
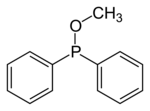
In organic chemistry, phosphinites are organophosphorus compounds with the formula P(OR)R2. They are used as ligands in homogeneous catalysis and coordination chemistry.
Preparation
Phosphinites are prepared by alcoholysis of organophosphinous chlorides. For example, treatment of chlorodiphenylphosphine with methanol and base gives methyl diphenylphosphinite:
- ClPPh2 + CH3OH → CH3OPPh2 + HCl
Although they are esters of phosphinous acids (R2POH), phosphinites are not made via such intermediates.
Reactions
Oxidation of phosphinites gives phosphinates:
- 2 P(OR)R2 + O2 → 2 OP(OR)R2
Phosphinites are ligands, giving derivatives similar to metal phosphine complexes. They are stronger pi-acceptors than typical phosphine ligands.
References
- D. E. C. Corbridge (1995). Phosphorus: An Outline of its Chemistry, Biochemistry, and Technology (5th ed.). Amsterdam: Elsevier. ISBN 0-444-89307-5.
- Rajanbabu, T. V. Babu (2012). "Phosphinite and Phosphonite Ligands". Phosphorus(III) Ligands in Homogeneous Catalysis: Design and Synthesis. pp. 159–232. doi:10.1002/9781118299715.ch5. ISBN 9781118299715.
See also
- Phosphine - PR3
- Phosphine oxide - OPR3
- Phosphonite - P(OR)2R
- Phosphite - P(OR)3
- Phosphinate - OP(OR)R2
- Phosphonate - OP(OR)2R
- Phosphate - OP(OR)3
| Organophosphorus | |
|---|---|