| Seminiferous tubule | |
|---|---|
 Seminiferous tubule in cross-section (large tubular structure – center of image) with sperm (black, tiny, ovoid bodies furthest from the outer edge of the tubular structure). H&E stain. Seminiferous tubule in cross-section (large tubular structure – center of image) with sperm (black, tiny, ovoid bodies furthest from the outer edge of the tubular structure). H&E stain. | |
 1: Testicular septa 1: Testicular septa2: Convoluted seminiferous tubules 3: Testicular lobules 4: Straight seminiferous tubules 5: Efferent ductules 6: Rete testis | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | tubuli seminiferi |
| MeSH | D012671 |
| TA98 | A09.3.01.022 |
| TA2 | 3599 |
| FMA | 19825 |
| Anatomical terminology[edit on Wikidata] | |
Seminiferous tubules are located within the testicles, and are the specific location of meiosis, and the subsequent creation of male gametes, namely spermatozoa.
Structure
The epithelium of the tubule consists of a type of sustentacular cells known as Sertoli cells, which are tall, columnar type cells that line the tubule.
In between the Sertoli cells are spermatogenic cells, which differentiate through meiosis to sperm cells. Sertoli cells function to nourish the developing sperm cells. They secrete androgen-binding protein, a binding protein which increases the concentration of testosterone.
There are two types: convoluted and straight, convoluted toward the lateral side, and straight as the tubule comes medially to form ducts that will exit the testis.
The seminiferous tubules are formed from the testis cords that develop from the primitive gonadal cords, formed from the gonadal ridge.
Function
Main article: SpermatogenesisSpermatogenesis, the process for producing spermatozoa, takes place in the seminiferous tubules. During spermatogenesis, the DNA of spermatogenic cells in the seminiferous tubules is subject to damage from such sources as reactive oxygen species. The genomic integrity of spermatogenic cells is protected by DNA repair processes. Deficiencies in the enzymes employed in these repair processes may lead to infertility.
Additional images
-
 Seminiferous tubule (right) with sperm (black, tiny, ovoid). H&E stain.
Seminiferous tubule (right) with sperm (black, tiny, ovoid). H&E stain.
-
 Longitudinal section through the left side of the scrotum and the left testis (seminiferous tubules visible in center, but not labeled).
Longitudinal section through the left side of the scrotum and the left testis (seminiferous tubules visible in center, but not labeled).
-
Seminiferous tubule (transverse section).
-
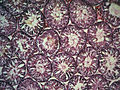 Photomicrograph of section through rat testis, showing seminiferous tubules.
Photomicrograph of section through rat testis, showing seminiferous tubules.
See also
References
- Mahfouz R, Sharma R, Thiyagarajan A, Kale V, Gupta S, Sabanegh E, Agarwal A (2010). "Semen characteristics and sperm DNA fragmentation in infertile men with low and high levels of seminal reactive oxygen species". Fertil. Steril. 94 (6): 2141–6. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.12.030. PMID 20117780.
- ^ Gunes S, Al-Sadaan M, Agarwal A (2015). "Spermatogenesis, DNA damage and DNA repair mechanisms in male infertility". Reprod. Biomed. Online. 31 (3): 309–19. doi:10.1016/j.rbmo.2015.06.010. PMID 26206278.
External links
- Histology image: 17802loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University
- Image
- Diagram Archived 2007-02-19 at the Wayback Machine