| Superior thyroid artery | |
|---|---|
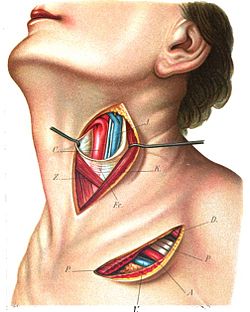 Superficial dissection of the left side of the neck, showing the carotid and subclavian arteries. Superficial dissection of the left side of the neck, showing the carotid and subclavian arteries. | |
 The fascia and middle thyroid veins. (Superior thyroid artery labelled at upper left.) The fascia and middle thyroid veins. (Superior thyroid artery labelled at upper left.) | |
| Details | |
| Source | External carotid artery |
| Branches | Hyoid artery Sternocleidomastoid artery superior laryngeal artery cricothyroid artery |
| Vein | Superior thyroid vein |
| Supplies | Thyroid |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria thyreoidea superior |
| TA98 | A12.2.05.002 |
| TA2 | 4370 |
| FMA | 49472 |
| Anatomical terminology[edit on Wikidata] | |
The superior thyroid artery arises from the external carotid artery just below the level of the greater cornu of the hyoid bone and ends in the thyroid gland.
Structure
From its origin under the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid the superior thyroid artery runs upward and forward for a short distance in the carotid triangle, where it is covered by the skin, platysma, and fascia; it then arches downward beneath the omohyoid, sternohyoid, and sternothyroid muscles.
To its medial side are the inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle and the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve.
Branches
It distributes twigs to the adjacent muscles, and numerous branches to the thyroid gland, connecting with its fellow of the opposite side, and with the inferior thyroid arteries. The branches to the gland are generally two in number. One, the larger, supplies principally the anterior surface; on the isthmus of the gland it connects with the corresponding artery of the opposite side. A second branch descends on the posterior surface of the gland and anastomoses with the inferior thyroid artery.
Besides the arteries distributed to the muscles and to the thyroid gland, the branches of the superior thyroid are:
- The infrahyoid branch (or hyoid artery): a small artery that runs along the lower border of the hyoid bone beneath the thyrohyoid muscle. This artery connects with the infrahyoid branch of the opposite side. The infrahyoid branch is a derivative of the second aortic arch.
- The sternocleidomastoid branch runs downward and laterally across the sheath of the common carotid artery, and supplies the sternocleidomastoideus muscle and neighboring muscles and skin; it frequently arises as a separate branch from the external carotid artery.
- The superior laryngeal artery accompanies the internal laryngeal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve, beneath the thyrohyoid muscle. This artery branches from the superior thyroid artery near its bifurcation from the external carotid artery. Together with the internal laryngeal nerve, it pierces the lateral thyrohyoid membrane, and supplies blood to the muscles, mucous membrane, and glands of the larynx, connecting with the branch from the opposite side.
- The cricothyroid artery may contribute to the supply of the larynx. It follows a variable course either superficial or deep to the sternothyroid muscle. If superficial, it may be accompanied by branches of the ansa cervicalis, and if deep, it may be related to the external laryngeal nerve. It can connect with the artery of the opposite side and with the laryngeal arteries.
Clinical significance
This artery must be ligated at the thyroid when conducting a thyroidectomy. If the artery is severed, but not ligated, it will bleed profusely. In order to gain control of the bleeding, the surgeon may need to extend the original incision laterally to ligate the artery at its origin at the external carotid artery. Furthermore, the external laryngeal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve courses close to the superior thyroid artery, making it at risk of injury during surgery.
See also
Additional images
-
 Diagram showing the origins of the main branches of the carotid arteries.
Diagram showing the origins of the main branches of the carotid arteries.
-
 The internal carotid and vertebral arteries. Right side. (Superior thyroid visible at center.)
The internal carotid and vertebral arteries. Right side. (Superior thyroid visible at center.)
-
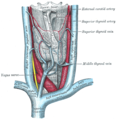 The thyroid gland and its relations.
The thyroid gland and its relations.
-
 Side of neck, showing chief surface markings.
Side of neck, showing chief surface markings.
-
Superior thyroid artery
-
Muscles, arteries and nerves of neck.Newborn dissection.
-
Muscles, nerves and arteries of neck.Deep dissection. Anterior view.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 552 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 552 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Anatomy figure: 26:02-02 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- lesson5 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (antthyroidgland)
| Arteries of the head and neck | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCA |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ScA |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||