame as moving with speed v along the x-axis, where c is the
where (t, x, y, z) and (t′, x′, y′, z′) are the coordinates of an event in two frames with the spatial origins coinciding at t=t′=0, where the primed frame is seen from the unprimed frame as moving with speed v along the x-axis, where c is the  is the
is the  grows without bound. The value of v must be smaller than c for the transformation to make sense.
grows without bound. The value of v must be smaller than c for the transformation to make sense.
 an equivalent form of the transformation is
an equivalent form of the transformation is






 (lowercase
(lowercase 
 which shows much more clearly the symmetry in the transformation. From the allowed ranges of v and the definition of β, it follows −1 < β < 1. The use of β and γ is standard throughout the literature.
which shows much more clearly the symmetry in the transformation. From the allowed ranges of v and the definition of β, it follows −1 < β < 1. The use of β and γ is standard throughout the literature.
 is in an arbitrary vector direction with the boost vector
is in an arbitrary vector direction with the boost vector  , then the transformation from an unprimed spacetime coordinate system to a primed coordinate system is given by,
, then the transformation from an unprimed spacetime coordinate system to a primed coordinate system is given by,
 . The
. The  . The inverse of the transformation is given by reversing the sign of
. The inverse of the transformation is given by reversing the sign of  . The quantity
. The quantity  is invariant under the transformation.
is invariant under the transformation.


 provides the link between a constant value of rapidity, and the
provides the link between a constant value of rapidity, and the 



 with inverse relations
with inverse relations

 in accordance with the
in accordance with the  , so the events are no longer simultaneous according to a moving observer.
, so the events are no longer simultaneous according to a moving observer. then the transformations are
then the transformations are
 where · is the
where · is the 


 and the "rapidity vector" can be defined as
and the "rapidity vector" can be defined as
 each of which serves as a useful abbreviation in some contexts. The magnitude of ζ is the absolute value of the rapidity scalar confined to 0 ≤ ζ < ∞, which agrees with the range 0 ≤ β < 1.
each of which serves as a useful abbreviation in some contexts. The magnitude of ζ is the absolute value of the rapidity scalar confined to 0 ≤ ζ < ∞, which agrees with the range 0 ≤ β < 1.


 implies the quantities transform under Lorentz transformations similar to the transformation of spacetime coordinates;
implies the quantities transform under Lorentz transformations similar to the transformation of spacetime coordinates;

 the spacetime interval takes the form (superscript T denotes
the spacetime interval takes the form (superscript T denotes  and is
and is  where Λ is a square matrix which can depend on parameters.
where Λ is a square matrix which can depend on parameters.
 in this article is denoted
in this article is denoted  . This set together with matrix multiplication forms a
. This set together with matrix multiplication forms a  and this matrix equation contains the general conditions on the Lorentz transformation to ensure invariance of the spacetime interval. Taking the
and this matrix equation contains the general conditions on the Lorentz transformation to ensure invariance of the spacetime interval. Taking the 
 carrying out the block matrix multiplications obtains general conditions on Γ, a, b, M to ensure relativistic invariance. Not much information can be directly extracted from all the conditions, however one of the results
carrying out the block matrix multiplications obtains general conditions on Γ, a, b, M to ensure relativistic invariance. Not much information can be directly extracted from all the conditions, however one of the results
 is useful; bb ≥ 0 always so it follows that
is useful; bb ≥ 0 always so it follows that










 ,
,  ,
,  , and
, and  all form subgroups, the sets containing improper and/or antichronous transformations without enough proper orthochronous transformations (e.g.
all form subgroups, the sets containing improper and/or antichronous transformations without enough proper orthochronous transformations (e.g.  ,
,  ,
,  ) do not form subgroups.
) do not form subgroups.
 , and the same measurement made in another inertial frame (with the same orientation and origin) gives result
, and the same measurement made in another inertial frame (with the same orientation and origin) gives result  , the two results will be related by
, the two results will be related by
 where the boost matrix
where the boost matrix  represents the rotation-free Lorentz transformation between the unprimed and primed frames and
represents the rotation-free Lorentz transformation between the unprimed and primed frames and  is the velocity of the primed frame as seen from the unprimed frame. The matrix is given by
is the velocity of the primed frame as seen from the unprimed frame. The matrix is given by

 is the magnitude of the velocity and
is the magnitude of the velocity and  is the Lorentz factor. This formula represents a passive transformation, as it describes how the coordinates of the measured quantity changes from the unprimed frame to the primed frame. The active transformation is given by
is the Lorentz factor. This formula represents a passive transformation, as it describes how the coordinates of the measured quantity changes from the unprimed frame to the primed frame. The active transformation is given by  .
.
 and the composition of the two boosts connects the coordinates in F′′ and F,
and the composition of the two boosts connects the coordinates in F′′ and F,
 Successive transformations act on the left. If u and v are
Successive transformations act on the left. If u and v are  where R(ρ) is a 3d
where R(ρ) is a 3d  will serve as a useful abbreviation.
will serve as a useful abbreviation.
 with matrix multiplication as the operation of composition forms a group, called the "restricted Lorentz group", and is the
with matrix multiplication as the operation of composition forms a group, called the "restricted Lorentz group", and is the  where the higher order terms not shown are negligible because ζ is small, and Bx is simply the boost matrix in the x direction. The
where the higher order terms not shown are negligible because ζ is small, and Bx is simply the boost matrix in the x direction. The 
 where the
where the 


 which compactly reproduce the boost and rotation matrices as given in the previous section.
which compactly reproduce the boost and rotation matrices as given in the previous section.
 is commutative because only linear terms are required (products like (θ·J)(ζ·K) and (ζ·K)(θ·J) count as higher order terms and are negligible). Taking the limit as before leads to the finite transformation in the form of an exponential
is commutative because only linear terms are required (products like (θ·J)(ζ·K) and (ζ·K)(θ·J) count as higher order terms and are negligible). Taking the limit as before leads to the finite transformation in the form of an exponential

 because the generators do not commute. For a description of how to find the factors of a general Lorentz transformation in terms of a boost and a rotation in principle (this usually does not yield an intelligible expression in terms of generators J and K), see
because the generators do not commute. For a description of how to find the factors of a general Lorentz transformation in terms of a boost and a rotation in principle (this usually does not yield an intelligible expression in terms of generators J and K), see  together with the operations of ordinary
together with the operations of ordinary  where the bracket = AB − BA is known as the
where the bracket = AB − BA is known as the  . In summary, a Lie algebra is defined as a
. In summary, a Lie algebra is defined as a  provides a one-to-one correspondence between small enough neighborhoods of the origin of the Lie algebra and neighborhoods of the identity element of the Lie group. In the case of the Lorentz group, the exponential map is just the
provides a one-to-one correspondence between small enough neighborhoods of the origin of the Lie algebra and neighborhoods of the identity element of the Lie group. In the case of the Lorentz group, the exponential map is just the  which negates all the spatial coordinates only, and
which negates all the spatial coordinates only, and  which negates the time coordinate only, because these transformations leave the spacetime interval invariant. Here I is the 3d
which negates the time coordinate only, because these transformations leave the spacetime interval invariant. Here I is the 3d  where C is a constant column containing translations in time and space. If C ≠ 0, this is an inhomogeneous Lorentz transformation or
where C is a constant column containing translations in time and space. If C ≠ 0, this is an inhomogeneous Lorentz transformation or  allows the transformation of other physical quantities that cannot be expressed as four-vectors; e.g.,
allows the transformation of other physical quantities that cannot be expressed as four-vectors; e.g., 

 in which the primed indices denote the indices of A in the primed frame. For a general n-component object one may write
in which the primed indices denote the indices of A in the primed frame. For a general n-component object one may write  where Π is the appropriate
where Π is the appropriate  where η is the
where η is the  where, when viewed as matrices, η is the inverse of ημν. As it happens, η = ημν. This is referred to as raising an index. To transform a covariant vector Aμ, first raise its index, then transform it according to the same rule as for contravariant 4-vectors, then finally lower the index;
where, when viewed as matrices, η is the inverse of ημν. As it happens, η = ημν. This is referred to as raising an index. To transform a covariant vector Aμ, first raise its index, then transform it according to the same rule as for contravariant 4-vectors, then finally lower the index;


 and may in this notation write
and may in this notation write

 is running over a row index of the matrix representing Λ. Thus, in terms of matrices, this transformation should be thought of as the inverse transpose of Λ acting on the column vector Aμ. That is, in pure matrix notation,
is running over a row index of the matrix representing Λ. Thus, in terms of matrices, this transformation should be thought of as the inverse transpose of Λ acting on the column vector Aμ. That is, in pure matrix notation,

 (T1)
(T1)
 (T2)
(T2)
 (T3)
(T3)
 in
in  where the field tensor is displayed side by side for easiest possible reference in the manipulations below.
where the field tensor is displayed side by side for easiest possible reference in the manipulations below.



 and are independent of the metric signature. For SI units, substitute E → E⁄c.
and are independent of the metric signature. For SI units, substitute E → E⁄c.  and make a strong point of the ease with which results that are difficult to achieve using the 3 + 1 view can be obtained and understood. Only objects that have well defined Lorentz transformation properties (in fact under any smooth coordinate transformation) are geometric objects. In the geometric view, the electromagnetic field is a six-dimensional geometric object in spacetime as opposed to two interdependent, but separate, 3-vector fields in space and time. The fields E (alone) and B (alone) do not have well defined Lorentz transformation properties. The mathematical underpinnings are equations
and make a strong point of the ease with which results that are difficult to achieve using the 3 + 1 view can be obtained and understood. Only objects that have well defined Lorentz transformation properties (in fact under any smooth coordinate transformation) are geometric objects. In the geometric view, the electromagnetic field is a six-dimensional geometric object in spacetime as opposed to two interdependent, but separate, 3-vector fields in space and time. The fields E (alone) and B (alone) do not have well defined Lorentz transformation properties. The mathematical underpinnings are equations 


 (T4)
(T4)


