| Medial lemniscus | |
|---|---|
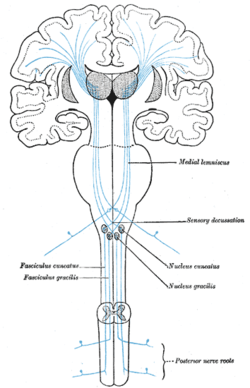 The sensory tract. (Medial lemniscus labeled at top right.) The sensory tract. (Medial lemniscus labeled at top right.) | |
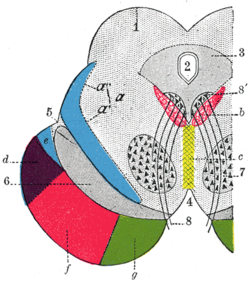 Coronal section through mid-brain. ("e" is Portion of medial lemniscus, which runs to the lentiform nucleus and insula. "a’" is also the medial lemniscus.) Coronal section through mid-brain. ("e" is Portion of medial lemniscus, which runs to the lentiform nucleus and insula. "a’" is also the medial lemniscus.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | lemniscus medialis |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_887 |
| TA98 | A14.1.04.111 A14.1.08.672 A14.1.06.207 |
| TA2 | 5861 |
| FMA | 83675 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy[edit on Wikidata] | |
The medial lemniscus, also known as Reil's band or Reil's ribbon (for German anatomist Johann Christian Reil), is a large ascending bundle of heavily myelinated axons that decussate in the brainstem, specifically in the medulla oblongata. The medial lemniscus is formed by the crossings of the internal arcuate fibers. The internal arcuate fibers are composed of axons of the gracile nucleus and the cuneate nucleus. The cell bodies of the nuclei lie contralaterally.
The medial lemniscus is part of the somatosensory dorsal column–medial lemniscus pathway, which ascends in the spinal cord to the thalamus. Lesions of the medial lemniscus cause an impairment of vibratory and touch-pressure sense.
Etymology
Lemniscus means "ribbon", reflecting the elongated tract of the medial lemniscus.
Anatomy
Path
After neurons carrying somatosensory proprioceptive or fine touch information synapse at the gracile and cuneate nuclei, axons from second-order neurons decussate at the level of the medulla and travel up the brainstem as the medial lemniscus on the contralateral (opposite) side. It is part of the posterior column-medial lemniscus pathway, which transmits touch, vibration sense, as well as the pathway for proprioception.
The medial lemniscus carries axons from most of the body and terminates by synapsing with third-order neurons in the ventral posterolateral nucleus of the thalamus. at the level of the mamillary bodies. Sensory axons transmitting information from the head and neck via the trigeminal nerve synapse at the ventral posteromedial nucleus of the thalamus.
Location through the brainstem
The cuneate and gracile nuclei reside at the closed (lower) medulla, so the medial lemniscus is not formed at this level. Fibres from these nuclei will pass to the contralateral side of the brainstem, as the internal arcuate fibres. In the midbrain, it is situated dorsal to the substantia nigra, and medial to either red nucleus.
Additional images
-
 Horizontal section through the lower part of the pons. The medial lemniscus is labeled #17.
Horizontal section through the lower part of the pons. The medial lemniscus is labeled #17.
-
 Tractography showing medial lemniscus
Tractography showing medial lemniscus
References
- Kamali A, Kramer LA, Butler IJ, Hasan KM. Diffusion tensor tractography of the somatosensory system in the human brainstem: initial findings using high isotropic spatial resolution at 3.0 T. Eur Radiol. 2009 19:1480-8. doi:10.1007/s00330-009-1305-x.
- Purves, Dale (2012). Neuroscience (5th ed.). Sunderland, Mass: Sinauer Associates. p. 198. ISBN 9780878936953.
- Purves, Dale (2018). Neuroscience (Sixth ed.). New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 202–204. ISBN 9781605353807.
- "medial lemniscus - Dictionnaire médical de l'Académie de Médecine". www.academie-medecine.fr. Retrieved 2024-07-27. The cuneate and gracile nuclei reside at the closed (lower) medulla, so the lemniscus is not formed at this level. Fibres from these nuclei will pass to the contralateral side of the brainstem, as the internal arcuate fibres.
External links
| Anatomy of the medulla | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grey matter |
| ||||||||||
| White matter |
| ||||||||||
| Surface |
| ||||||||||
| Grey | |||||||||||
| Anatomy of the pons | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dorsal/ (tegmentum) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Ventral/ (base) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Other grey: Raphe/ reticular | |||||||||||||||
| Anatomy of the midbrain | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tectum (Dorsal) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CSF | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Peduncle (Ventral) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sensory receptors | |
|---|---|
| Touch |
|
| Pain | |
| Temperature | |
| Proprioception | |
| Other | |