 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
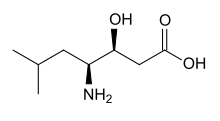
| IUPAC name (3S,4S)-4-amino-3-hydroxy-6-methylheptanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Abbreviations | AHMHA, Sta |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.161.428 |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C8H17NO3 |
| Molar mass | 175.228 g·mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Statine is a gamma amino acid that occurs twice in the sequence of pepstatin, a protease inhibitor that is active against pepsin and other acid proteases. It is thought to be responsible for the inhibitory activity of pepstatin because it mimics the tetrahedral transition state of peptide catalysis.
References
- Umezawa, H.; Aoyagi, T.; Morishima, H.; Matsuzaki, M.; Hamada, M.; Takeuchi, T. (1970). "Pepstatin, a new pepsin inhibitor produced by Actinomycetes". The Journal of Antibiotics. 23 (5): 259–262. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.23.259. PMID 4912600.
- Marciniszyn Jr, J.; Hartsuck, J. A.; Tang, J. (1976). "Mode of inhibition of acid proteases by pepstatin". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 251 (22): 7088–7094. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(17)32945-9. PMID 993206.
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |