Pharmaceutical compound
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Trocoxil |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATCvet code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.248.948 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
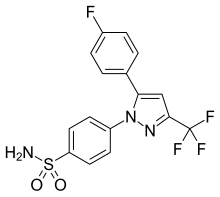
| Formula | C16H11F4N3O2S |
| Molar mass | 385.34 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Mavacoxib (trade name Trocoxil) is a veterinary drug used to treat pain and inflammation in dogs with degenerative joint disease. It acts as a COX-2 inhibitor.
Mavacoxib, along with several other COX-2 selective inhibitors, including celecoxib, valdecoxib, and parecoxib, were discovered by a team at the Searle division of Monsanto led by John Talley.
References
- "Trocoxil EPAR". European Medicines Agency. 22 September 2008. Retrieved 26 June 2024.
- European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Trocoxil Archived 17 March 2018 at the Wayback Machine, European Medicines Agency
- Cox SR, Lesman SP, Boucher JF, Krautmann MJ, Hummel BD, Savides M, et al. (October 2010). "The pharmacokinetics of mavacoxib, a long-acting COX-2 inhibitor, in young adult laboratory dogs". Journal of Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 33 (5): 461–70. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2885.2010.01165.x. PMID 20840390.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: overridden setting (link) - Langreth R (23 June 2003). "The Chemical Cobbler". Forbes.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: overridden setting (link) - "Dr. John Talley: 2001 St. Louis Awardee" (PDF). Chemical Bond. 52 (5). St. Louis Section, American Chemical Society: 2. May 2001. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 April 2018.
| Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (primarily M01A and M02A, also N02BA) | |
|---|---|
| pyrazolones / pyrazolidines | |
| salicylates | |
| acetic acid derivatives and related substances | |
| oxicams | |
| propionic acid derivatives (profens) |
|
| n-arylanthranilic acids (fenamates) | |
| COX-2 inhibitors (coxibs) | |
| other | |
| NSAID combinations | |
| Key: underline indicates initially developed first-in-class compound of specific group; WHO-Essential Medicines; withdrawn drugs; veterinary use. | |
This veterinary medicine–related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |
This drug article relating to the musculoskeletal system is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |