| This article's lead section may be too technical for most readers to understand. Please help improve it to make it understandable to non-experts, without removing the technical details. (December 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Metacarpophalangeal joint | |
|---|---|
 The palmar aspect of the hand showing the epiphyses of the hand exploded. MCP joints in red. The palmar aspect of the hand showing the epiphyses of the hand exploded. MCP joints in red. | |
 The DIP, PIP and MCP joints of the hand: MetaCarpoPhalangeal joints, and the interphalangeal joints of the hand: The DIP, PIP and MCP joints of the hand: MetaCarpoPhalangeal joints, and the interphalangeal joints of the hand:
| |
| Details | |
| System | 099 |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | articulationes metacarpophalangeae |
| MeSH | D008662 |
| TA98 | A03.5.11.501 |
| TA2 | 1835 |
| FMA | 35246 |
| Anatomical terminology[edit on Wikidata] | |
The metacarpophalangeal joints (MCP) are situated between the metacarpal bones and the proximal phalanges of the fingers. These joints are of the condyloid kind, formed by the reception of the rounded heads of the metacarpal bones into shallow cavities on the proximal ends of the proximal phalanges. Being condyloid, they allow the movements of flexion, extension, abduction, adduction and circumduction (see anatomical terms of motion) at the joint.
Structure
Ligaments
 Metacarpophalangeal articulation and articulations of digit. Palmar aspect.
Metacarpophalangeal articulation and articulations of digit. Palmar aspect.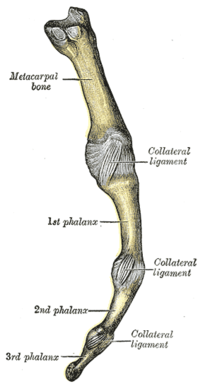 Metacarpophalangeal articulation and articulations of digit. Ulnar aspect.
See also: Palmar plate
Metacarpophalangeal articulation and articulations of digit. Ulnar aspect.
See also: Palmar plate
Each joint has:
- palmar ligaments of metacarpophalangeal articulations
- collateral ligaments of metacarpophalangeal articulations
Dorsal surfaces
The dorsal surfaces of these joints are covered by the expansions of the Extensor tendons, together with some loose areolar tissue which connects the deep surfaces of the tendons to the bones.
Function
The movements which occur in these joints are flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, and circumduction; the movements of abduction and adduction are very limited, and cannot be performed while the fingers form a fist.
The muscles of flexion and extension are as follows:
| Location | Flexion | Extension |
|---|---|---|
| fingers | Flexor digitorum superficialis and profundus, lumbricals, and interossei, assisted in the case of the little finger by the flexor digiti minimi brevis | extensor digitorum communis, extensor indicis proprius, and extensor digiti minimi muscle |
| thumb | flexor pollicis longus and brevis | extensor pollicis longus and brevis |
Clinical significance
Arthritis of the MCP is a distinguishing feature of rheumatoid arthritis, as opposed to the distal interphalangeal joint in osteoarthritis.
Other animals
In many quadrupeds, particularly horses and other larger animals, the metacarpophalangeal joint is referred to as the "fetlock". This term is translated literally as "foot-lock". In fact, although the term fetlock does not specifically apply to other species' metacarpophalangeal joints (for instance, humans), the "second" or "mid-finger" knuckle of the human hand does anatomically correspond to the fetlock on larger quadrupeds. For lack of a better term, the shortened name may seem more practical.
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 332 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 332 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Drake, Vogl and Mitchell (2015). Grey's Anatomy for Students, 3rd Edition. Churchill Livingstone, Elsevier. p. 796. ISBN 9780702051319.
- Gray's Anatomy (1918), see infobox