

In mathematics, tetration (or hyper-4) is an operation based on iterated, or repeated, exponentiation. There is no standard notation for tetration, though Knuth's up arrow notation and the left-exponent are common.
Under the definition as repeated exponentiation, means , where n copies of a are iterated via exponentiation, right-to-left, i.e. the application of exponentiation times. n is called the "height" of the function, while a is called the "base," analogous to exponentiation. It would be read as "the nth tetration of a". For example, 2 tetrated to 4 (or the fourth tetration of 2) is .
It is the next hyperoperation after exponentiation, but before pentation. The word was coined by Reuben Louis Goodstein from tetra- (four) and iteration.
Tetration is also defined recursively as
allowing for attempts to extend tetration to non-natural numbers such as real, complex, and ordinal numbers.
The two inverses of tetration are called super-root and super-logarithm, analogous to the nth root and the logarithmic functions. None of the three functions are elementary.
Tetration is used for the notation of very large numbers.
Introduction
The first four hyperoperations are shown here, with tetration being considered the fourth in the series. The unary operation succession, defined as , is considered to be the zeroth operation.
- Addition n copies of 1 added to a combined by succession.
- Multiplication n copies of a combined by addition.
- Exponentiation n copies of a combined by multiplication.
- Tetration n copies of a combined by exponentiation, right-to-left.
Importantly, nested exponents are interpreted from the top down: means and not
Succession, , is the most basic operation; while addition () is a primary operation, for addition of natural numbers it can be thought of as a chained succession of successors of ; multiplication () is also a primary operation, though for natural numbers it can analogously be thought of as a chained addition involving numbers of . Exponentiation can be thought of as a chained multiplication involving numbers of and tetration () as a chained power involving numbers . Each of the operations above are defined by iterating the previous one; however, unlike the operations before it, tetration is not an elementary function.
The parameter is referred to as the base, while the parameter may be referred to as the height. In the original definition of tetration, the height parameter must be a natural number; for instance, it would be illogical to say "three raised to itself negative five times" or "four raised to itself one half of a time." However, just as addition, multiplication, and exponentiation can be defined in ways that allow for extensions to real and complex numbers, several attempts have been made to generalize tetration to negative numbers, real numbers, and complex numbers. One such way for doing so is using a recursive definition for tetration; for any positive real and non-negative integer , we can define recursively as:
The recursive definition is equivalent to repeated exponentiation for natural heights; however, this definition allows for extensions to the other heights such as , , and as well – many of these extensions are areas of active research.
Terminology
There are many terms for tetration, each of which has some logic behind it, but some have not become commonly used for one reason or another. Here is a comparison of each term with its rationale and counter-rationale.
- The term tetration, introduced by Goodstein in his 1947 paper Transfinite Ordinals in Recursive Number Theory (generalizing the recursive base-representation used in Goodstein's theorem to use higher operations), has gained dominance. It was also popularized in Rudy Rucker's Infinity and the Mind.
- The term superexponentiation was published by Bromer in his paper Superexponentiation in 1987. It was used earlier by Ed Nelson in his book Predicative Arithmetic, Princeton University Press, 1986.
- The term hyperpower is a natural combination of hyper and power, which aptly describes tetration. The problem lies in the meaning of hyper with respect to the hyperoperation sequence. When considering hyperoperations, the term hyper refers to all ranks, and the term super refers to rank 4, or tetration. So under these considerations hyperpower is misleading, since it is only referring to tetration.
- The term power tower is occasionally used, in the form "the power tower of order n" for . Exponentiation is easily misconstrued: note that the operation of raising to a power is right-associative (see below). Tetration is iterated exponentiation (call this right-associative operation ^), starting from the top right side of the expression with an instance a^a (call this value c). Exponentiating the next leftward a (call this the 'next base' b), is to work leftward after obtaining the new value b^c. Working to the left, use the next a to the left, as the base b, and evaluate the new b^c. 'Descend down the tower' in turn, with the new value for c on the next downward step.
Owing in part to some shared terminology and similar notational symbolism, tetration is often confused with closely related functions and expressions. Here are a few related terms:
| Terminology | Form |
|---|---|
| Tetration | |
| Iterated exponentials | |
| Nested exponentials (also towers) | |
| Infinite exponentials (also towers) |
In the first two expressions a is the base, and the number of times a appears is the height (add one for x). In the third expression, n is the height, but each of the bases is different.
Care must be taken when referring to iterated exponentials, as it is common to call expressions of this form iterated exponentiation, which is ambiguous, as this can either mean iterated powers or iterated exponentials.
Notation
There are many different notation styles that can be used to express tetration. Some notations can also be used to describe other hyperoperations, while some are limited to tetration and have no immediate extension.
| Name | Form | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Knuth's up-arrow notation | Allows extension by putting more arrows, or, even more powerfully, an indexed arrow. | |
| Conway chained arrow notation | Allows extension by increasing the number 2 (equivalent with the extensions above), but also, even more powerfully, by extending the chain. | |
| Ackermann function | Allows the special case to be written in terms of the Ackermann function. | |
| Iterated exponential notation | Allows simple extension to iterated exponentials from initial values other than 1. | |
| Hooshmand notations | Used by M. H. Hooshmand . | |
| Hyperoperation notations | Allows extension by increasing the number 4; this gives the family of hyperoperations. | |
| Double caret notation | a^^n
|
Since the up-arrow is used identically to the caret (^), tetration may be written as (^^); convenient for ASCII.
|
One notation above uses iterated exponential notation; this is defined in general as follows:
- with n as.
There are not as many notations for iterated exponentials, but here are a few:
| Name | Form | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Standard notation | Euler coined the notation , and iteration notation has been around about as long. | |
| Knuth's up-arrow notation | Allows for super-powers and super-exponential function by increasing the number of arrows; used in the article on large numbers. | |
| Text notation | exp_a^n(x)
|
Based on standard notation; convenient for ASCII. |
| J Notation | x^^:(n-1)x
|
Repeats the exponentiation. See J (programming language) |
| Infinity barrier notation | Jonathan Bowers coined this, and it can be extended to higher hyper-operations |
Examples
Because of the extremely fast growth of tetration, most values in the following table are too large to write in scientific notation. In these cases, iterated exponential notation is used to express them in base 10. The values containing a decimal point are approximate.
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 4 (2) | 16 (2) | 65,536 (2) | 2.00353 × 10 | (10) | (10) |
| 3 | 27 (3) | 7,625,597,484,987 (3) | (1.25801 × 10 ) | |||
| 4 | 256 (4) | 1.34078 × 10 (4) | (10) | |||
| 5 | 3,125 (5) | 1.91101 × 10 (5) | (10) | |||
| 6 | 46,656 (6) | 2.65912 × 10 (6) | (10) | |||
| 7 | 823,543 (7) | 3.75982 × 10 (7) | (3.17742 × 10 digits) | |||
| 8 | 16,777,216 (8) | 6.01452 × 10 | (5.43165 × 10 digits) | |||
| 9 | 387,420,489 (9) | 4.28125 × 10 | (4.08535 × 10 digits) | |||
| 10 | 10,000,000,000 (10) | 10 | (10 + 1 digits) |
Remark: If x does not differ from 10 by orders of magnitude, then for all . For example, in the above table, and the difference is even smaller for the following rows.
Extensions
Tetration can be extended in two different ways; in the equation , both the base a and the height n can be generalized using the definition and properties of tetration. Although the base and the height can be extended beyond the non-negative integers to different domains, including , complex functions such as , and heights of infinite n, the more limited properties of tetration reduce the ability to extend tetration.
Extension of domain for bases
Base zero
The exponential is not consistently defined. Thus, the tetrations are not clearly defined by the formula given earlier. However, is well defined, and exists:
Thus we could consistently define . This is analogous to defining .
Under this extension, , so the rule from the original definition still holds.
Complex bases

Since complex numbers can be raised to powers, tetration can be applied to bases of the form z = a + bi (where a and b are real). For example, in z with z = i, tetration is achieved by using the principal branch of the natural logarithm; using Euler's formula we get the relation:
This suggests a recursive definition for i = a′ + b′i given any i = a + bi:
The following approximate values can be derived:
| Approximate value | |
|---|---|
| i | |
| 0.2079 | |
| 0.9472 + 0.3208i | |
| 0.0501 + 0.6021i | |
| 0.3872 + 0.0305i | |
| 0.7823 + 0.5446i | |
| 0.1426 + 0.4005i | |
| 0.5198 + 0.1184i | |
| 0.5686 + 0.6051i |
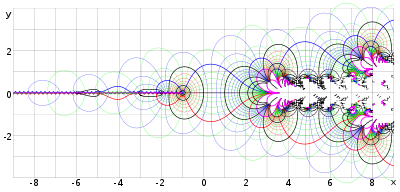
Solving the inverse relation, as in the previous section, yields the expected i = 1 and i = 0, with negative values of n giving infinite results on the imaginary axis. Plotted in the complex plane, the entire sequence spirals to the limit 0.4383 + 0.3606i, which could be interpreted as the value where n is infinite.
Such tetration sequences have been studied since the time of Euler, but are poorly understood due to their chaotic behavior. Most published research historically has focused on the convergence of the infinitely iterated exponential function. Current research has greatly benefited by the advent of powerful computers with fractal and symbolic mathematics software. Much of what is known about tetration comes from general knowledge of complex dynamics and specific research of the exponential map.
Extensions of the domain for different heights
Infinite heights


Tetration can be extended to infinite heights; i.e., for certain a and n values in , there exists a well defined result for an infinite n. This is because for bases within a certain interval, tetration converges to a finite value as the height tends to infinity. For example, converges to 2, and can therefore be said to be equal to 2. The trend towards 2 can be seen by evaluating a small finite tower:
In general, the infinitely iterated exponential , defined as the limit of as n goes to infinity, converges for e ≤ x ≤ e, roughly the interval from 0.066 to 1.44, a result shown by Leonhard Euler. The limit, should it exist, is a positive real solution of the equation y = x. Thus, x = y. The limit defining the infinite exponential of x does not exist when x > e because the maximum of y is e. The limit also fails to exist when 0 < x < e.
This may be extended to complex numbers z with the definition:
where W represents Lambert's W function.
As the limit y = x (if existent on the positive real line, i.e. for e ≤ x ≤ e) must satisfy x = y we see that x ↦ y = x is (the lower branch of) the inverse function of y ↦ x = y.
Negative heights
We can use the recursive rule for tetration,
to prove :
Substituting −1 for k gives
- .
Smaller negative values cannot be well defined in this way. Substituting −2 for k in the same equation gives
which is not well defined. They can, however, sometimes be considered sets.
For , any definition of is consistent with the rule because
- for any .
Real heights
| This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (July 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
At this time there is no commonly accepted solution to the general problem of extending tetration to the real or complex values of n. There have, however, been multiple approaches towards the issue, and different approaches are outlined below.
In general, the problem is finding — for any real a > 0 — a super-exponential function over real x > −2 that satisfies
- for all real
To find a more natural extension, one or more extra requirements are usually required. This is usually some collection of the following:
- A continuity requirement (usually just that is continuous in both variables for ).
- A differentiability requirement (can be once, twice, k times, or infinitely differentiable in x).
- A regularity requirement (implying twice differentiable in x) that:
- for all
The fourth requirement differs from author to author, and between approaches. There are two main approaches to extending tetration to real heights; one is based on the regularity requirement, and one is based on the differentiability requirement. These two approaches seem to be so different that they may not be reconciled, as they produce results inconsistent with each other.
When is defined for an interval of length one, the whole function easily follows for all x > −2.
Linear approximation for real heights

A linear approximation (solution to the continuity requirement, approximation to the differentiability requirement) is given by:
hence:
| Approximation | Domain |
|---|---|
| for −1 < x < 0 | |
| for 0 < x < 1 | |
| for 1 < x < 2 |
and so on. However, it is only piecewise differentiable; at integer values of x the derivative is multiplied by . It is continuously differentiable for if and only if . For example, using these methods and
A main theorem in Hooshmand's paper states: Let . If is continuous and satisfies the conditions:
- is differentiable on (−1, 0),
- is a nondecreasing or nonincreasing function on (−1, 0),
then is uniquely determined through the equation
where denotes the fractional part of x and is the -iterated function of the function .
The proof is that the second through fourth conditions trivially imply that f is a linear function on [−1, 0].
The linear approximation to natural tetration function is continuously differentiable, but its second derivative does not exist at integer values of its argument. Hooshmand derived another uniqueness theorem for it which states:
If is a continuous function that satisfies:
- is convex on (−1, 0),
then . [Here is Hooshmand's name for the linear approximation to the natural tetration function.]
The proof is much the same as before; the recursion equation ensures that and then the convexity condition implies that is linear on (−1, 0).
Therefore, the linear approximation to natural tetration is the only solution of the equation and which is convex on (−1, +∞). All other sufficiently-differentiable solutions must have an inflection point on the interval (−1, 0).
Higher order approximations for real heights
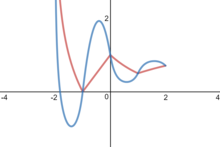
Beyond linear approximations, a quadratic approximation (to the differentiability requirement) is given by:
which is differentiable for all , but not twice differentiable. For example, If this is the same as the linear approximation.
Because of the way it is calculated, this function does not "cancel out", contrary to exponents, where . Namely,
- .
Just as there is a quadratic approximation, cubic approximations and methods for generalizing to approximations of degree n also exist, although they are much more unwieldy.
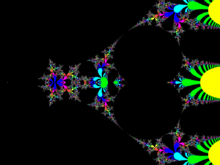
Complex heights
In 2017, it was proven that there exists a unique function F which is a solution of the equation F(z + 1) = exp(F(z)) and satisfies the additional conditions that F(0) = 1 and F(z) approaches the fixed points of the logarithm (roughly 0.318 ± 1.337i) as z approaches ±i∞ and that F is holomorphic in the whole complex z-plane, except the part of the real axis at z ≤ −2. This proof confirms a previous conjecture. The construction of such a function was originally demonstrated by Kneser in 1950. The complex map of this function is shown in the figure at right. The proof also works for other bases besides e, as long as the base is greater than . Subsequent work extended the construction to all complex bases.
The requirement of the tetration being holomorphic is important for its uniqueness. Many functions S can be constructed as
where α and β are real sequences which decay fast enough to provide the convergence of the series, at least at moderate values of Im z.
The function S satisfies the tetration equations S(z + 1) = exp(S(z)), S(0) = 1, and if αn and βn approach 0 fast enough it will be analytic on a neighborhood of the positive real axis. However, if some elements of {α} or {β} are not zero, then function S has multitudes of additional singularities and cutlines in the complex plane, due to the exponential growth of sin and cos along the imaginary axis; the smaller the coefficients {α} and {β} are, the further away these singularities are from the real axis.
The extension of tetration into the complex plane is thus essential for the uniqueness; the real-analytic tetration is not unique.
Ordinal tetration
Tetration can be defined for ordinal numbers via transfinite induction. For all α and all β > 0:
Non-elementary recursiveness
Tetration (restricted to ) is not an elementary recursive function. One can prove by induction that for every elementary recursive function f, there is a constant c such that
We denote the right hand side by . Suppose on the contrary that tetration is elementary recursive. is also elementary recursive. By the above inequality, there is a constant c such that . By letting , we have that , a contradiction.
Inverse operations
Exponentiation has two inverse operations; roots and logarithms. Analogously, the inverses of tetration are often called the super-root, and the super-logarithm (In fact, all hyperoperations greater than or equal to 3 have analogous inverses); e.g., in the function , the two inverses are the cube super-root of y and the super-logarithm base y of x.
Super-root
"Super-root" redirects here. For the directory supported by some Unixes, see super-root (computing).The super-root is the inverse operation of tetration with respect to the base: if , then y is an nth super-root of x ( or ).
For example,
so 2 is the 4th super-root of 65,536 .
Square super-root

The 2nd-order super-root, square super-root, or super square root has two equivalent notations, and . It is the inverse of and can be represented with the Lambert W function:
- or
The function also illustrates the reflective nature of the root and logarithm functions as the equation below only holds true when :
Like square roots, the square super-root of x may not have a single solution. Unlike square roots, determining the number of square super-roots of x may be difficult. In general, if , then x has two positive square super-roots between 0 and 1 calculated using formulas:; and if , then x has one positive square super-root greater than 1 calculated using formulas: . If x is positive and less than it does not have any real square super-roots, but the formula given above yields countably infinitely many complex ones for any finite x not equal to 1. The function has been used to determine the size of data clusters.
At :
Other super-roots

One of the simpler and faster formulas for a third-degree super-root is the recursive formula. If then one can use:
For each integer n > 2, the function x is defined and increasing for x ≥ 1, and 1 = 1, so that the nth super-root of x, , exists for x ≥ 1.
However, if the linear approximation above is used, then if −1 < y ≤ 0, so cannot exist.
In the same way as the square super-root, terminology for other super-roots can be based on the normal roots: "cube super-roots" can be expressed as ; the "4th super-root" can be expressed as ; and the "nth super-root" is . Note that may not be uniquely defined, because there may be more than one n root. For example, x has a single (real) super-root if n is odd, and up to two if n is even.
Just as with the extension of tetration to infinite heights, the super-root can be extended to n = ∞, being well-defined if 1/e ≤ x ≤ e. Note that and thus that . Therefore, when it is well defined, and, unlike normal tetration, is an elementary function. For example, .
It follows from the Gelfond–Schneider theorem that super-root for any positive integer n is either integer or transcendental, and is either integer or irrational. It is still an open question whether irrational super-roots are transcendental in the latter case.
Super-logarithm
Main article: Super-logarithmOnce a continuous increasing (in x) definition of tetration, a, is selected, the corresponding super-logarithm or is defined for all real numbers x, and a > 1.
The function sloga x satisfies:
Open questions
Other than the problems with the extensions of tetration, there are several open questions concerning tetration, particularly when concerning the relations between number systems such as integers and irrational numbers:
- It is not known whether there is an integer for which π is an integer, because we could not calculate precisely enough the numbers of digits after the decimal points of . It is similar for e for , as we are not aware of any other methods besides some direct computation. In fact, since , then . Given and , then for . It is believed that e is not an integer for any positive integer n, due to the algebraic independence of , given Schanuel's conjecture.
- It is not known whether q is rational for any positive integer n and positive non-integer rational q. For example, it is not known whether the positive root of the equation x = 2 is a rational number.
- It is not known whether π or e are rationals or not.
Applications
For each graph H on h vertices and each ε > 0, define
Then each graph G on n vertices with at most n/D copies of H can be made H-free by removing at most εn edges.
See also
- Ackermann function
- Big O notation
- Double exponential function
- Hyperoperation
- Iterated logarithm
- Symmetric level-index arithmetic
Notes
References
- ^ Neyrinck, Mark. An Investigation of Arithmetic Operations. Retrieved 9 January 2019.
- R. L. Goodstein (1947). "Transfinite ordinals in recursive number theory". Journal of Symbolic Logic. 12 (4): 123–129. doi:10.2307/2266486. JSTOR 2266486. S2CID 1318943.
- N. Bromer (1987). "Superexponentiation". Mathematics Magazine. 60 (3): 169–174. doi:10.1080/0025570X.1987.11977296. JSTOR 2689566.
- J. F. MacDonnell (1989). "Somecritical points of the hyperpower function ". International Journal of Mathematical Education. 20 (2): 297–305. doi:10.1080/0020739890200210. MR 0994348.
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Power Tower". MathWorld.
- ^ Hooshmand, M. H. (2006). "Ultra power and ultra exponential functions". Integral Transforms and Special Functions. 17 (8): 549–558. doi:10.1080/10652460500422247. S2CID 120431576.
- "Power Verb". J Vocabulary. J Software. Retrieved 2011-10-28.
- "Spaces". Retrieved 2022-02-17.
- DiModica, Thomas. Tetration Values. Retrieved 15 October 2023.
- "Climbing the ladder of hyper operators: tetration". math.blogoverflow.com. Stack Exchange Mathematics Blog. Retrieved 2019-07-25.
- Euler, L. "De serie Lambertina Plurimisque eius insignibus proprietatibus." Acta Acad. Scient. Petropol. 2, 29–51, 1783. Reprinted in Euler, L. Opera Omnia, Series Prima, Vol. 6: Commentationes Algebraicae. Leipzig, Germany: Teubner, pp. 350–369, 1921. (facsimile)
- ^ Müller, M. "Reihenalgebra: What comes beyond exponentiation?" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-12-02. Retrieved 2018-12-12.
- Trappmann, Henryk; Kouznetsov, Dmitrii (2010-06-28). "5+ methods for real analytic tetration". Retrieved 2018-12-05.
- Andrew Robbins. Solving for the Analytic Piecewise Extension of Tetration and the Super-logarithm. The extensions are found in part two of the paper, "Beginning of Results".
- Paulsen, W.; Cowgill, S. (March 2017). "Solving in the complex plane" (PDF). Advances in Computational Mathematics. 43: 1–22. doi:10.1007/s10444-017-9524-1. S2CID 9402035.
- Kouznetsov, D. (July 2009). "Solution of in complex -plane" (PDF). Mathematics of Computation. 78 (267): 1647–1670. doi:10.1090/S0025-5718-09-02188-7.
- Kneser, H. (1950). "Reelle analytische Lösungen der Gleichung und verwandter Funktionalgleichungen". Journal für die reine und angewandte Mathematik (in German). 187: 56–67.
- Paulsen, W. (June 2018). "Tetration for complex bases". Advances in Computational Mathematics. 45: 243–267. doi:10.1007/s10444-018-9615-7. S2CID 67866004.
- ^ Corless, R. M.; Gonnet, G. H.; Hare, D. E. G.; Jeffrey, D. J.; Knuth, D. E. (1996). "On the Lambert W function" (PostScript). Advances in Computational Mathematics. 5: 333. arXiv:1809.07369. doi:10.1007/BF02124750. S2CID 29028411.
- Krishnam, R. (2004), "Efficient Self-Organization Of Large Wireless Sensor Networks" – Dissertation, BOSTON UNIVERSITY, COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING. pp. 37–40
- ^ Marshall, Ash J., and Tan, Yiren, "A rational number of the form a with a irrational", Mathematical Gazette 96, March 2012, pp. 106–109.
- Bischoff, Manon (2024-01-24). "A Wild Claim about the Powers of Pi Creates a Transcendental Mystery". Scientific American. Archived from the original on 2024-04-24. Retrieved 2024-04-23.
- Cheng, Chuangxun; Dietel, Brian; Herblot, Mathilde; Huang, Jingjing; Krieger, Holly; Marques, Diego; Mason, Jonathan; Mereb, Martin; Wilson, S. Robert (2009). "Some consequences of Schanuel's conjecture". Journal of Number Theory. 129: 1464–1467. arXiv:0804.3550.
- Jacob Fox, A new proof of the graph removal lemma, arXiv preprint (2010). arXiv:1006.1300
External Links
- Daniel Geisler, Tetration
- Ioannis Galidakis, On extending hyper4 to nonintegers (undated, 2006 or earlier) (A simpler, easier to read review of the next reference)
- Ioannis Galidakis, On Extending hyper4 and Knuth's Up-arrow Notation to the Reals (undated, 2006 or earlier).
- Robert Munafo, Extension of the hyper4 function to reals (An informal discussion about extending tetration to the real numbers.)
- Lode Vandevenne, Tetration of the Square Root of Two. (2004). (Attempt to extend tetration to real numbers.)
- Ioannis Galidakis, Mathematics, (Definitive list of references to tetration research. Much information on the Lambert W function, Riemann surfaces, and analytic continuation.)
- Joseph MacDonell, Some Critical Points of the Hyperpower Function Archived 2010-01-17 at the Wayback Machine.
- Dave L. Renfro, Web pages for infinitely iterated exponentials
- Knobel, R. (1981). "Exponentials Reiterated". American Mathematical Monthly. 88 (4): 235–252. doi:10.1080/00029890.1981.11995239.
- Hans Maurer, "Über die Funktion für ganzzahliges Argument (Abundanzen)." Mittheilungen der Mathematische Gesellschaft in Hamburg 4, (1901), p. 33–50. (Reference to usage of from Knobel's paper.)
- The Fourth Operation
- Luca Moroni, The strange properties of the infinite power tower (https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.05559)
Further reading
- Galidakis, Ioannis; Weisstein, Eric Wolfgang. "Power Tower". MathWorld. Retrieved 2019-07-05.
| Hyperoperations | |
|---|---|
| Primary | |
| Inverse for left argument | |
| Inverse for right argument | |
| Related articles | |
| Large numbers | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Examples in numerical order | |||||
| Expression methods |
| ||||
| Related articles (alphabetical order) | |||||
 , with
, with  , for n = 2, 3, 4, ..., showing convergence to the infinitely iterated exponential between the two dots
, for n = 2, 3, 4, ..., showing convergence to the infinitely iterated exponential between the two dots and the left-exponent
and the left-exponent  are common.
are common.
 means
means  , where n copies of a are iterated via exponentiation, right-to-left, i.e. the application of exponentiation
, where n copies of a are iterated via exponentiation, right-to-left, i.e. the application of exponentiation  times. n is called the "height" of the function, while a is called the "base," analogous to exponentiation. It would be read as "the nth tetration of a". For example, 2 tetrated to 4 (or the fourth tetration of 2) is
times. n is called the "height" of the function, while a is called the "base," analogous to exponentiation. It would be read as "the nth tetration of a". For example, 2 tetrated to 4 (or the fourth tetration of 2) is  .
.

 , is considered to be the zeroth operation.
, is considered to be the zeroth operation.
 n copies of 1 added to a combined by succession.
n copies of 1 added to a combined by succession. n copies of a combined by addition.
n copies of a combined by addition. n copies of a combined by multiplication.
n copies of a combined by multiplication. n copies of a combined by exponentiation, right-to-left.
n copies of a combined by exponentiation, right-to-left. means
means  and not
and not 
 , is the most basic operation; while addition (
, is the most basic operation; while addition ( ) is a primary operation, for addition of natural numbers it can be thought of as a chained succession of
) is a primary operation, for addition of natural numbers it can be thought of as a chained succession of  successors of
successors of  ; multiplication (
; multiplication ( ) is also a primary operation, though for natural numbers it can analogously be thought of as a chained addition involving
) is also a primary operation, though for natural numbers it can analogously be thought of as a chained addition involving  ) as a chained power involving
) as a chained power involving  and non-negative
and non-negative  , we can define
, we can define  recursively as:
recursively as:

 ,
,  , and
, and  as well – many of these extensions are areas of active research.
as well – many of these extensions are areas of active research.
 . Exponentiation is easily misconstrued: note that the operation of raising to a power is right-associative (see
. Exponentiation is easily misconstrued: note that the operation of raising to a power is right-associative (see 






 to be written in terms of the Ackermann function.
to be written in terms of the Ackermann function.



 with n as.
with n as.
 , and iteration notation
, and iteration notation  has been around about as long.
has been around about as long.









 (10)
(10)
 (10)
(10)
 (1.25801 × 10 )
(1.25801 × 10 )



 (10)
(10)



 (10)
(10)



 (10)
(10)



 (3.17742 × 10 digits)
(3.17742 × 10 digits)



 (5.43165 × 10 digits)
(5.43165 × 10 digits)



 (4.08535 × 10 digits)
(4.08535 × 10 digits)



 (10 + 1 digits)
(10 + 1 digits)



 . For example,
. For example,  in the above table, and the difference is even smaller for the following rows.
in the above table, and the difference is even smaller for the following rows.
 , both the base a and the height n can be generalized using the definition and properties of tetration. Although the base and the height can be extended beyond the non-negative integers to different
, both the base a and the height n can be generalized using the definition and properties of tetration. Although the base and the height can be extended beyond the non-negative integers to different  , complex functions such as
, complex functions such as  , and heights of infinite n, the more limited properties of tetration reduce the ability to extend tetration.
, and heights of infinite n, the more limited properties of tetration reduce the ability to extend tetration.
 is not consistently defined. Thus, the tetrations
is not consistently defined. Thus, the tetrations  are not clearly defined by the formula given earlier. However,
are not clearly defined by the formula given earlier. However,  is well defined, and exists:
is well defined, and exists:

 . This is analogous to defining
. This is analogous to defining  .
.
 , so the rule
, so the rule  from the original definition still holds.
from the original definition still holds.












 of the infinitely iterated exponential converges for the bases
of the infinitely iterated exponential converges for the bases 
 on the complex plane, showing the real-valued infinitely iterated exponential function (black curve)
on the complex plane, showing the real-valued infinitely iterated exponential function (black curve) , there exists a well defined result for an infinite n. This is because for bases within a certain interval, tetration converges to a finite value as the height tends to
, there exists a well defined result for an infinite n. This is because for bases within a certain interval, tetration converges to a finite value as the height tends to  converges to 2, and can therefore be said to be equal to 2. The trend towards 2 can be seen by evaluating a small finite tower:
converges to 2, and can therefore be said to be equal to 2. The trend towards 2 can be seen by evaluating a small finite tower:

 , defined as the limit of
, defined as the limit of 

 :
:

 .
.
 , any definition of
, any definition of  is consistent with the rule because
is consistent with the rule because
 for any
for any  .
. over real x > −2 that satisfies
over real x > −2 that satisfies


 for all real
for all real 
 is continuous in both variables for
is continuous in both variables for  ).
). for all
for all  is defined for an interval of length one, the whole function easily follows for all x > −2.
is defined for an interval of length one, the whole function easily follows for all x > −2.
 using linear approximation
using linear approximation



 . It is continuously differentiable for
. It is continuously differentiable for  if and only if
if and only if  . For example, using these methods
. For example, using these methods  and
and 
 . If
. If  is continuous and satisfies the conditions:
is continuous and satisfies the conditions:

 is differentiable on (−1, 0),
is differentiable on (−1, 0), is a nondecreasing or nonincreasing function on (−1, 0),
is a nondecreasing or nonincreasing function on (−1, 0),

 denotes the fractional part of x and
denotes the fractional part of x and  is the
is the  -
- .
.
 is continuously differentiable, but its second derivative does not exist at integer values of its argument. Hooshmand derived another uniqueness theorem for it which states:
is continuously differentiable, but its second derivative does not exist at integer values of its argument. Hooshmand derived another uniqueness theorem for it which states:


 . [Here
. [Here  and then the convexity condition implies that
and then the convexity condition implies that  and
and  which is
which is  , from x = −2 to x = 2
, from x = −2 to x = 2
 If
If  . Namely,
. Namely,
 .
. of tetration to the complex plane. Levels
of tetration to the complex plane. Levels  and levels
and levels  are shown with thick curves.
are shown with thick curves. . Subsequent work extended the construction to all complex bases.
. Subsequent work extended the construction to all complex bases.



 ) is not an
) is not an 
 . Suppose on the contrary that tetration is elementary recursive.
. Suppose on the contrary that tetration is elementary recursive.  is also elementary recursive. By the above inequality, there is a constant c such that
is also elementary recursive. By the above inequality, there is a constant c such that  . By letting
. By letting  , we have that
, we have that  , a contradiction.
, a contradiction.
 , the two inverses are the cube super-root of y and the super-logarithm base y of x.
, the two inverses are the cube super-root of y and the super-logarithm base y of x.
 , then y is an nth super-root of x (
, then y is an nth super-root of x ( or
or  ).
).

 .
.

 and
and  . It is the inverse of
. It is the inverse of  and can be represented with the
and can be represented with the  or
or
 :
:

 , then x has two positive square super-roots between 0 and 1 calculated using formulas:
, then x has two positive square super-roots between 0 and 1 calculated using formulas: ; and if
; and if  , then x has one positive square super-root greater than 1 calculated using formulas:
, then x has one positive square super-root greater than 1 calculated using formulas:  . If x is positive and less than
. If x is positive and less than  it does not have any
it does not have any  :
:


 then one can use:
then one can use:


 if −1 < y ≤ 0, so
if −1 < y ≤ 0, so  cannot exist.
cannot exist.
 ; the "4th super-root" can be expressed as
; the "4th super-root" can be expressed as  and thus that
and thus that  . Therefore, when it is well defined,
. Therefore, when it is well defined,  and, unlike normal tetration, is an
and, unlike normal tetration, is an  .
.
 for any positive integer n is either integer or
for any positive integer n is either integer or  is either integer or irrational. It is still an open question whether irrational super-roots are transcendental in the latter case.
is either integer or irrational. It is still an open question whether irrational super-roots are transcendental in the latter case.
 or
or  is defined for all real numbers x, and a > 1.
is defined for all real numbers x, and a > 1.

 for which
for which  . It is similar for
. It is similar for  , as we are not aware of any other methods besides some direct computation. In fact, since
, as we are not aware of any other methods besides some direct computation. In fact, since  , then
, then  . Given
. Given  and
and  , then
, then  for
for  , given
, given 
 "
" in the complex plane"
in the complex plane" in complex
in complex  -plane"
-plane" und verwandter Funktionalgleichungen".
und verwandter Funktionalgleichungen". ![{\displaystyle y=x^{}]}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ab69cf15b7afca0a5f9cc89da314bbb89b61a749) für ganzzahliges Argument (Abundanzen)." Mittheilungen der Mathematische Gesellschaft in Hamburg 4, (1901), p. 33–50. (Reference to usage of
für ganzzahliges Argument (Abundanzen)." Mittheilungen der Mathematische Gesellschaft in Hamburg 4, (1901), p. 33–50. (Reference to usage of  from Knobel's paper.)
from Knobel's paper.)