
The whiplash or whiplash line is a motif of decorative art and design that was particularly popular in Art Nouveau. It is an asymmetrical, sinuous line, often in an ornamental S-curve, usually inspired by natural forms such as plants and flowers, which suggests dynamism and movement. It took its name from a woven fabric panel "Cyclamen", by the German artist Hermann Obrist (1895) which depicted the stems and roots of the cyclamen plant, which critics dubbed "Coup de Fouet" ('whiplash'). The panel was later reproduced by the textile workshop of the Darmstadt Artists Colony.
Curling whiplash lines were modelled after natural and vegetal forms, particularly the cyclamen, iris, orchid, thistle, mistletoe, holly, water lily, and from the stylized lines of the swan, peacock, dragonfly, and butterfly.
In architecture, furniture, and other decorative arts, the decoration was entirely integrated with the structure. The whiplash lines were frequently interlaced and combined with twists and scrolls to inspire a poetic and romantic association. Femininity and romanticism were represented by the lines of long curling hair intertwined with flowers.
Designers such as Henry van de Velde used the whiplash line to create a sense of tension and dynamism. He wrote: "A line is a force like other elementary forces. Several lines put together but opposed act like the presence of multiple forces.
The "whiplash" curves of roots and stems Embroidered wall hanging "Cyclamen" (1895) design by Hermann Obrist
Embroidered wall hanging "Cyclamen" (1895) design by Hermann Obrist Simplified outline of "Cyclamen"
Simplified outline of "Cyclamen"
Noted designers who used the whiplash line included Aubrey Beardsley, Hector Guimard, Alphonse Mucha, and Victor Horta. In the Art Nouveau period, the whiplash line appeared frequently in furniture design, railings, and other ornamental iron work, floor tiles, posters, and jewelry. It became so common that critics of Art Nouveau ridiculed it as "the noodle style".
Origins
Twisting and curving line forms have a long history in art and design. Whiplash curves have similarities with the arabesque design, used particularly in Islamic art, such as the ceramic tiles of the mosque of Samarkand in Central Asia. Curvilinear design is a noticeable element of Gothic architecture, in, for example, church window tracery. Swirling lines featured prominently in the lavish decoration of the rocaille or rococo style in the early 18th century. Whiplash curves were a more naturalistic, less constrained expression of such recurrent trends. Where the whiplash line was less formalised than its forbears was in its asymmetry and anchoring.
They appear in the Japanese prints of Katsushika Hokusai, which became popular in France just as the Art Nouveau movement was beginning; these particularly inspired the paintings of flowers by Vincent van Gogh, such as The Irises (1890). The use of sinuous curves on the title page of the 1883 publication Wren's City Churches by architect and designer Arthur Heygate Mackmurdo, led Nikolaus Pevsner to identify it as "the first work of Art Nouveau which can be traced". Mackmurdo repeated the curving-line motifs in a chair of innovative design made at about this time. The serpentine lines of the chair's fretwork back is recognised as a precursor of Art Nouveau.
-
Curvilinear window, Limoges Cathedral nave
-
 Arabesque pattern on a tile from Samarkand (15th century)
Arabesque pattern on a tile from Samarkand (15th century)
-
 Rocaille or rococo table design by Juste-Aurèle Meissonnier (1730)
Rocaille or rococo table design by Juste-Aurèle Meissonnier (1730)
-
Waterfall of Kirifuri by Katsushika Hokusai (1830–1834)
-
 Irises by Vincent van Gogh (1890)
Irises by Vincent van Gogh (1890)
-
 "Seaweed" wallpaper design by William Morris and J. H. Dearle (1890)
"Seaweed" wallpaper design by William Morris and J. H. Dearle (1890)
-
 Title page of Wren's City Churches by Arthur H. Mackmurdo (1883)
Title page of Wren's City Churches by Arthur H. Mackmurdo (1883)
-
 Decoration for a title page by Aubrey Beardsley (1890)
Decoration for a title page by Aubrey Beardsley (1890)
-
 Another view of Obrist's "Cyclamen" ("Whiplash"; 1895)
Another view of Obrist's "Cyclamen" ("Whiplash"; 1895)
Architecture
The Belgian architect Victor Horta was among the first to introduce the whiplash curve into Art Nouveau architecture, particularly in the wrought iron stairways and complementary ceramic floors and painted walls of the Hôtel Tassel in Brussels (1892–93). The lines were inspired by the curving stems of plants and flowers. The French architect Hector Guimard also adapted the curving lines, particularly in the gateway, stairway, and interior decoration of the Castel Béranger in Paris (1894–1898), and in the edicules over the entrances of the Paris Métro that he designed for the Paris Universal Exposition of 1900. Guimard also used the curving whiplash line on a large scale on the facade of the house he built for he ceramics manufacturer Coilliot in Lille (1898–1900).
Another major figure using the whiplash form was the furniture designer Louis Majorelle, who incorporated the twisting whiplash line not only into his furniture, but also into cast iron staircase railings and stained-glass windows.
The whiplash line in ceramics was also sometimes used for exterior decoration, for example under the peristyle in the courtyard of the Petit Palais in Paris, built for the 1900 Paris Universal Exposition. It also appears in the curving cast iron staircase and ceramic floors of the interior of the Petit Palais. The architect Jules Lavirotte covered the facade of several of houses in Paris, particularly the Lavirotte Building on Avenue Rapp, with curling ceramic whiplash designs made by the ceramics firm of Alexandre Bigot.
-
Floor of the Hôtel Tassel in Brussels, with the characteristic whiplash design (1892–93)
-
 Entrance of Castel Béranger in Paris by Hector Guimard (1894–1898)
Entrance of Castel Béranger in Paris by Hector Guimard (1894–1898)
-
 Facade of the Maison Coilliot in Lille by Guimard (1898–1900)
Facade of the Maison Coilliot in Lille by Guimard (1898–1900)
-
 Details of the Maison Beukman in Brussels by Albert Roosenboom (1900)
Details of the Maison Beukman in Brussels by Albert Roosenboom (1900)
-
 Whiplash line on floor of the gallery of the Petit Palais of the 1900 Paris Exposition
Whiplash line on floor of the gallery of the Petit Palais of the 1900 Paris Exposition
-
 Entrance of the Lavirotte Building in Paris by Jules Lavirotte
Entrance of the Lavirotte Building in Paris by Jules Lavirotte
-
 Facade of Atelier Elivira in Munich, in Jugendstil, by August Endell (1896–97)
Facade of Atelier Elivira in Munich, in Jugendstil, by August Endell (1896–97)
Wrought iron and cast iron
The use of wrought iron or cast iron in scrolling whiplash forms on doorways, balconies, and gratings became one of the prominent features of the Art Nouveau style. The architect Victor Horta, who had worked on the construction of iron and glass Royal Greenhouses of Laeken in Belgium, was one of the first to create Art Nouveau ironwork, followed quickly by Hector Guimard, whose iron edibles for the entrances of the Paris Métro became an emblem of the style.
-
 Gate of La Hublotière, country house of Hector Guimard (1896)
Gate of La Hublotière, country house of Hector Guimard (1896)
-
 Main stairway of the Castel Béranger by Guimard (1895–1898)
Main stairway of the Castel Béranger by Guimard (1895–1898)
-
 Art Nouveau stairway of the Petit Palais in Paris (1900)
Art Nouveau stairway of the Petit Palais in Paris (1900)
-
Paris Métro station entrance at Boissière by Guimard (1900)
-
 Cast iron Paris Métro medallion by Guimard (1900)
Cast iron Paris Métro medallion by Guimard (1900)
-
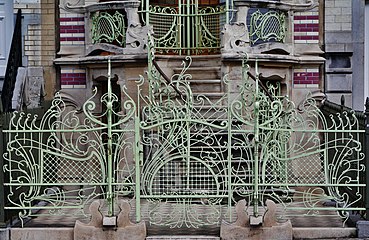 Entrance fence of the Saint-Cyr House in Brussels by Gustave Strauven (1901–1903)
Entrance fence of the Saint-Cyr House in Brussels by Gustave Strauven (1901–1903)
-
Entrance grill of the Villa Majorelle in Nancy (1901–02)
-
 Entrance gate of Güell Pavilions in Barcelona by Antoni Gaudí (1883–87)
Entrance gate of Güell Pavilions in Barcelona by Antoni Gaudí (1883–87)
Graphic arts and painting

The whiplash line was especially popular in posters and the graphic arts. In the posters of Alphonse Mucha and Koloman Moser, it was frequently used to depict women's hair, which became a central motif of the posters. After 1900 the whiplash lines tended to be more styled and abstract.
The line also appeared in decorative paintings, such as the series of wall paintings made by Margaret Macdonald Mackintosh of the Glasgow School. Her paintings, particularly the White Rose and Red Rose decorative panels (1903), were exhibited at gallery Vienna Secession, where they may have influenced the decorative paintings of Gustav Klimt at the Stoclet Palace made the following year.
-
 Salome by Aubrey Beardsley (1893)
Salome by Aubrey Beardsley (1893)
-
 Design by Otto Eckmann based upon stems of wheat (1895)
Design by Otto Eckmann based upon stems of wheat (1895)
-
 Poster for tea by Henri Meunier, with the steam rising in a whiplash form (1897)
Poster for tea by Henri Meunier, with the steam rising in a whiplash form (1897)
-
 The Kiss by Peter Behrens (1898)
The Kiss by Peter Behrens (1898)
-
 Illustration from Ver Sacrum by Koloman Moser (1900)
Illustration from Ver Sacrum by Koloman Moser (1900)
-
 White Rose and Red Rose decorative panel, by Margaret Macdonald Mackintosh (1903)
White Rose and Red Rose decorative panel, by Margaret Macdonald Mackintosh (1903)
-
 Preparatory design of The Embrace by Gustav Klimt (1904)
Preparatory design of The Embrace by Gustav Klimt (1904)
Furniture and ornament
Art Nouveau was a comprehensive form of decoration, in which all the elements; furniture, lamps, ironwork, carpets, murals, and glassware, had to be in the same style, or the harmony was broken. Victor Horta, Hector Guimard, Henry van de Velde and other Art Nouveau architects designed chairs, tables, lamps, carpets, tapestries ceramics, and other furnishings with similar curling whiplash lines. The whiplash line was intended to show the clear break from the eclectic historical styles that had dominated furniture and decoration for most of the 19th century. Henry Van de Velde and Horta in particular integrated the whiplash lines into their furniture, both in the shapes of desks and tables, the legs, in the brassware handles, and in railings and lamps, as well as in the chairs. Right angles were nearly banished from the works.
An important furniture workshop was created in the French city of Nancy by Louis Majorelle. Many designs with the whiplash line inspired by water lilies and other natural forms were created by Majorelle's designers. In Belgium the most notable designer using the motif was Gustave Serrurier-Bovy After 1900, the whiplash lines became simpler and more stylized. In the Glasgow School in Scotland, the motif was used in furniture by Charles Rennie Mackintosh and in highly-stylized glass and paintings by his wife, Margaret Macdonald Mackintosh.
-
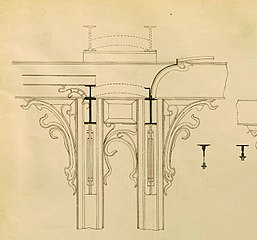 Interior design for the Hôtel Solvay in Brussels by Victor Horta (1898–1900)
Interior design for the Hôtel Solvay in Brussels by Victor Horta (1898–1900)
-
 Sketch of an ornament by Horta (Horta Museum, Brussels)
Sketch of an ornament by Horta (Horta Museum, Brussels)
-
 Buffet by Hector Guimard (1899–1900) (Bröhan Museum, Berlin)
Buffet by Hector Guimard (1899–1900) (Bröhan Museum, Berlin)
-
Desk, chair and lamps by Henry van de Velde (1898–99) (Musée d'Orsay, Paris)
-
Ceiling light by Van de Velde (1898)
-
 Bed and mirror by Gustave Serrurier-Bovy (1898–99) (Musée d'Orsay)
Bed and mirror by Gustave Serrurier-Bovy (1898–99) (Musée d'Orsay)
-
 Water Lily chair by Louis Majorelle (1900)
Water Lily chair by Louis Majorelle (1900)
-
 Bed by Majorelle, with lines inspired by the water lily (Musée d'Orsay)
Bed by Majorelle, with lines inspired by the water lily (Musée d'Orsay)
-
 Wall cabinet by Majorelle (late 19th century) (Walters Art Museum, Baltimore)
Wall cabinet by Majorelle (late 19th century) (Walters Art Museum, Baltimore)
-
 Detail of Vitrine by Majorelle (c. 1910)
Detail of Vitrine by Majorelle (c. 1910)
-
 Table by Émile Gallé, c. 1900 (Bröhan Museum)
Table by Émile Gallé, c. 1900 (Bröhan Museum)
-
 Credenza by Eugène Gaillard (c. 1900) (Art Institute of Chicago)
Credenza by Eugène Gaillard (c. 1900) (Art Institute of Chicago)
-
 Piano design by Charles Rennie Mackintosh in his House of an Art Lover
Piano design by Charles Rennie Mackintosh in his House of an Art Lover
Ceramics and glass
Main article: Art Nouveau glassGlass art was a medium in which Art Nouveau found new and varied ways of expression. Intense amount of experimentation went on to find new effects of transparency and opacity: in engraving with cameo, double layers, and acid engraving, a technique which permitted production in series. In ceramics and glass, the whiplash lines were mostly taken from floral and animal forms. After 1900, they kept the floral motifs but became simpler and more stylized.
-
 Par une telle nuit cup by Émile Gallé, France (1894)
Par une telle nuit cup by Émile Gallé, France (1894)
-
 Vase design by Georges de Feure (1901) (Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York City)
Vase design by Georges de Feure (1901) (Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York City)
-
 Glass vase by Louis Comfort Tiffany (c. 1893–1896)
Glass vase by Louis Comfort Tiffany (c. 1893–1896)
-
Porcelain and bronze vase by Otto Eckmann (1897–1899)
-
 Design for a Limoges ceramic vase by Georges de Feure (1903)
Design for a Limoges ceramic vase by Georges de Feure (1903)
-
 Glass vase by Daum studio, Nancy (c. 1910)
Glass vase by Daum studio, Nancy (c. 1910)
-
 Window for the House of an Art Lover, by Margaret Macdonald Mackintosh (1901)
Window for the House of an Art Lover, by Margaret Macdonald Mackintosh (1901)
-
 The ceramic Paris facades of architect Jules Lavirotte made lavish use of the whiplash lines
The ceramic Paris facades of architect Jules Lavirotte made lavish use of the whiplash lines
Jewelry
European jewelers were very quick to adapt the whiplash line to pendants and other ornaments. The Belgian designer Philippe Wolfers was one of the pioneers of the style. His drawings show how he carefully analysed the forms of flowers and plants and used them in his jewelry. His work often crossed the frontiers between sculpture and decorative art, inspired by the lines of forms ranging from dragonflies to bats to Grecian masks. He made not only jewelry, but also bronzes, lamps, vases, glassware, and other decorative objects, produced mostly for the Belgian glass factory of Val Saint Lambert.
In Paris, the most prominent jewelry designers were René Lalique and Fouquet. Their designers made abundant use of the whiplash line to suggest natural forms, from waterfalls to iris flowers. Other artists, including Alphonse Mucha, contributed jewelry designs incorporating the whiplash line.
-
 Design drawing of flower stems by Philippe Wolfers (1896)
Design drawing of flower stems by Philippe Wolfers (1896)
-
 Japanese lily ornament by Wolfers (1898)
Japanese lily ornament by Wolfers (1898)
-
 Plumes de Paon ("Peacock Feathers"), belt buckle by Wolfers (1898)
Plumes de Paon ("Peacock Feathers"), belt buckle by Wolfers (1898)
-
 Iris corsage ornament by Louis Comfort Tiffany (c. 1900)
Iris corsage ornament by Louis Comfort Tiffany (c. 1900)
-
 Jewelry designs for Fouquet jewellers by Alphonse Mucha (1901)
Jewelry designs for Fouquet jewellers by Alphonse Mucha (1901)
-
 Libelle ("Dragonfly"), pendant made of gold, opal, enamel, rubies, and diamonds by Wolfers (1902)
Libelle ("Dragonfly"), pendant made of gold, opal, enamel, rubies, and diamonds by Wolfers (1902)
-
Comb of horn, gold, and diamonds by René Lalique (c. 1902) (Musée d'Orsay)
Notes and citations
- ^ "The Whiplash". Victoria and Albert Museum. Retrieved 2 January 2020.
- ^ Renault & Lazé 2006, pp. 107–108.
- Fahr-Becker 2015, p. 152.
- Fahr-Becker 2015, pp. 14–15.
- Pevsner 1974, p. 90.
- "Arthur Heygate Mackmurdo: Chair ca. 1883 (made)". V&A Collections. Victoria and Albert Museum. 12 June 1998.
- Ducher 1948, pp. 200–201.
- Fahr-Becker 2015, pp. 152–159.
- De Morant 1970, pp. 445–447.
- Fahr-Becker 2015, pp. l151–1152.
Bibliography
- Fahr-Becker, Gabriele (2015). L'Art Nouveau (in French). H. F. Ullmann. ISBN 978-3-8480-0857-5.
- Ducher, Robert (1948). Caractéristique des styles (in French). Revised and corrected by Jean-François Boisset (Revised 1988 ed.). Paris: Flammarion. ISBN 978-2-08-011359-7.
- De Morant, Henry (1970). Histoire des arts décoratifs (in French). Librarie Hachette.
- Pevsner, Nikolaus (1974). "Art Nouveau". Pioneers of modern design, from William Morris to Walter Gropius. Harmondsworth, England: Penguin. pp. 90–117. ISBN 978-0-14-020497-1. p. 90:
If the long, sensitive curve ... can be regarded as the leitmotif of Art Nouveau, then the first work of Art Nouveau which can be traced is Arthur H. Mackmurdo's cover of his book on Wren's City Churches published in 1883.
- Renault, Christophe; Lazé, Christophe (2006). Les styles d'architecture et du mobilier (in French). Editions Jean-Paul Gisserot. ISBN 978-2-8774-7465-8.
External links
- Lloyd, Clive (12 March 2016). "Skipper's Art Nouveau Building". Colonel Unthank's Norwich: History, Decorative Arts, Buildings. .