| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Pythagorean means" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

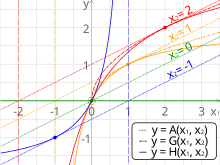
In mathematics, the three classical Pythagorean means are the arithmetic mean (AM), the geometric mean (GM), and the harmonic mean (HM). These means were studied with proportions by Pythagoreans and later generations of Greek mathematicians because of their importance in geometry and music.
Definition
They are defined by:
Properties
Each mean, , has the following properties:
- First-order homogeneity
- Invariance under exchange
- for any and .
- Monotonicity
- Idempotence
Monotonicity and idempotence together imply that a mean of a set always lies between the extremes of the set:
The harmonic and arithmetic means are reciprocal duals of each other for positive arguments,
while the geometric mean is its own reciprocal dual:
Inequalities among means
There is an ordering to these means (if all of the are positive) with equality holding if and only if the are all equal.
This is a generalization of the inequality of arithmetic and geometric means and a special case of an inequality for generalized means. The proof follows from the arithmetic–geometric mean inequality, , and reciprocal duality ( and are also reciprocal dual to each other).
The study of the Pythagorean means is closely related to the study of majorization and Schur-convex functions. The harmonic and geometric means are concave symmetric functions of their arguments, and hence Schur-concave, while the arithmetic mean is a linear function of its arguments and hence is both concave and convex.
History
Almost everything that we know about the Pythagorean means came from arithmetic handbooks written in the first and second century. Nicomachus of Gerasa says that they were "acknowledged by all the ancients, Pythagoras, Plato and Aristotle." Their earliest known use is a fragment of the Pythagorean philosopher Archytas of Tarentum:
There are three means in music: one is arithmetic, second is the geometric, third is sub-contrary, which they call harmonic. The mean is arithmetic when three terms are in proportion such that the excess by which the first exceeds the second is that by which the second exceeds the third. In this proportion it turns out that the interval of the greater terms is less, but that of the lesser terms greater. The mean is the geometric when they are such that as the first is to the second, so the second is to the third. Of these terms the greater and the lesser have the interval between them equal. Subcontrary, which we call harmonic, is the mean when they are such that, by whatever part of itself the first term exceeds the second, by that part of the third the middle term exceeds the third. It turns out that in this proportion the interval between the greater terms is greater and that between the lesser terms is less.
— Archytas of Tarentum,
The name "harmonic mean", according to Iamblichus, was coined by Archytas and Hippasus. The Pythagorean means also appear in Plato's Timaeus. Another evidence of their early use is a commentary by Pappus.
It was Theaetetus who distinguished the powers which are commensurable in length from those which are incommensurable, and who divided the more generally known irrational lines according to the different means, assigning the medial lines to geometry, the binomial to arithmetic, and the apotome to harmony, as is stated by Eudemus, the Peripatetic.
The term "mean" (Ancient Greek μεσότης, mesótēs) appears in the Neopythagorean arithmetic handbooks in connection with the term "proportion" (Ancient Greek ἀναλογία, analogía).
Smallest distinct positive integer means
| a | b | HM | GM | AM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 45 | 9 | 15 | 25 |
| 10 | 40 | 16 | 20 | 25 |

Of all pairs of different natural numbers of the form (a, b) such that a < b, the smallest (as defined by least value of a + b) for which the arithmetic, geometric and harmonic means are all also natural numbers are (5, 45) and (10, 40).
See also
Notes
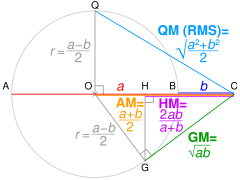
- If AC = a and BC = b. OC = AM of a and b, and radius r = QO = OG.
Using Pythagoras' theorem, QC² = QO² + OC² ∴ QC = √QO² + OC² = QM.
Using Pythagoras' theorem, OC² = OG² + GC² ∴ GC = √OC² − OG² = GM.
Using similar triangles, HC/GC = GC/OC ∴ HC = GC²/OC = HM.
References
- Heath, Thomas. History of Ancient Greek Mathematics.
- Gerasa.), Nicomachus (of (1926). Introduction to Arithmetic. Macmillan.
- Huffman, Carl (2005). Archytas of Tarentum: Pythagorean, philosopher and mathematician king. Cambridge University Press. p. 163. ISBN 1139444077.
- Huffman, Carl (2014). A History of Pythagoreanism. Cambridge University Press. p. 168. ISBN 978-1139915984.
- Virginia Tech Mathematics Department, 39th VTRMC, 2017, Solutions, part 5
External links
- Cantrell, David W. "Pythagorean Means". MathWorld.

 , has the following properties:
, has the following properties:


 and
and  .
.




 are positive)
are positive)
 with equality holding if and only if the
with equality holding if and only if the  , and reciprocal duality (
, and reciprocal duality ( and
and  are also reciprocal dual to each other).
are also reciprocal dual to each other).