| Revision as of 00:07, 26 October 2018 editAnomieBOT (talk | contribs)Bots6,588,573 edits Rescuing orphaned refs ("Wink" from rev 865746810)← Previous edit | Revision as of 05:24, 26 October 2018 edit undoपाटलिपुत्र (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users74,386 edits Restored to last clean version by Wario-ManNext edit → | ||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
| {{Use Indian English|date=December 2015}} | {{Use Indian English|date=December 2015}} | ||
| {{Infobox former country | {{Infobox former country | ||
| |native_name = {{native name|xbc|Κυϸανο}}<br/>{{lang|grc|Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν}} <span class="languageicon" style="font-size:81%;font-weight:normal;">(])</span> | |native_name = {{native name|xbc|Κυϸανο}}<br/>{{native name|sa|कुषाण साम्राज्य}}<br/>{{lang|grc|Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν}} <span class="languageicon" style="font-size:81%;font-weight:normal;">(])</span> | ||
| |conventional_long_name = Kushan Empire | |conventional_long_name = Kushan Empire | ||
| |common_name = Kushan Empire | |common_name = Kushan Empire | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
| |capital = ] <small>(])</small><br/>] <small>(])</small><br/>] <small>(''Takṣaśilā'')</small><br/>] <small>(''Mathurā'')</small> | |capital = ] <small>(])</small><br/>] <small>(])</small><br/>] <small>(''Takṣaśilā'')</small><br/>] <small>(''Mathurā'')</small> | ||
| |common_languages = ] <small>(official until ca. 127)</small><ref name="Greek">The Kushans at first retained the ] for administrative purposes but soon began to use Bactrian. The Bactrian ] (discovered in 1993 and deciphered in 2000) records that the Kushan king ] (c. 127 AD), discarded Greek (Ionian) as the language of administration and adopted Bactrian ("Arya language"), from Falk (2001): "The yuga of Sphujiddhvaja and the era of the Kuṣâṇas." Harry Falk. Silk Road Art and Archaeology VII, p. 133.</ref><br/>]<ref name="The Bactrian 2000 p. 133">The Bactrian ] (discovered in 1993 and deciphered in 2000) records that the Kushan king ] (c. 127 AD), discarded Greek (Ionian) as the language of administration and adopted Bactrian ("Arya language"), from Falk (2001): "The yuga of Sphujiddhvaja and the era of the Kuṣâṇas." Harry Falk. Silk Road Art and Archaeology VII, p. 133.</ref> <small>(official from ca. 127)</small><br/>Unofficial regional languages:<br/>], ], ], ], ], ]<br/>Liturgical language:<br/>] | |common_languages = ] <small>(official until ca. 127)</small><ref name="Greek">The Kushans at first retained the ] for administrative purposes but soon began to use Bactrian. The Bactrian ] (discovered in 1993 and deciphered in 2000) records that the Kushan king ] (c. 127 AD), discarded Greek (Ionian) as the language of administration and adopted Bactrian ("Arya language"), from Falk (2001): "The yuga of Sphujiddhvaja and the era of the Kuṣâṇas." Harry Falk. Silk Road Art and Archaeology VII, p. 133.</ref><br/>]<ref name="The Bactrian 2000 p. 133">The Bactrian ] (discovered in 1993 and deciphered in 2000) records that the Kushan king ] (c. 127 AD), discarded Greek (Ionian) as the language of administration and adopted Bactrian ("Arya language"), from Falk (2001): "The yuga of Sphujiddhvaja and the era of the Kuṣâṇas." Harry Falk. Silk Road Art and Archaeology VII, p. 133.</ref> <small>(official from ca. 127)</small><br/>Unofficial regional languages:<br/>], ], ], ], ], ]<br/>Liturgical language:<br/>] | ||
| |religion = Mahayana|Buddhism]]<ref>The Silk Road in World History By Xinru Liu, Pg.61 </ref><br/>]<br/>]{{sfn|Golden|1992|p=56}} | |religion = ]<ref name="Wink">André Wink, ''Al-Hind, the Making of the Indo-Islamic World: The Slavic Kings and the Islamic conquest, 11th-13th centuries'', (Oxford University Press, 1997), 57.</ref><br/>]<ref>The Silk Road in World History By Xinru Liu, Pg.61 </ref><br/>]<br/>]{{sfn|Golden|1992|p=56}} | ||
| |currency = ] | |currency = ] | ||
| |government_type = Monarchy | |government_type = Monarchy | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
| |stat_area1 = 2500000<ref name="Taagepera132">{{cite journal|date=1979|title=Size and Duration of Empires: Growth-Decline Curves, 600 B.C. to 600 A.D.|jstor=1170959|journal=]|volume=3|issue=3/4|page=132|doi=10.2307/1170959|last1=Taagepera|first1=Rein}}</ref> | |stat_area1 = 2500000<ref name="Taagepera132">{{cite journal|date=1979|title=Size and Duration of Empires: Growth-Decline Curves, 600 B.C. to 600 A.D.|jstor=1170959|journal=]|volume=3|issue=3/4|page=132|doi=10.2307/1170959|last1=Taagepera|first1=Rein}}</ref> | ||
| |stat_year1=200}} | |stat_year1=200}} | ||
| The '''Kushan Empire''' ({{lang-grc|Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν}}; {{lang-xbc|Κυϸανο}}, {{transl|xbc|Kushano}}; ]: 貴霜帝國; {{lang-xpr|Kušan-xšaθr}}<ref>''The Dynasty Arts of the Kushans'', University of California Press, 1967, </ref>) was a syncretic empire, formed by the ], in the ]n territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of ],<ref>http://www.kushan.org/general/other/part1.htm and Si-Yu-Ki, Buddhist Records of the Western World, (Tr. Samuel Beal: Travels of Fa-Hian, The Mission of Sung-Yun and Hwei-S?ng, Books 1–5), Kegan Paul, Trench, Trubner & Co. Ltd. London. 1906 and Hill (2009), pp. 29, 318–350</ref> |
The '''Kushan Empire''' ({{lang-grc|Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν}}; {{lang-xbc|Κυϸανο}}, {{transl|xbc|Kushano}}; {{lang-sa|कुषाण साम्राज्य}}, {{transl|sa|Kuṣāṇa Sāmrājya}}; ]: ''{{IAST|Guṣāṇa-vaṃśa}}''; ]: 貴霜帝國; {{lang-xpr|Kušan-xšaθr}}<ref>''The Dynasty Arts of the Kushans'', University of California Press, 1967, </ref>) was a syncretic empire, formed by the ], in the ]n territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of ],<ref>http://www.kushan.org/general/other/part1.htm and Si-Yu-Ki, Buddhist Records of the Western World, (Tr. Samuel Beal: Travels of Fa-Hian, The Mission of Sung-Yun and Hwei-S?ng, Books 1–5), Kegan Paul, Trench, Trubner & Co. Ltd. London. 1906 and Hill (2009), pp. 29, 318–350</ref> and then the northern parts of the ] at least as far as ] and ] near ] (Benares), where inscriptions have been found dating to the era of the Kushan Emperor ].<ref>which began about 127 CE. "Falk 2001, pp. 121–136", Falk (2001), pp. 121–136, Falk, Harry (2004), pp. 167–176 and Hill (2009), pp. 29, 33, 368–371.</ref> Emperor Kanishka was a great patron of ]; however, as Kushans expanded southward, the deities of their later coinage came to reflect its new ] majority.<ref>{{cite book |author=Grégoire Frumkin |title=Archaeology in Soviet Central Asia |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=gdUUAAAAIAAJ&pg=PA51 |year=1970 |publisher=Brill Archive |pages=51– |id=GGKEY:4NPLATFACBB}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |author=Rafi U. Samad |title=The Grandeur of Gandhara: The Ancient Buddhist Civilization of the Swat, Peshawar, Kabul and Indus Valleys |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=pNUwBYGYgxsC&pg=PA93 |year=2011 |publisher=Algora Publishing |isbn=978-0-87586-859-2 |pages=93–}}</ref><ref name="Wink"/> They played an important role in the establishment of Buddhism in the Indian subcontinent and its spread to Central Asia and China. | ||
| The Kushans were one of five branches of the ] confederation,<ref>{{cite book |last=Runion |first=Meredith L. |title=The history of Afghanistan |year=2007 |publisher=Greenwood Press |location=Westport |isbn=978-0-313-33798-7 |page=46 |quote=The Yuezhi people conquered Bactria in the second century BCE. and divided the country into five chiefdoms, one of which would become the Kushan Empire. Recognizing the importance of unification, these five tribes combined under the one dominate Kushan tribe, and the primary rulers descended from the Yuezhi.}}</ref><ref name=liu156>{{cite book |last=Liu |first=Xinrui |title=Agricultural and pastoral societies in ancient and classical history |year=2001 |publisher=Temple University Press |location=Philadelphia |isbn=978-1-56639-832-9 |page=156 |editor=Adas, Michael}}</ref> a possibly ]<ref name="EKH">{{harvnb|Enoki|Koshelenko|Haidary|1994|pp=171–191}}</ref><ref name="EB_Ancient_Iran_Yuezhi">{{cite web |url=http://global.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/851961/ancient-Iran/32124/The-Seleucids |title=Ancient Iran: The movement of Iranian peoples |last1=Girshman |first1=Roman |author-link=Roman Ghirshman |last2= |first2= |date= |website=] |publisher=] |access-date=29 May 2015 |quote=At the end of the 3rd century, there began in Chinese Turkistan a long migration of the Yuezhi, an Iranian people who invaded Bactria about 130 bc, putting an end to the Greco-Bactrian kingdom there. (In the 1st century bc they created the Kushān dynasty, whose rule extended from Afghanistan to the Ganges River and from Russian Turkistan to the estuary of the Indus.)}}</ref> or ],<ref name="Pulleyblank">{{harvnb|Pulleyblank|1966|pp=9–39}}</ref><ref name="Mallory_1989">{{harvnb|Mallory|1989|pp=59–60}}</ref><ref name="EOIC">{{harvnb|Mallory|1997|pp=591–593}}</ref>{{sfnp|Mallory|Mair|2000|pp=270–297}}<ref name="TCHAC">{{harvnb|Loewe|Shaughnessy|1999|pp=87–88}}</ref><ref name="Benjamin_Marshak">{{cite journal |last=Benjamin |first=Craig |author-link=Craig Benjamin |last2= |first2= |date=October 2003 |title=The Yuezhi Migration and Sogdia |url=http://www.transoxiana.org/Eran/Articles/benjamin.html |journal=Transoxiana Webfestschrift |publisher=Transoxiana |volume=1 |issue=Ēran ud Anērān |pages= |doi= |access-date=29 May 2015}}</ref> ]<ref name="TCHAC"/><ref name="EB_Zhang_Qian">{{cite web |url=http://global.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/105520/Zhang-Qian |title=Zhang Qian |last1= |first1= |author-link= |last2= |first2= |date= |website=] |publisher=] |access-date=29 May 2015 |quote=}}</ref><ref name="EPAO">{{harvnb|West|2009|pp=713–717}}</ref><ref>"They are, by almost unanimous opinion, Indo-Europeans, probably the most oriental of those who occupied the steppes." Roux, p.90</ref> nomadic people who migrated from ] and settled in ancient ].<ref name=liu156/> The Kushans possibly used the ] initially for administrative purposes, but soon began to use ].<ref name="The Bactrian 2000 p. 133">The Bactrian ] (discovered in 1993 and deciphered in 2000) records that the Kushan king ] (c. 127 AD), discarded Greek (Ionian) as the language of administration and adopted Bactrian ("Arya language"), from Falk (2001): "The yuga of Sphujiddhvaja and the era of the Kuṣâṇas." Harry Falk. Silk Road Art and Archaeology VII, p. 133.</ref> Kanishka sent his armies north of the ], capturing territories as far as ], ] and ], in the ] of modern-day ], ]. A direct road from ] to China remained under Kushan control for more than a century, encouraging travel across the Karakoram and facilitating the ] to China. | The Kushans were one of five branches of the ] confederation,<ref>{{cite book |last=Runion |first=Meredith L. |title=The history of Afghanistan |year=2007 |publisher=Greenwood Press |location=Westport |isbn=978-0-313-33798-7 |page=46 |quote=The Yuezhi people conquered Bactria in the second century BCE. and divided the country into five chiefdoms, one of which would become the Kushan Empire. Recognizing the importance of unification, these five tribes combined under the one dominate Kushan tribe, and the primary rulers descended from the Yuezhi.}}</ref><ref name=liu156>{{cite book |last=Liu |first=Xinrui |title=Agricultural and pastoral societies in ancient and classical history |year=2001 |publisher=Temple University Press |location=Philadelphia |isbn=978-1-56639-832-9 |page=156 |editor=Adas, Michael}}</ref> a possibly ]<ref name="EKH">{{harvnb|Enoki|Koshelenko|Haidary|1994|pp=171–191}}</ref><ref name="EB_Ancient_Iran_Yuezhi">{{cite web |url=http://global.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/851961/ancient-Iran/32124/The-Seleucids |title=Ancient Iran: The movement of Iranian peoples |last1=Girshman |first1=Roman |author-link=Roman Ghirshman |last2= |first2= |date= |website=] |publisher=] |access-date=29 May 2015 |quote=At the end of the 3rd century, there began in Chinese Turkistan a long migration of the Yuezhi, an Iranian people who invaded Bactria about 130 bc, putting an end to the Greco-Bactrian kingdom there. (In the 1st century bc they created the Kushān dynasty, whose rule extended from Afghanistan to the Ganges River and from Russian Turkistan to the estuary of the Indus.)}}</ref> or ],<ref name="Pulleyblank">{{harvnb|Pulleyblank|1966|pp=9–39}}</ref><ref name="Mallory_1989">{{harvnb|Mallory|1989|pp=59–60}}</ref><ref name="EOIC">{{harvnb|Mallory|1997|pp=591–593}}</ref>{{sfnp|Mallory|Mair|2000|pp=270–297}}<ref name="TCHAC">{{harvnb|Loewe|Shaughnessy|1999|pp=87–88}}</ref><ref name="Benjamin_Marshak">{{cite journal |last=Benjamin |first=Craig |author-link=Craig Benjamin |last2= |first2= |date=October 2003 |title=The Yuezhi Migration and Sogdia |url=http://www.transoxiana.org/Eran/Articles/benjamin.html |journal=Transoxiana Webfestschrift |publisher=Transoxiana |volume=1 |issue=Ēran ud Anērān |pages= |doi= |access-date=29 May 2015}}</ref> ]<ref name="TCHAC"/><ref name="EB_Zhang_Qian">{{cite web |url=http://global.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/105520/Zhang-Qian |title=Zhang Qian |last1= |first1= |author-link= |last2= |first2= |date= |website=] |publisher=] |access-date=29 May 2015 |quote=}}</ref><ref name="EPAO">{{harvnb|West|2009|pp=713–717}}</ref><ref>"They are, by almost unanimous opinion, Indo-Europeans, probably the most oriental of those who occupied the steppes." Roux, p.90</ref> nomadic people who migrated from ] and settled in ancient ].<ref name=liu156/> The Kushans possibly used the ] initially for administrative purposes, but soon began to use ].<ref name="The Bactrian 2000 p. 133">The Bactrian ] (discovered in 1993 and deciphered in 2000) records that the Kushan king ] (c. 127 AD), discarded Greek (Ionian) as the language of administration and adopted Bactrian ("Arya language"), from Falk (2001): "The yuga of Sphujiddhvaja and the era of the Kuṣâṇas." Harry Falk. Silk Road Art and Archaeology VII, p. 133.</ref> Kanishka sent his armies north of the ], capturing territories as far as ], ] and ], in the ] of modern-day ], ]. A direct road from ] to China remained under Kushan control for more than a century, encouraging travel across the Karakoram and facilitating the ] to China. | ||
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
| In the 1st century BCE, the ''Guishuang'' (Ch: 貴霜) gained prominence over the other Yuezhi tribes, and welded them into a tight confederation under ''yabgu'' (Commander) Kujula Kadphises. The name ''Guishuang'' was adopted in the West and modified into ''Kushan'' to designate the confederation, although the Chinese continued to call them ''Yuezhi''. | In the 1st century BCE, the ''Guishuang'' (Ch: 貴霜) gained prominence over the other Yuezhi tribes, and welded them into a tight confederation under ''yabgu'' (Commander) Kujula Kadphises. The name ''Guishuang'' was adopted in the West and modified into ''Kushan'' to designate the confederation, although the Chinese continued to call them ''Yuezhi''. | ||
| Gradually wresting control of the area from the ] tribes, the Kushans expanded south into the region traditionally known as ] (an area primarily in ]'s ] and ] region but going in an arc to include the Kabul valley and part of ] in Afghanistan){{Citation needed|date=February 2011}} and established twin capitals in ]<ref>S. Frederick Starr, ''Lost Enlightenment: Central Asia's Golden Age from the Arab Conquest to Tamerlane''. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 2013, p. 53</ref> and ], then known as Kapisa and |
Gradually wresting control of the area from the ] tribes, the Kushans expanded south into the region traditionally known as ] (an area primarily in ]'s ] and ] region but going in an arc to include the Kabul valley and part of ] in Afghanistan){{Citation needed|date=February 2011}} and established twin capitals in ]<ref>S. Frederick Starr, ''Lost Enlightenment: Central Asia's Golden Age from the Arab Conquest to Tamerlane''. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 2013, p. 53</ref> and ], then known as Kapisa and Pushklavati respectively. | ||
| ], with the addition of the letter ] (associated with the Greek ]).]] | ], with the addition of the letter ] (associated with the Greek ]).]] | ||
| The Kushans adopted elements of the ] culture of Bactria. They adopted the ] to suit their own language (with the additional development of the letter Þ "sh", as in "Kushan") and soon began minting coinage on the Greek model. On their coins they used Greek language legends combined with Pali legends (in the ] script), until the first few years of the reign of Kanishka. After that date,{{Vague|date=April 2010}}{{When|date=April 2010}}{{Dubious|date=April 2010}} they used Kushan language legends (in an adapted Greek script), combined with legends in Greek (Greek script) and legends in Prakrit (Kharoshthi script). | The Kushans adopted elements of the ] culture of Bactria. They adopted the ] to suit their own language (with the additional development of the letter Þ "sh", as in "Kushan") and soon began minting coinage on the Greek model. On their coins they used Greek language legends combined with Pali legends (in the ] script), until the first few years of the reign of Kanishka. After that date,{{Vague|date=April 2010}}{{When|date=April 2010}}{{Dubious|date=April 2010}} they used Kushan language legends (in an adapted Greek script), combined with legends in Greek (Greek script) and legends in Prakrit (Kharoshthi script). | ||
| The Kushans "adopted many local beliefs and customs, including ] and the two rising religions in the region, the Greek cults and ]".<ref>Starr, p. 53</ref> From the time of ], many Kushans started adopting aspects of ] culture, and like the Egyptians, they absorbed the strong remnants of the Greek culture of the Hellenistic Kingdoms, becoming at least partly ]d. The great Kushan emperor ] may have embraced ] (a sect of ]), as surmised by coins minted during the period. The following Kushan emperors represented a wide variety of faiths including Zoroastrianism, Buddhism, and possibly Saivism. | |||
| The rule of the Kushans linked the seagoing trade of the ] with the commerce of the ] through the long-civilized ]. At the height of the dynasty, the Kushans loosely ruled a territory that extended to the ] through present-day ], ], and ] into northern India. | The rule of the Kushans linked the seagoing trade of the ] with the commerce of the ] through the long-civilized ]. At the height of the dynasty, the Kushans loosely ruled a territory that extended to the ] through present-day ], ], and ] into northern India. | ||
Revision as of 05:24, 26 October 2018
Not to be confused with Kingdom of Kush. "Kushan" redirects here. For the village in Iran, see Kushan, Iran. For the fictional video game race, see Homeworld.
| Kushan EmpireΚυϸανο (Bactrian) कुषाण साम्राज्य (Sanskrit) Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν (Greek) | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30–375 | |||||||||||||||||||
 Kushan territories (full line) and maximum extent of Kushan dominions under Kanishka the Great (dotted line), according to the Rabatak inscription. Kushan territories (full line) and maximum extent of Kushan dominions under Kanishka the Great (dotted line), according to the Rabatak inscription. | |||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Nomadic empire | ||||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Bagram (Kapiśi) Peshawar (Puruṣapura) Taxila (Takṣaśilā) Mathura (Mathurā) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Greek (official until ca. 127) Bactrian (official from ca. 127) Unofficial regional languages: Gurjari-Gandhari, Sogdian, Chorasmian, Tocharian, Saka dialects, Prakrit Liturgical language: Sanskrit | ||||||||||||||||||
| Religion | Hinduism Buddhism Bactrian religion Zoroastrianism | ||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||||||||||
| Emperor | |||||||||||||||||||
| • 30–80 | Kujula Kadphises | ||||||||||||||||||
| • 350–375 | Kipunada | ||||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Classical Antiquity | ||||||||||||||||||
| • Kujula Kadphises unites Yuezhi tribes into a confederation | 30 | ||||||||||||||||||
| • Subjugated by the Sasanians, Guptas, and Hepthalites | 375 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||||
| 200 | 2,500,000 km (970,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Currency | Kushan drachma | ||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
The Kushan Empire (Template:Lang-grc; Template:Lang-xbc, Kushano; Template:Lang-sa, Kuṣāṇa Sāmrājya; BHS: Guṣāṇa-vaṃśa; Chinese: 貴霜帝國; Template:Lang-xpr) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, in the Bactrian territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of Afghanistan, and then the northern parts of the Indian subcontinent at least as far as Saketa and Sarnath near Varanasi (Benares), where inscriptions have been found dating to the era of the Kushan Emperor Kanishka the Great. Emperor Kanishka was a great patron of Buddhism; however, as Kushans expanded southward, the deities of their later coinage came to reflect its new Hindu majority. They played an important role in the establishment of Buddhism in the Indian subcontinent and its spread to Central Asia and China.
The Kushans were one of five branches of the Yuezhi confederation, a possibly Iranic or Tocharian, Indo-European nomadic people who migrated from Gansu and settled in ancient Bactria. The Kushans possibly used the Greek language initially for administrative purposes, but soon began to use Bactrian language. Kanishka sent his armies north of the Karakoram mountains, capturing territories as far as Kashgar, Khotan and Yarkant, in the Tarim Basin of modern-day Xinjiang, China. A direct road from Gandhara to China remained under Kushan control for more than a century, encouraging travel across the Karakoram and facilitating the spread of Mahayana Buddhism to China.
The Kushan dynasty had diplomatic contacts with the Roman Empire, Sasanian Persia, the Aksumite Empire and Han Dynasty of China. While much philosophy, art, and science was created within its borders, the only textual record of the empire's history today comes from inscriptions and accounts in other languages, particularly Chinese.
The Kushan empire fragmented into semi-independent kingdoms in the 3rd century AD, which fell to the Sasanians invading from the west, establishing the Kushano-Sasanian Kingdom in the areas of Sogdiana, Bactria and Gandhara. In the 4th century, the Guptas, an Indian dynasty also pressed from the east. The last of the Kushan and Kushano-Sasanian kingdoms were eventually overwhelmed by invaders from the north, known as the Kidarites, and then the Hepthalites.
Origins
Chinese sources describe the Guishuang (貴霜), i.e. the Kushans, as one of the five aristocratic tribes of the Yuezhi, with some people claiming they were a loose confederation of Indo-European peoples, though many scholars are still unconvinced that they originally spoke an Indo-European language. As the historian John E. Hill has put it: "For well over a century ... there have been many arguments about the ethnic and linguistic origins of the Great Yuezhi or Da Yuezhi (大月氏), Kushans (貴霜), and the Tochari, and still there is little consensus".

The Yuezhi were described in the Records of the Great Historian 史記 and the Book of Han 漢書 as living in the grasslands of Gansu, in the northwest of modern-day China, until their King was beheaded by the Huns from Siberia (the Xiongnu 匈奴) who were also at war with China, which eventually forced them to migrate west in 176–160 BCE. The five tribes constituting the Yuezhi are known in Chinese history as Xiūmì (休密), Guìshuāng (貴霜), Shuāngmǐ (雙靡), Xìdùn (肸頓), and Dūmì (都密).
The Yuezhi reached the Hellenic kingdom of Greco-Bactria (in northern Afghanistan and Uzbekistan) around 135 BC. The displaced Greek dynasties resettled to the southeast in areas of the Hindu Kush and the Indus basin (in present-day Afghanistan and Pakistan), occupying the western part of the Indo-Greek Kingdom.
Early Kushans

Some traces remain of the presence of the Kushans in the area of Bactria and Sogdiana. Archaeological structures are known in Takht-I-Sangin, Surkh Kotal (a monumental temple), and in the palace of Khalchayan. Various sculptures and friezes are known, representing horse-riding archers, and, significantly, men with artificially deformed skulls, such as the Kushan prince of Khalchayan (a practice well attested in nomadic Central Asia). The Chinese first referred to these people as the Yuezhi and said they established the Kushan Empire, although the relationship between the Yuezhi and the Kushans is still unclear. On the ruins of ancient Hellenistic cities such as Ai-Khanoum, the Kushans are known to have built fortresses.

The earliest documented ruler, and the first one to proclaim himself as a Kushan ruler, was Heraios. He calls himself a "tyrant" in Greek on his coins, and also exhibits skull deformation. He may have been an ally of the Greeks, and he shared the same style of coinage. Heraios may have been the father of the first Kushan emperor Kujula Kadphises.
Ban Gu's Book of Han tells us the Kushans (Kuei-shuang) divided up Bactria in 128 BC. Fan Ye's Book of the Later Han "relates how the chief of the Kushans, Ch'iu-shiu-ch'ueh (the Kujula Kadphises of coins), founded by means of the submission of the other Yueh-chih clans the Kushan Empire, known to the Greeks and Romans under the name of Empire of the Indo-Scythians."
The Chinese Hou Hanshu 後漢書 chronicles gives an account of the formation of the Kushan empire based on a report made by the Chinese general Ban Yong to the Chinese Emperor c. 125 AD:
More than a hundred years later , the prince of Guishuang (Badakhshan) established himself as king, and his dynasty was called that of the Guishuang (Kushan) King. He invaded Anxi (Indo-Parthia), and took the Gaofu (Kabul) region. He also defeated the whole of the kingdoms of Puda (Paktiya) and Jibin (Kapisha and Gandhara). Qiujiuque (Kujula Kadphises) was more than eighty years old when he died. His son, Yangaozhen , became king in his place. He defeated Tianzhu and installed Generals to supervise and lead it. The Yuezhi then became extremely rich. All the kingdoms call the Guishuang king, but the Han call them by their original name, Da Yuezhi.
— Hou Hanshu
Diverse cultural influences


In the 1st century BCE, the Guishuang (Ch: 貴霜) gained prominence over the other Yuezhi tribes, and welded them into a tight confederation under yabgu (Commander) Kujula Kadphises. The name Guishuang was adopted in the West and modified into Kushan to designate the confederation, although the Chinese continued to call them Yuezhi.
Gradually wresting control of the area from the Scythian tribes, the Kushans expanded south into the region traditionally known as Gandhara (an area primarily in Pakistan's Pothowar and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa region but going in an arc to include the Kabul valley and part of Qandahar in Afghanistan) and established twin capitals in Begram and Peshawar, then known as Kapisa and Pushklavati respectively.
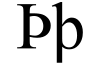
The Kushans adopted elements of the Hellenistic culture of Bactria. They adopted the Greek alphabet to suit their own language (with the additional development of the letter Þ "sh", as in "Kushan") and soon began minting coinage on the Greek model. On their coins they used Greek language legends combined with Pali legends (in the Kharoshthi script), until the first few years of the reign of Kanishka. After that date, they used Kushan language legends (in an adapted Greek script), combined with legends in Greek (Greek script) and legends in Prakrit (Kharoshthi script).
The Kushans "adopted many local beliefs and customs, including Zoroastrianism and the two rising religions in the region, the Greek cults and Buddhism". From the time of Vima Takto, many Kushans started adopting aspects of Buddhist culture, and like the Egyptians, they absorbed the strong remnants of the Greek culture of the Hellenistic Kingdoms, becoming at least partly Hellenised. The great Kushan emperor Vima Kadphises may have embraced Saivism (a sect of Hinduism), as surmised by coins minted during the period. The following Kushan emperors represented a wide variety of faiths including Zoroastrianism, Buddhism, and possibly Saivism.
The rule of the Kushans linked the seagoing trade of the Indian Ocean with the commerce of the Silk Road through the long-civilized Indus Valley. At the height of the dynasty, the Kushans loosely ruled a territory that extended to the Aral Sea through present-day Uzbekistan, Afghanistan, and Pakistan into northern India.
The loose unity and comparative peace of such a vast expanse encouraged long-distance trade, brought Chinese silks to Rome, and created strings of flourishing urban centers.
Territorial expansion

Rosenfield notes that archaeological evidence of a Kushan rule of long duration is present in an area stretching from Surkh Kotal, Begram, the summer capital of the Kushans, Peshawar, the capital under Kanishka I, Taxila, and Mathura, the winter capital of the Kushans.
Other areas of probable rule include Khwarezm, Kausambi (excavations of Allahabad University), Sanchi and Sarnath (inscriptions with names and dates of Kushan kings), Malwa and Maharashtra, and Odisha (imitation of Kushan coins, and large Kushan hoards).

Kushan invasions in the 1st century CE had been given as an explanation for the migration of Indians from the Indian Subcontinent toward Southeast Asia according to proponents of a Greater India theory by 20th-century Indian nationalists. However, there is no evidence to support this hypothesis.
The recently discovered Rabatak inscription confirms the account of the Hou Hanshu, Weilüe, and inscriptions dated early in the Kanishka era (incept probably 127 CE), that large Kushan dominions expanded into the heartland of northern India in the early 2nd century CE. Lines 4 to 7 of the inscription describe the cities which were under the rule of Kanishka, among which six names are identifiable: Ujjain, Kundina, Saketa, Kausambi, Pataliputra, and Champa (although the text is not clear whether Champa was a possession of Kanishka or just beyond it). The Kushan state was bounded to the south by the Pārata state of Balochistan, western Pakistan, Afghanistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan. Turkmenistan was known for the kushan Buddhist city of Merv. As late as the 3rd century AD, decorated coins of Huvishka were dedicated at Bodh Gaya together with other gold offerings under the "Enlightenment Throne" of the Buddha, suggesting direct Kushan influence in the area during that period.
Northward, in the 2nd century AD, the Kushans under Kanishka made various forays into the Tarim Basin, where they had various contacts with the Chinese. Both archaeological findings and literary evidence suggest Kushan rule, in Kashgar, Yarkand, and Khotan.
Main Kushan rulers

Kujula Kadphises (c. 30 – c. 80)
...the prince of Guishuang, named thilac , attacked and exterminated the four other xihou. He established himself as king, and his dynasty was called that of the Guishuang King. He invaded Anxi and took the Gaofu region. He also defeated the whole of the kingdoms of Puda and Jibin . Qiujiuque was more than eighty years old when he died."
— Hou Hanshu
These conquests probably took place sometime between 45 and 60 and laid the basis for the Kushan Empire which was rapidly expanded by his descendants.
Kujula issued an extensive series of coins and fathered at least two sons, Sadaṣkaṇa (who is known from only two inscriptions, especially the Rabatak inscription, and apparently never ruled), and seemingly Vima Takto.
Kujula Kadphises was the great-grandfather of Kanishka.
Vima Taktu or Sadashkana (c. 80 – c. 95)
Vima Takto (Ancient Chinese: 閻膏珍 Yangaozhen) is mentioned in the Rabatak inscription (another son, Sadashkana, is mentioned in an inscription of Senavarman, the King of Odi). He was the predecessor of Vima Kadphises, and Kanishka I. He expanded the Kushan Empire into the northwest of South Asia. The Hou Hanshu says:
"His son, Yangaozhen , became king in his place. He defeated Tianzhu and installed Generals to supervise and lead it. The Yuezhi then became extremely rich. All the kingdoms call the Guishuang king, but the Han call them by their original name, Da Yuezhi."
— Hou Hanshu
Vima Kadphises (c. 95 – c. 127)
Vima Kadphises (Kushan language: Οοημο Καδφισης) was a Kushan emperor from around 90–100 CE, the son of Sadashkana and the grandson of Kujula Kadphises, and the father of Kanishka I, as detailed by the Rabatak inscription.
Vima Kadphises added to the Kushan territory by his conquests in Afghanistan and north-west Pakistan. He issued an extensive series of coins and inscriptions. He issued gold coins in addition to the existing copper and silver coinage.
Kanishka I (c. 127 – c. 140)
Main article: Kanishka
The rule of Kanishka the Great, fifth Kushan king, lasted for about 13 years from c. 127. Upon his accession, Kanishka ruled a huge territory (virtually all of northern India), south to Ujjain and Kundina and east beyond Pataliputra, according to the Rabatak inscription:

In the year one, it has been proclaimed unto India, unto the whole realm of the governing class, including Koonadeano (Kaundiny, Kundina) and the city of Ozeno (Ozene, Ujjain) and the city of Zageda (Saketa) and the city of Kozambo (Kausambi) and the city of Palabotro (Pataliputra) and so long unto (i.e., as far as) the city of Ziri-tambo (Sri-Champa).
— Rabatak inscription, Lines 4–6
His territory was administered from two capitals: Purushapura (now Peshawar in northwestern Pakistan) and Mathura, in northern India. He is also credited (along with Raja Dab) for building the massive, ancient Fort at Bathinda (Qila Mubarak), in the modern city of Bathinda, Indian Punjab.
The Kushans also had a summer capital in Bagram (then known as Kapisa), where the "Begram Treasure", comprising works of art from Greece to China, has been found. According to the Rabatak inscription, Kanishka was the son of Vima Kadphises, the grandson of Sadashkana, and the great-grandson of Kujula Kadphises. Kanishka's era is now generally accepted to have begun in 127 on the basis of Harry Falk's ground-breaking research. Kanishka's era was used as a calendar reference by the Kushans for about a century, until the decline of the Kushan realm.
Vāsishka (c. 140 – c. 160)
Vāsishka was a Kushan emperor who seems to have had a 20-year reign following Kanishka. His rule is recorded as far south as Sanchi (near Vidisa), where several inscriptions in his name have been found, dated to the year 22 (the Sanchi inscription of "Vaksushana" – i.e., Vasishka Kushana) and year 28 (the Sanchi inscription of Vasaska – i.e., Vasishka) of the Kanishka era.
Huvishka (c. 160 – c. 190)
Huvishka (Kushan: Οοηϸκι, "Ooishki") was a Kushan emperor from about 20 years after the death of Kanishka (assumed on the best evidence available to be in 140) until the succession of Vasudeva I about thirty years later. His rule was a period of retrenchment and consolidation for the Empire. In particular he devoted time and effort early in his reign to the exertion of greater control over the city of Mathura.
Vasudeva I (c. 190 – c. 230)
Vasudeva I (Kushan: Βαζοδηο "Bazodeo", Chinese: 波調 "Bodiao") was the last of the "Great Kushans". Named inscriptions dating from year 64 to 98 of Kanishka's era suggest his reign extended from at least 191 to 225 AD. He was the last great Kushan emperor, and the end of his rule coincides with the invasion of the Sasanians as far as northwestern India, and the establishment of the Indo-Sasanians or Kushanshahs in what is nowadays Afghanistan, Pakistan and northwestern India from around 240 AD.
Kushan deities


The Kushan religious pantheon is extremely varied, as revealed by their coins that were made in gold, silver, and copper. These coins contained more than thirty different gods, belonging mainly to their own Iranic, Greek, and Indo-Aryan worlds as well. Kushan coins had images of Kushan Kings, Buddha, and figures from the Indo-Aryan and Iranian pantheons. Greek deities, with Greek names are represented on early coins. During Kanishka's reign, the language of the coinage changes to Bactrian (though it remained in Greek script for all kings). After Huvishka, only two divinities appear on the coins: Ardoxsho and Oesho (see details below).
The Iranic entities depicted on coinage include:
- Αρδοχþο (ardoxsho, Ashi Vanghuhi)
- Aþαειχþo (ashaeixsho, Asha Vahishta)
- Αθþο (athsho, Atar)
- Φαρρο (pharro, Khwarenah)
- Λροοασπο (lrooaspa, Drvaspa)
- Μαναοβαγο, (manaobago, Vohu Manah)
- Μαο (mao, Mah)
- Μιθρο, Μιιρο, Μιορο, Μιυρο (mithro and variants, Mithra)
- Μοζδοοανο (mozdooano, Mazda *vana "Mazda the victorious?")
- Νανα, Ναναια, Ναναϸαο (variations of pan-Asiatic nana, Sogdian nny, Nana)
- Οαδο (oado Vata)
- Oαxþo (oaxsho, "Oxus")
- Ooρoμoζδο (ooromozdo, Ahura Mazda)
- Οραλαγνο (orlagno, Verethragna)
- Τιερο (tiero, Tir)
Representation of entities from Greek mythology and Hellenistic syncretism are:
- Ηλιος (Helios), Ηφαηστος (Hephaistos), Σαληνη (Selene), Ανημος (Anemos). Further, the coins of Huvishka also portray the demi-god erakilo Heracles, and the Egyptian god sarapo Sarapis
The Indic entities represented on coinage include:
- Βοδδο (boddo, Buddha)
- Μετραγο Βοδδο (metrago boddo, bodhisattava Maitreya)
- Mαασηνo (maaseno, Mahasena)
- Σκανδo koμαρo (skando komaro, Skanda Kumara)
- þακαμανο Βοδδο (shakamano boddho, Shakyamuni Buddha)
- Οηϸο (oesho), long considered to represent Indic Shiva, but also identified as Avestan Vayu conflated with Shiva.
- Two copper coins of Huvishka bear a 'Ganesa' legend, but instead of depicting the typical theriomorphic figure of Ganesha, have a figure of an archer holding a full-length bow with string inwards and an arrow. This is typically a depiction of Rudra, but in the case of these two coins is generally assumed to represent Shiva.
-
 Kushan worshipper with Zeus/Serapis/Ohrmazd, Bactria, 3rd century CE.
Kushan worshipper with Zeus/Serapis/Ohrmazd, Bactria, 3rd century CE.
-
 Kushan worshipper with Pharro, Bactria, 3rd century AD.
Kushan worshipper with Pharro, Bactria, 3rd century AD.
-
 Kushan worshipper with Shiva/Oesho, Bactria, 3rd century CE.
Kushan worshipper with Shiva/Oesho, Bactria, 3rd century CE.
-
 Mahasena on a coin of Huvishka
Mahasena on a coin of Huvishka
-
Four-faced Oesho
-
Rishti
-
Manaobago
-
Pharro
-
Ardochsho
-
 Oesho or Shiva
Oesho or Shiva
-
 Oesho or Shiva with bull
Oesho or Shiva with bull
-
 Skanda and Visakha
Skanda and Visakha
-
 Gold coin of Kanishka the Great, with a depiction of the Buddha, with the legend "Boddo" in Greek script;Ahin Posh
Gold coin of Kanishka the Great, with a depiction of the Buddha, with the legend "Boddo" in Greek script;Ahin Posh
-
 Herakles.
Herakles.
-
 Kushan Carnelian seal representing the "ΑΔϷΟ" (adsho Atar), with triratana symbol left, and Kanishka the Great's dynastic mark right
Kushan Carnelian seal representing the "ΑΔϷΟ" (adsho Atar), with triratana symbol left, and Kanishka the Great's dynastic mark right
-
 Buddha
Buddha

Kushans and Buddhism


The Kushans inherited the Greco-Buddhist traditions of the Indo-Greek Kingdom they replaced, and their patronage of Buddhist institutions allowed them to grow as a commercial power. Between the mid-1st century and the mid-3rd century, Buddhism, patronized by the Kushans, extended to China and other Asian countries through the Silk Road.
Kanishka is renowned in Buddhist tradition for having convened a great Buddhist council in Kashmir. Along with his predecessors in the region, the Indo-Greek king Menander I (Milinda) and the Indian emperors Ashoka and Harsha Vardhana, Kanishka is considered by Buddhism as one of its greatest benefactors.
During the 1st century AD, Buddhist books were being produced and carried by monks, and their trader patrons. Also, monasteries were being established along these land routes that went from China and other parts of Asia. With the development of Buddhist books, it caused a new written language called Gandhara. Gandhara consists of eastern Afghanistan and northern Pakistan. Scholars are said to have found many Buddhist scrolls that contained the Gandhari language.
The reign of Huvishka corresponds to the first known epigraphic evidence of the Buddha Amitabha, on the bottom part of a 2nd-century statue which has been found in Govindo-Nagar, and now at the Mathura Museum. The statue is dated to "the 28th year of the reign of Huvishka", and dedicated to "Amitabha Buddha" by a family of merchants. There is also some evidence that Huvishka himself was a follower of Mahāyāna Buddhism. A Sanskrit manuscript fragment in the Schøyen Collection describes Huvishka as one who has "set forth in the Mahāyāna."
Kushan art

The art and culture of Gandhara, at the crossroads of the Kushan hegemony, continued the traditions of Greco-Buddhist art and are the best known expressions of Kushan influences to Westerners. Several direct depictions of Kushans are known from Gandhara, where they are represented with a tunic, belt and trousers and play the role of devotees to the Buddha, as well as the Bodhisattva and future Buddha Maitreya.
During the Kushan Empire, many images of Gandhara share a strong resemblance to the features of Greek, Syrian, Persian and Indian figures. These Western-looking stylistic signatures often include heavy drapery and curly hair, representing a composite (the Greeks, for example, often possessed curly hair).
In the iconography, they are never associated however with the very Hellenistic "Standing Buddha" statues, which might therefore correspond to an earlier historical period.
Contacts with Rome
Main article: Roman trade with India
Several Roman sources describe the visit of ambassadors from the Kings of Bactria and India during the 2nd century, probably referring to the Kushans.

Historia Augusta, speaking of Emperor Hadrian (117–138) tells:
Reges Bactrianorum legatos ad eum, amicitiae petendae causa, supplices miserunt "The kings of the Bactrians sent supplicant ambassadors to him, to seek his friendship."
Also in 138, according to Aurelius Victor (Epitome‚ XV, 4), and Appian (Praef., 7), Antoninus Pius, successor to Hadrian, received some Indian, Bactrian, and Hyrcanian ambassadors.
"Precious things from Da Qin can be found there , as well as fine cotton cloths, fine wool carpets, perfumes of all sorts, sugar candy, pepper, ginger, and black salt."
— Hou Hanshu
The summer capital of the Kushan Empire in Begram has yielded a considerable amount of goods imported from the Roman Empire--in particular, various types of glassware.
Contacts with China


During the 1st and 2nd century, the Kushan Empire expanded militarily to the north and occupied parts of the Tarim Basin, their original grounds, putting them at the center of the profitable Central Asian commerce with the Roman Empire. They are related to have collaborated militarily with the Chinese against nomadic incursion, particularly when they collaborated with the Han Dynasty general Ban Chao against the Sogdians in 84, when the latter were trying to support a revolt by the king of Kashgar. Around 85, they also assisted the Chinese general in an attack on Turpan, east of the Tarim Basin.
In recognition for their support to the Chinese, the Kushans requested a Han princess, but were denied, even after they had sent presents to the Chinese court. In retaliation, they marched on Ban Chao in 86 with a force of 70,000, but were defeated by a smaller Chinese force. The Yuezhi retreated and paid tribute to the Chinese Empire during the reign of emperor He of Han (89–106).
Later, around 116, the Kushans under Kanishka established a kingdom centered on Kashgar, also taking control of Khotan and Yarkand, which were Chinese dependencies in the Tarim Basin, modern Xinjiang. They introduced the Brahmi script, the Indian Prakrit language for administration, and expanded the influence of Greco-Buddhist art which developed into Serindian art.

The Kushans are again recorded to have sent presents to the Chinese court in 158–159 during the reign of emperor Huan of Han.
Following these interactions, cultural exchanges further increased, and Kushan Buddhist missionaries, such as Lokaksema, became active in the Chinese capital cities of Loyang and sometimes Nanjing, where they particularly distinguished themselves by their translation work. They were the first recorded promoters of Hinayana and Mahayana scriptures in China, greatly contributing to the Silk Road transmission of Buddhism.
Decline

After the death of Vasudeva I in 225, the Kushan empire split into western and eastern halves. The Western Kushans (in Afghanistan) were soon subjugated by the Persian Sasanian Empire and lost Sogdiana, Bactria, and Gandhara to them. The Sasanians deposed the Western dynasty and replaced them with Persian vassals known as the Kushanshas (also called Indo-Sasanians or Kushano-Sasanians).
The Eastern Kushan kingdom was based in the Punjab. Around 270 their territories on the Gangetic plain became independent under local dynasties such as the Yaudheyas. Then in the mid-4th century they were subjugated by the Gupta Empire under Samudragupta.
In 360 a Kidarite Hun named Kidara overthrew the Indo-Sasanians and remnants of the old Kushan dynasty, and established the Kidarite Kingdom. The Kushan style of Kidarite coins indicates they claimed Kushan heritage. The Kidarite seem to have been rather prosperous, although on a smaller scale than their Kushan predecessors.
These remnants of the Kushan empire were ultimately wiped out in the 5th century by the invasions of the Hephthalites, the Alchon Huns and the Nezak Huns in the northwest, and the rise of the Gupta Empire in the east.
Rulers

- Heraios (c. 1 – 30), first Kushan ruler, generally Kushan ruling period is disputed
- Kujula Kadphises (c. 30 – c. 80)
- Vima Takto (c. 80 – c. 95), alias Soter Megas or "Great Saviour."
- Vima Kadphises (c. 95 – c. 127) the first great Kushan emperor
- Kanishka the Great (127 – c. 140)
- Vāsishka (c. 140 – c. 160)
- Huvishka (c. 160 – c. 190)
- Vasudeva I (c. 190 – to at least 230), the last of the great Kushan emperors
- Kanishka II (c. 230 – 240)
- Vashishka (c. 240 – 250)
- Kanishka III (c. 250 – 275)
- Vasudeva II (c. 275 – 310)
- Vasudeva III reported son of Vasudeva II, a King, uncertain.
- Vasudeva IV reported possible child of Vasudeva III, ruling in Kandahar, uncertain.
- Vasudeva V, or "Vasudeva of Kabul", reported possible child of Vasudeva IV, ruling in Kabul, uncertain.
- Chhu (c. 310? – 325?)
- Shaka I (c. 325 – 345)
- Kipunada (c. 345 – 375)
See also
- Ancient history of Afghanistan
- Indo-Parthian Kingdom
- Kucha, another Tocharian-speaking kingdom (with a related etymology)
- History of Pakistan
- Mathura
- Taxila
Notes

| Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of Tajikistan |
| Timeline |
|
|
- "The Rabatak inscription claims that in the year 1 Kanishka I's authority was proclaimed in India, in all the satrapies and in different cities like Koonadeano (Kundina), Ozeno (Ujjain), Kozambo (Kausambi), Zagedo (Saketa), Palabotro (Pataliputra), and Ziri-Tambo (Janjgir-Champa). These cities lay to the east and south of Mathura, up to which locality Wima had already carried his victorious arm. Therefore they must have been captured or subdued by Kanishka I himself." "Ancient Indian Inscriptions", S. R. Goyal, p. 93. See also the analysis of Sims-Williams and J.Cribb, who had a central role in the decipherment: "A new Bactrian inscription of Kanishka the Great", in "Silk Road Art and Archaeology" No4, 1995–1996. Also Mukherjee B.N. "The Great Kushanan Testament", Indian Museum Bulletin.
- The Kushans at first retained the Greek language for administrative purposes but soon began to use Bactrian. The Bactrian Rabatak inscription (discovered in 1993 and deciphered in 2000) records that the Kushan king Kanishka the Great (c. 127 AD), discarded Greek (Ionian) as the language of administration and adopted Bactrian ("Arya language"), from Falk (2001): "The yuga of Sphujiddhvaja and the era of the Kuṣâṇas." Harry Falk. Silk Road Art and Archaeology VII, p. 133.
- ^ The Bactrian Rabatak inscription (discovered in 1993 and deciphered in 2000) records that the Kushan king Kanishka the Great (c. 127 AD), discarded Greek (Ionian) as the language of administration and adopted Bactrian ("Arya language"), from Falk (2001): "The yuga of Sphujiddhvaja and the era of the Kuṣâṇas." Harry Falk. Silk Road Art and Archaeology VII, p. 133.
- ^ André Wink, Al-Hind, the Making of the Indo-Islamic World: The Slavic Kings and the Islamic conquest, 11th-13th centuries, (Oxford University Press, 1997), 57.
- The Silk Road in World History By Xinru Liu, Pg.61
- Golden 1992, p. 56.
- ^ "Afghanistan: Central Asian and Sassanian Rule, ca. 150 B.C.-700 A.D." United States: Library of Congress Country Studies. 1997. Retrieved 16 August 2012.
- Taagepera, Rein (1979). "Size and Duration of Empires: Growth-Decline Curves, 600 B.C. to 600 A.D.". Social Science History. 3 (3/4): 132. doi:10.2307/1170959. JSTOR 1170959.
- The Dynasty Arts of the Kushans, University of California Press, 1967, p. 5
- http://www.kushan.org/general/other/part1.htm and Si-Yu-Ki, Buddhist Records of the Western World, (Tr. Samuel Beal: Travels of Fa-Hian, The Mission of Sung-Yun and Hwei-S?ng, Books 1–5), Kegan Paul, Trench, Trubner & Co. Ltd. London. 1906 and Hill (2009), pp. 29, 318–350
- which began about 127 CE. "Falk 2001, pp. 121–136", Falk (2001), pp. 121–136, Falk, Harry (2004), pp. 167–176 and Hill (2009), pp. 29, 33, 368–371.
- Grégoire Frumkin (1970). Archaeology in Soviet Central Asia. Brill Archive. pp. 51–. GGKEY:4NPLATFACBB.
- Rafi U. Samad (2011). The Grandeur of Gandhara: The Ancient Buddhist Civilization of the Swat, Peshawar, Kabul and Indus Valleys. Algora Publishing. pp. 93–. ISBN 978-0-87586-859-2.
- Runion, Meredith L. (2007). The history of Afghanistan. Westport: Greenwood Press. p. 46. ISBN 978-0-313-33798-7.
The Yuezhi people conquered Bactria in the second century BCE. and divided the country into five chiefdoms, one of which would become the Kushan Empire. Recognizing the importance of unification, these five tribes combined under the one dominate Kushan tribe, and the primary rulers descended from the Yuezhi.
- ^ Liu, Xinrui (2001). Adas, Michael (ed.). Agricultural and pastoral societies in ancient and classical history. Philadelphia: Temple University Press. p. 156. ISBN 978-1-56639-832-9.
- Enoki, Koshelenko & Haidary 1994, pp. 171–191
- Girshman, Roman. "Ancient Iran: The movement of Iranian peoples". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Retrieved 29 May 2015.
At the end of the 3rd century, there began in Chinese Turkistan a long migration of the Yuezhi, an Iranian people who invaded Bactria about 130 bc, putting an end to the Greco-Bactrian kingdom there. (In the 1st century bc they created the Kushān dynasty, whose rule extended from Afghanistan to the Ganges River and from Russian Turkistan to the estuary of the Indus.)
- Pulleyblank 1966, pp. 9–39
- Mallory 1989, pp. 59–60
- Mallory 1997, pp. 591–593
- Mallory & Mair (2000), pp. 270–297.
- ^ Loewe & Shaughnessy 1999, pp. 87–88
- Benjamin, Craig (October 2003). "The Yuezhi Migration and Sogdia". Transoxiana Webfestschrift. 1 (Ēran ud Anērān). Transoxiana. Retrieved 29 May 2015.
- "Zhang Qian". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Retrieved 29 May 2015.
- West 2009, pp. 713–717
- "They are, by almost unanimous opinion, Indo-Europeans, probably the most oriental of those who occupied the steppes." Roux, p.90
- Hill (2009), p. 36 and notes.
- "Kushan Empire (ca. 2nd century B.C.–3rd century A.D.) | Thematic Essay | Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History | The Metropolitan Museum of Art". metmuseum.org. Retrieved 23 October 2015.
- Hill (2009), p. 311.
- Loewe, Michael A.N. (1979). "Introduction". In Hulsewé, Anthony François Paulus (ed.). China in Central Asia: The Early Stage: 125 BC – AD 23; an Annotated Translation of Chapters 61 and 96 of the History of the Former Han Dynasty. Brill. pp. 1–70. ISBN 978-90-04-05884-2. pp. 23–24.
- Lebedynsky, p. 62.
- Lebedynsky, p. 15.
- Grousset, Rene (1970). The Empire of the Steppes. Rutgers University Press. p. 32. ISBN 0-8135-1304-9.
- ^ Hill (2009), p. 29.
- Chavannes (1907), pp. 190–192.
- S. Frederick Starr, Lost Enlightenment: Central Asia's Golden Age from the Arab Conquest to Tamerlane. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 2013, p. 53
- Starr, p. 53
- ^ Rosenfield, p. 41.
- For "Malwa and Maharashtra, for which it is speculated that the Kushans had an alliance with the Western Kshatrapas", see: Rosenfield, p. 41.
- Hall, D.G.E. (1981). A History of South-East Asia, Fourth Edition. Hong Kong: Macmillan Education Ltd. p. 17. ISBN 0-333-24163-0.
- For a translation of the full text of the Rabatak inscription see: Mukherjee, B.N., "The Great Kushana Testament", Indian Museum Bulletin, Calcutta, 1995. This translation is quoted in: Goyal (2005), p.88.
- For quotation: "The Rabatak inscription claims that in the year 1 Kanishka I's authority was proclaimed in India, in all the satrapies and in different cities like Koonadeano (Kundina), Ozeno (Ujjain), Kozambo (Kausambi), Zagedo (Saketa), Palabotro (Pataliputra) and Ziri-Tambo (Janjgir-Champa). These cities lay to the east and south of Mathura, up to which locality Wima had already carried his victorious arm. Therefore they must have been captured or subdued by Kanishka I himself." see: Goyal, p. 93.
- See also the analysis of Sims-Williams and J. Cribb, specialists of the field, who had a central role in the decipherment: "A new Bactrian inscription of Kanishka the Great", in Silk Road Art and Archaeology No. 4, 1995–1996. pp.75–142.
- Sims-Williams, Nicholas. "Bactrian Documents from Ancient Afghanistan". Archived from the original on 10 June 2007. Retrieved 24 May 2007.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - British Museum display, Asian Art room.
- The Sino-Kharosthi coins of Khotan part 2, Numismatic Chronicle (1984), pp.129-152., by Joe Cribb
- Falk (2001), pp. 121–136.
- Falk (2004), pp. 167–176.
- Xinru Liu, The Silk Road in World History (New York: Oxford University Press, 2010), 47.
- Sivaramamurti, p. 56-59.
- ^ Loeschner, Hans (2012) The Stūpa of the Kushan Emperor Kanishka the Great Sino-Platonic Papers, No. 227 (July 2012); page 11
- ^ Bopearachchi, O. (2007). Some observations on the chronology of the early Kushans. Res Orientales, 17, 41-53
- Sims-Williams, Nicolas. "Bactrian Language". Encyclopaedia Iranica. Vol. 3. London: Routledge & Kegan Paul.
- H. Humbach, 1975, p.402-408. K.Tanabe, 1997, p.277, M.Carter, 1995, p.152. J.Cribb, 1997, p.40. References cited in "De l'Indus à l'Oxus".
- ^ Metropolitan Museum of Art exhibition
- Perkins, J. (2007). Three-headed Śiva on the Reverse of Vima Kadphises's Copper Coinage. South Asian Studies, 23(1), 31-37
- Xinru Liu, The Silk Road in World History (New York: Oxford University Press, 2010), 42.
- Xinru Liu, The Silk Road in World History (New York: Oxford University Press, 2010), 58.
- Neelis, Jason. Early Buddhist Transmission and Trade Networks. 2010. p. 141
- Birmingham Museum of Art (2010). Birmingham Museum of Art: guide to the collection. : Birmingham Museum of Art. p. 51. ISBN 978-1-904832-77-5.
- Hill (2009), p. 31.
- ^ de Crespigny, Rafe. (2007). A Biographical Dictionary of Later Han to the Three Kingdoms (23-220 AD). Leiden: Koninklijke Brill. page 5-6. ISBN 90-04-15605-4.
- ^ Torday, Laszlo. (1997). Mounted Archers: The Beginnings of Central Asian History. Durham: The Durham Academic Press. page 393. ISBN 1-900838-03-6.
- Joe Cribb, 1974, "Chinese lead ingots with barbarous Greek inscriptions in Coin Hoards" pp.76-8
- ^ The Glorious History of Kushana Empire, Adesh Katariya, 2012, p.69
References
- Avari, Burjor (2007). India: The Ancient Past. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-35616-9.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Bopearachchi, Osmund (2003). De l'Indus à l'Oxus, Archéologie de l'Asie Centrale (in French). Lattes: Association imago-musée de Lattes. ISBN 2-9516679-2-2.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Chavannes, Édouard (1906). Trois Généraux Chinois de la dynastie des Han Orientaux. Pan Tch'ao (32–102 p.C.); – son fils Pan Yong; – Leang K'in (112 p.C.). Chapitre LXXVII du Heou Han chou. T'oung pao 7.
{{cite book}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - Faccenna, Domenico (1980). Butkara I (Swāt, Pakistan) 1956–1962, Volume III 1 (in English). Rome: IsMEO (Istituto Italiano Per Il Medio Ed Estremo Oriente).
- Chavannes, Édouard (1907). Les pays d'occident d'après le Heou Han chou. T'oung pao 8. pp. 149–244.
{{cite book}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - Enoki, K.; Koshelenko, G. A.; Haidary, Z. (1 January 1994). "The Yu'eh-chih and their migrations". In Harmatta, János (ed.). History of Civilizations of Central Asia: The Development of Sedentary and Nomadic Civilizations, 700 B. C. to A. D. 250. UNESCO. pp. 171–191. ISBN 9231028464. Retrieved 29 May 2015.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Falk, Harry. 1995–1996. Silk Road Art and Archaeology IV.
- Falk, Harry. 2001. "The yuga of Sphujiddhvaja and the era of the Kuṣāṇas." Silk Road Art and Archaeology VII, pp. 121–136.
- Falk, Harry. 2004. "The Kaniṣka era in Gupta records." Harry Falk. Silk Road Art and Archaeology X, pp. 167–176.
- Golden, Peter B. (1992). An Introduction to the History of the Turkic Peoples. Harrassowitz Verlag.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Goyal, S. R. "Ancient Indian Inscriptions" Kusumanjali Book World, Jodhpur (India), 2005.
- Hill, John E. 2004. The Peoples of the West from the Weilüe 魏略 by Yu Huan 魚豢: A Third Century Chinese Account Composed between 239 and 265 CE. Draft annotated English translation.
- Hill, John E. (2009). Through the Jade Gate to Rome: A Study of the Silk Routes during the Later Han Dynasty, First to Second Centuries CE. BookSurge. ISBN 978-1-4392-2134-1.
- Lebedynsky, Iaroslav (2006). Les Saces. Paris: Editions Errance. ISBN 2-87772-337-2.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Loewe, Michael; Shaughnessy, Edward L. (1999). The Cambridge History of Ancient China: From the Origins of Civilization to 221 BC. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-5214-7030-7. Retrieved 1 November 2013.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Mallory, J. P. (1989). In Search of the Indo-Europeans: Language, Archaeology, and Myth. Thames and Hudson. ISBN 050005052X. Retrieved 29 May 2015.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Mallory, J. P. (1997). Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 1884964982. Retrieved 29 May 2015.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Mallory, J. P.; Mair, Victor H. (2000). "The Tarim Mummies: Ancient China and the Mystery of the Earliest Peoples from the West". London: Thames & Hudson. ISBN 0-500-05101-1.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Invalid|ref=harv(help). - Pulleyblank, Edwin G. (1966). Chinese and Indo-Europeans. University of British Columbia, Department of Asian Studies. Retrieved 14 February 2015.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Rosenfield, John M. (1993). The Dynastic Art of the Kushans. New Delhi: Munshiram Manoharlal. ISBN 81-215-0579-8.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Sivaramamurti, C. (1976). Śatarudrīya: Vibhūti of Śiva's Iconography. Delhi: Abhinav Publications.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Roux, Jean-Paul, L'Asie Centrale, Histoire et Civilization (French), Fayard, 1997, ISBN 978-2-213-59894-9
- "Red Sandstone Railing Pillar." The British Museum Quarterly, vol. 30, no. 1/2, 1965, pp. 64–64. www.jstor.org/stable/4422925.
- Masson, V. M. "The Forgotten Kushan Empire: New Discoveries at Zar-Tepe." Archaeology, vol. 37, no. 1, 1984, pp. 32–37. www.jstor.org/stable/41728802.
- Hoey, W. "The Word Kozola as Used of Kadphises on Ku͟s͟hān Coins." Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland, 1902, pp. 428–429. www.jstor.org/stable/25208419.
- West, Barbara A. (1 January 2009). Encyclopedia of the Peoples of Asia and Oceania. Infobase Publishing. ISBN 1438119135. Retrieved 29 May 2015.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)
Further reading
- Benjamin, Craig (2007). The Yuezhi: Origin, Migration and the Conquest of Northern Bactria. ISD. ISBN 250352429X. Retrieved 29 May 2015.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Dorn'eich, Chris M. (2008). Chinese sources on the History of the Niusi-Wusi-Asi (oi)-Rishi (ka)-Arsi-Arshi-Ruzhi and their Kueishuang-Kushan Dynasty. Shiji 110/Hanshu 94A: The Xiongnu: Synopsis of Chinese original Text and several Western Translations with Extant Annotations. Berlin. To read or download go to:
- Foucher, M. A. 1901. "Notes sur la geographie ancienne du Gandhâra (commentaire à un chaptaire de Hiuen-Tsang)." BEFEO No. 4, Oct. 1901, pp. 322–369.
- Hargreaves, H. (1910–11): "Excavations at Shāh-jī-kī Dhērī"; Archaeological Survey of India, 1910–11, pp. 25–32.
- Iloliev, A. "King of Men: ῾Ali ibn Abi Talib in Pamiri Folktales." Journal of Shi'a Islamic Studies, vol. 8 no. 3, 2015, pp. 307–323. Project MUSE, doi:10.1353/isl.2015.0036.
- Harmatta, János, ed., 1994. History of civilizations of Central Asia, Volume II. The development of sedentary and nomadic civilizations: 700 B.C. to A.D. 250. Paris, UNESCO Publishing.
- Kennedy, J. "The Later Kushans." Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland, 1913, pp. 1054–1064. www.jstor.org/stable/25189078.
- Konow, Sten. Editor. 1929. Kharoshthī Inscriptions with Exception of those of Asoka. Corpus Inscriptionum Indicarum, Vol. II, Part I. Reprint: Indological Book House, Varanasi, 1969.
- Lerner, Martin (1984). The flame and the lotus: Indian and Southeast Asian art from the Kronos collections. New York: The Metropolitan Museum of Art. ISBN 0-87099-374-7.
- Litvinsky, B. A., ed., 1996. History of civilizations of Central Asia, Volume III. The crossroads of civilizations: A.D. 250 to 750. Paris, UNESCO Publishing.
- Liu, Xinru 2001 "Migration and Settlement of the Yuezhi-Kushan: Interaction and Interdependence of Nomadic and Sedentary Societies." Journal of World History, Volume 12, No. 2, Fall 2001. University of Hawaii Press, pp. 261–292. .
- Rife, J. L. "The Making of Roman India by Grant Parker (review)." American Journal of Philology, vol. 135 no. 4, 2014, pp. 672–675. Project MUSE, doi:10.1353/ajp.2014.0046.
- Sarianidi, Viktor. 1985. The Golden Hoard of Bactria: From the Tillya-tepe Excavations in Northern Afghanistan. Harry N. Abrams, Inc. New York.
- Sims-Williams, Nicholas. 1998. "Further notes on the Bactrian inscription of Rabatak, with an Appendix on the names of Kujula Kadphises and Vima Taktu in Chinese." Proceedings of the Third European Conference of Iranian Studies Part 1: Old and Middle Iranian Studies. Edited by Nicholas Sims-Williams. Wiesbaden. 1998, pp. 79–93.
- Spooner, D. B. 1908–9. "Excavations at Shāh-jī-kī Dhērī."; Archaeological Survey of India, 1908–9, pp. 38–59.
- Watson, Burton. Trans. 1993. Records of the Grand Historian of China: Han Dynasty II. Translated from the Shiji of Sima Qian. Chapter 123: "The Account of Dayuan", Columbia University Press. Revised Edition. ISBN 0-231-08166-9; ISBN 0-231-08167-7 (pbk.)
- Zürcher, E. (1968). "The Yüeh-chih and Kaniṣka in the Chinese sources." Papers on the Date of Kaniṣka. Basham, A. L., ed., 1968. Leiden: E. J. Brill. pp. 346–393.
External links
- Kushan dynasty in Encyclopædia Britannica
- Metropolitan Museum capsule history
- New documents help fix controversial Kushan dating at the Wayback Machine (archived 2005-02-04)
- Coins of the Kushans on wildwinds.com
- Antique Indian Coins at the Library of Congress Web Archives (archived 2013-02-07)
- Brief Guide to Kushan History
- The CoinIndia Online Catalogue of Kushan Coins
- Dedicated resource to study of Kushan Empire
| Ancient India and Central Asia | |
|---|---|
| Archaeology and prehistory | |
| Historical peoples and clans | |
| States | |
| Mythology and literature | |
| Middle kingdoms of India | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Empires | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ancient (colonies) | |||
| Post-classical |
| ||
| Modern |
| ||
| Lists | |||
| Miscellaneous |
| ||
- Ancient history of Afghanistan
- Ancient history of Pakistan
- Buddhism in Afghanistan
- Buddhism in India
- Buddhism in Pakistan
- Dynasties of India
- Empires and kingdoms of India
- Former empires in Asia
- Iranian empires
- History of Buddhism
- History of Tajikistan
- Lists of monarchs
- Nomadic groups in Eurasia
- Yuezhi
- 1st-century establishments in India
- 375 disestablishments
- 4th-century disestablishments in India

