| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
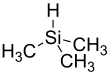
| Preferred IUPAC name Trimethylsilane | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.366 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| PubChem CID | |||
| UNII | |||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Chemical formula | C3H10Si | ||
| Molar mass | 74.198 g·mol | ||
| Density | 0.638 g cm | ||
| Melting point | −135.9 °C (−212.6 °F; 137.2 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 6.7 °C (44.1 °F; 279.8 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
| Pictograms |  
| ||
| Signal word | Danger | ||
| Hazard statements | H220, H224, H315, H319, H335 | ||
| Precautionary statements | P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P370+P378, P377, P381, P403, P403+P233, P403+P235, P405, P410+P403, P501 | ||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |||
Trimethylsilane is the organosilicon compound with the formula (CH3)3SiH. It is a trialkylsilane. The Si-H bond is reactive. Being a gas, it is less commonly used as a reagent than the related triethylsilane, which is a liquid at room temperature.
Trimethylsilane is used in the semiconductor industry as precursor to deposit dielectrics and barrier layers via plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PE-CVD). It is also used a source gas to deposit TiSiCN hard coatings via plasma-enhanced magnetron sputtering (PEMS). It has also been used to deposit silicon carbide hard coatings via low-pressure chemical vapor deposition (LP-CVD) at relatively low temperatures under 1000 °C. It is an expensive gas but safer to use than silane (SiH4); and produces properties in the coatings that cannot be undertaken by multiple source gases containing silicon and carbon.
See also
- Dimethylsilane
- Trimethylsilyl functional group
References
- Chen, Sheng-Wen; Wang, Yu-Sheng; Hu, Shao-Yu; Lee, Wen-Hsi; Chi, Chieh-Cheng; Wang, Ying-Lang (2012). "A Study of Trimethylsilane (3MS) and Tetramethylsilane (4MS) Based α-SiCN:H/α-SiCO:H Diffusion Barrier Films". Materials. 5 (3): 377–384. Bibcode:2012Mate....5..377C. doi:10.3390/ma5030377. PMC 5448926. PMID 28817052.