| Riħama Battery | |
|---|---|
| Batterija ta' Riħama | |
| Marsaskala, Malta | |
 View of Riħama Battery View of Riħama Battery | |
 Map of Riħama Battery in its present condition Map of Riħama Battery in its present condition | |
| Coordinates | 35°50′59.3″N 14°33′56.1″E / 35.849806°N 14.565583°E / 35.849806; 14.565583 |
| Type | Artillery battery |
| Site information | |
| Owner | Government of Malta |
| Controlled by | Għaqda Bajja San Tumas |
| Open to the public | No |
| Condition | Mostly intact |
| Site history | |
| Built | 1714–1716 |
| Built by | Order of Saint John |
| In use | 1716–1830s |
| Materials | Limestone |
Riħama Battery (Maltese: Batterija ta' Riħama) is an artillery battery in Marsaskala, Malta. It was built by the Order of Saint John in 1714–1716 as one of a series of coastal fortifications around the coasts of the Maltese Islands. The battery still exists, although it is in a dilapidated state with part of it having collapsed.
Riħama Battery is also known as Ducluseaux Battery (Maltese: Batterija ta' Ducluseaux), Tal-Franċiż Battery (Maltese: Batterija tal-Franċiż, literally "Frenchman's Battery") or Tan-Naz Battery (Maltese: Batterija tan-Naz).
History
Riħama Battery was built in 1714–1716 as part of the first building programme of coastal batteries in Malta. It defended St. Thomas Bay along with the now-demolished Maħsel Battery on the opposite side of the bay, and St. Thomas Tower and Battery commanding the headland to the north of the bay. The battery was also known as Ducluseaux Battery, possibly after the French knight Ducluseaux de Handessus. It cost 1179.11.19.2 scudi to build.

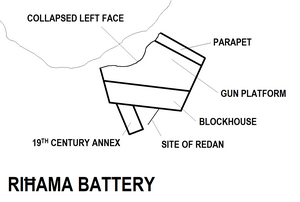
Riħama Battery consisted of a pentagonal gun platform. Its right face had a parapet with three embrasures, while its left face had a low parapet for mounting guns en barbette. The battery's gorge was sealed by a rectangular blockhouse, which was among the largest ever constructed in Malta, having three rooms and its roof being supported by 17 arches. The entrance to the battery was protected by a redan, and part of structure was surrounded by a ditch.
The battery was armed with seven guns. Three 8-pounder iron guns were mounted on the right face with the embrasures, while four 4-pounder guns were mounted en barbette on the left face. The ammunition was stored within the blockhouse.

Riħama Battery only saw use during the French invasion of Malta in 1798, but it was outflanked by the invading forces. It was decommissioned in the early 1830s, along with most of Malta's coastal fortifications. It was handed over to the civil government, and was used initially as a seaside residence, and later as a soap factory and slaughterhouse. Some alterations were made to the blockhouse in the 19th and early 20th centuries, including the construction of an annex. The battery was leased until about 1979, when it was abandoned.
Present day

Today, most of the battery still exists although it is derelict and in a state of disrepair. Its redan no longer exists, while the left face of the gun platform has collapsed into the sea.
Since 2013, Riħama Battery has been managed by the local voluntary organization Għaqda Bajja San Tumas, which intends to restore the battery.
Gallery
-
 The rear of the battery with the 19th-century extension
The rear of the battery with the 19th-century extension
-
 Right face of the battery
Right face of the battery
-
 Parapet with embrasures
Parapet with embrasures
-
 Sign on the battery, using the name Tal-Franċiż Battery
Sign on the battery, using the name Tal-Franċiż Battery
-
 Illustration of the now-collapsed left face
Illustration of the now-collapsed left face
-
 Collapsed left face
Collapsed left face
References
- "The South East Malta Coastal Defence". Wirt iż-Żejtun. 18 May 2014. Retrieved 23 June 2015.
- Spiteri, Stephen C. (28 August 2012). "Campaigning for Rihama Battery". MilitaryArchitecture.com. Archived from the original on 2 October 2017. Retrieved 23 June 2015.
- Cappello, Alfred (Summer 2013). "Mill-Pinna tal-Editur..." Leħen ir-Ramla (in Maltese) (15): 3. Retrieved 23 June 2015.
External links
- National Inventory of the Cultural Property of the Maltese Islands
- YouTube video showing a 3D model of Riħama Battery
- Artillery battery fortifications in Malta
- Marsaskala
- Hospitaller fortifications in Malta
- Military installations established in 1715
- Ruins in Malta
- Limestone buildings in Malta
- Military installations closed in the 1830s
- National Inventory of the Cultural Property of the Maltese Islands
- 18th-century fortifications
- 1715 establishments in Malta
- 18th Century military history of Malta