| Revision as of 07:14, 24 May 2023 editBernanke's Crossbow (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users7,929 edits "Lithobenzene" only has one hit in the scholarly literature: a review article that's almost certainly citogenesis← Previous edit | Revision as of 07:30, 24 May 2023 edit undoBernanke's Crossbow (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users7,929 edits Fix dropped sentence, image markup, linebreaks, missing cite, and typoNext edit → | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
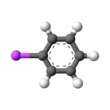
| |ImageName = Kekulé, skeletal formula of phenyllithium | |ImageName = Kekulé, skeletal formula of phenyllithium | ||
| |SystematicName = Phenyllithium<ref>{{Cite web | title = phenyllithium (CHEBI:51470) | url = https://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/searchId.do?chebiId=51470 | work = Chemical Entities of Biological Interest (ChEBI)| publisher = European Bioinformatics Institute | accessdate = 2013-06-01 | location = Cambridge, UK | date = 2009-01-22 | at = Main}}</ref> | |SystematicName = Phenyllithium<ref>{{Cite web | title = phenyllithium (CHEBI:51470) | url = https://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/searchId.do?chebiId=51470 | work = Chemical Entities of Biological Interest (ChEBI)| publisher = European Bioinformatics Institute | accessdate = 2013-06-01 | location = Cambridge, UK | date = 2009-01-22 | at = Main}}</ref> | ||
| |OtherNames = Lithiobenzene<ref>Typically used to describe substituted derivatives. See, e.g., Katsutoshi Kobayashi; Soichi Sato; Horn, Ernst; Naomichi Furukawa (1998), "First isolation and characterization of sulfenium cation salts stabilized by the coordination of two nitrogen atoms," ''Tetrahedron Letters'', '''39''': 17, pp. 2593-2596. ISSN 0040-4039. DOI .</ref> | |||
| |OtherNames = Lithiobenzene{{Citation needed|date = September 2011}} | |||
| |Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers | |Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers | ||
| |Abbreviations = LiPh, PhLi | |Abbreviations = LiPh, PhLi | ||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
| ==Preparation== | ==Preparation== | ||
| Phenyllithium was first produced by the reaction of lithium metal with ]:<ref>{{ cite encyclopedia |author1=Green, D. P. |author2=Zuev, D. | encyclopedia = Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis | year = 2008 | publisher = Wiley and Sons | doi = 10.1002/047084289X.rp076.pub2 | chapter-url = http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/o/eros/articles/rp076/frame.html |isbn=978-0471936237 |chapter=Phenyllithium }}</ref> | Phenyllithium was first produced by the reaction of lithium metal with ]:<ref>{{ cite encyclopedia |author1=Green, D. P. |author2=Zuev, D. | encyclopedia = Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis | year = 2008 | publisher = Wiley and Sons | doi = 10.1002/047084289X.rp076.pub2 | chapter-url = http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/o/eros/articles/rp076/frame.html |isbn=978-0471936237 |chapter=Phenyllithium }}</ref> | ||
| :(C<sub>6</sub>Η<sub>5</sub>)<sub>2</sub>Ηg + 2Li → 2C<sub>6</sub>Η<sub>5</sub>Li + Ηg | :(C<sub>6</sub>Η<sub>5</sub>)<sub>2</sub>Ηg + 2Li → 2C<sub>6</sub>Η<sub>5</sub>Li + Ηg | ||
| Line 64: | Line 63: | ||
| Phenyllithium can also be synthesized with a metal-halogen exchange reaction: | Phenyllithium can also be synthesized with a metal-halogen exchange reaction: | ||
| :n-BuLi + X-Ph → n-BuX + Ph-Li | :n-BuLi + X-Ph → n-BuX + Ph-Li | ||
| Line 71: | Line 69: | ||
| ==Reactions== | ==Reactions== | ||
| The primary use of PhLi is to facilitate formation of carbon-carbon bonds by nucleophilic addition and substitution reactions: | The primary use of PhLi is to facilitate formation of carbon-carbon bonds by nucleophilic addition and substitution reactions: | ||
| :PhLi + R<sub>2</sub>C=O → PhR<sub>2</sub>COLi | :PhLi + R<sub>2</sub>C=O → PhR<sub>2</sub>COLi | ||
| Line 78: | Line 75: | ||
| ==Structure and properties== | ==Structure and properties== | ||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| Phenyllithium is an ] compound that forms monoclinic crystals. Solid phenyllithium can be described as consisting of dimeric Li<sub>2</sub>Ph<sub>2</sub> subunits. The Li atoms and the '']'' carbons of the phenyl rings form a planar four-membered ring. The plane of the phenyl groups are perpendicular to the plane of this Li<sub>2</sub>C<sub>2</sub> ring. Additional strong |
Phenyllithium is an ] compound that forms monoclinic crystals. Solid phenyllithium can be described as consisting of dimeric Li<sub>2</sub>Ph<sub>2</sub> subunits. The Li atoms and the '']'' carbons of the phenyl rings form a planar four-membered ring. The plane of the phenyl groups are perpendicular to the plane of this Li<sub>2</sub>C<sub>2</sub> ring. Additional strong inter­molecular bonding occurs between these phenyllithium dimers and the π-electrons of the phenyl groups in the adjacent dimers, resulting in an infinite polymeric ladder structure.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Dinnebier | first1 = R. E. | last2 = Behrens | first2 = U. | last3 = Olbrich | first3 = F. | title = Lewis Base-Free Phenyllithium: Determination of the Solid-State Structure by Synchrotron Powder Diffraction | journal = ] | year = 1998 | volume = 120 | issue = 7 | pages = 1430–1433 | doi = 10.1021/ja972816e}}</ref> | ||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ⚫ | In solution, it takes a variety of structures dependent on the organic solvent. In ], it equilibrates between monomer and dimer states. In ether, as it is commonly sold, phenyllithium exists as a tetramer. Four Li atoms and four ipso carbon centers occupy |
||
| ] | ] groups omitted for clarity) of a phenyl­lithium etherate tetramer crystal]] | ||
| ⚫ | In solution, it takes a variety of structures dependent on the organic solvent. In ], it equilibrates between monomer and dimer states. In ether, as it is commonly sold, phenyllithium exists as a tetramer. Four Li atoms and four ipso carbon centers occupy alter­nating vertices of a distorted cube. Phenyl groups are at the faces of the tetrahedron and bind to three of the nearest Li atoms. | ||
| The C–Li bond lengths are an average of 2.33 Å. An ether molecule binds to each of the Li sites through its oxygen atom. In the presence of LiBr, a byproduct of directly reacting lithium with a phenyl halide, the complex instead becomes ] and Br atom sits in an adjacent carbon site.<ref>{{cite journal |author1=Hope, H. |author2=Power, P. P. | title = Isolation and Crystal Structures of the Halide-Free and Halide-Rich Phenyllithium Etherate Complexes and | journal = Journal of the American Chemical Society | year = 1983 | volume = 105 | issue = 16 | pages = 5320–5324 | doi = 10.1021/ja00354a022}}</ref> | The C–Li bond lengths are an average of 2.33 Å. An ether molecule binds to each of the Li sites through its oxygen atom. In the presence of LiBr, a byproduct of directly reacting lithium with a phenyl halide, the complex instead becomes . The Li atom of LiBr occupies one of the lithium sites in the ] and Br atom sits in an adjacent carbon site.<ref>{{cite journal |author1=Hope, H. |author2=Power, P. P. | title = Isolation and Crystal Structures of the Halide-Free and Halide-Rich Phenyllithium Etherate Complexes and | journal = Journal of the American Chemical Society | year = 1983 | volume = 105 | issue = 16 | pages = 5320–5324 | doi = 10.1021/ja00354a022}}</ref> | ||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 07:30, 24 May 2023
 | |||
| |||
 | |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name Phenyllithium | |||
| Other names Lithiobenzene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| Abbreviations | LiPh, PhLi | ||
| Beilstein Reference | 506502 | ||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.838 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| Gmelin Reference | 2849 | ||
| MeSH | phenyllithium | ||
| PubChem CID | |||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Chemical formula | LiC 6H 5 | ||
| Molar mass | 84.045 g mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless crystals | ||
| Density | 828 mg cm | ||
| Boiling point | 140 to 143 °C (284 to 289 °F; 413 to 416 K) | ||
| Solubility in water | Reacts | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH298) |
48.3-52.5 kJ mol | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
| Pictograms |   
| ||
| Signal word | Danger | ||
| Hazard statements | H226, H250, H261, H302, H312, H314, H332 | ||
| Precautionary statements | P210, P222, P231+P232, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P312, P301+P330+P331, P302+P334, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P312, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P312, P321, P322, P330, P363, P370+P378, P402+P404, P403+P235, P405, P422, P501 | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Related compounds | phenylcopper, phenylsodium, phenylcobalt | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |||
Phenyllithium is an organometallic agent with the empirical formula C6H5Li. It is most commonly used as a metalating agent in organic syntheses and a substitute for Grignard reagents for introducing phenyl groups in organic syntheses. Crystalline phenyllithium is colorless; however, solutions of phenyllithium are various shades of brown or red depending on the solvent used and the impurities present in the solute.
Preparation
Phenyllithium was first produced by the reaction of lithium metal with diphenylmercury:
- (C6Η5)2Ηg + 2Li → 2C6Η5Li + Ηg
Reaction of a phenyl halide with lithium metal produces phenyllithium:
- X-Ph + 2Li → Ph-Li + LiX
Phenyllithium can also be synthesized with a metal-halogen exchange reaction:
- n-BuLi + X-Ph → n-BuX + Ph-Li
The predominant method of producing phenyllithium today are the latter two syntheses.
Reactions
The primary use of PhLi is to facilitate formation of carbon-carbon bonds by nucleophilic addition and substitution reactions:
- PhLi + R2C=O → PhR2COLi
2-Phenylpyridine is prepared by the reaction of phenyl lithium with pyridine, a process that entails an addition-elimination pathway:
- C6H5Li + C5H5N → C6H5-C5H4N + LiH
Structure and properties

Phenyllithium is an organolithium compound that forms monoclinic crystals. Solid phenyllithium can be described as consisting of dimeric Li2Ph2 subunits. The Li atoms and the ipso carbons of the phenyl rings form a planar four-membered ring. The plane of the phenyl groups are perpendicular to the plane of this Li2C2 ring. Additional strong intermolecular bonding occurs between these phenyllithium dimers and the π-electrons of the phenyl groups in the adjacent dimers, resulting in an infinite polymeric ladder structure.

In solution, it takes a variety of structures dependent on the organic solvent. In tetrahydrofuran, it equilibrates between monomer and dimer states. In ether, as it is commonly sold, phenyllithium exists as a tetramer. Four Li atoms and four ipso carbon centers occupy alternating vertices of a distorted cube. Phenyl groups are at the faces of the tetrahedron and bind to three of the nearest Li atoms.
The C–Li bond lengths are an average of 2.33 Å. An ether molecule binds to each of the Li sites through its oxygen atom. In the presence of LiBr, a byproduct of directly reacting lithium with a phenyl halide, the complex instead becomes . The Li atom of LiBr occupies one of the lithium sites in the cubane-type cluster and Br atom sits in an adjacent carbon site.
References
- Typically used to describe substituted derivatives. See, e.g., Katsutoshi Kobayashi; Soichi Sato; Horn, Ernst; Naomichi Furukawa (1998), "First isolation and characterization of sulfenium cation salts stabilized by the coordination of two nitrogen atoms," Tetrahedron Letters, 39: 17, pp. 2593-2596. ISSN 0040-4039. DOI 10.1016/S0040-4039(98)00277-9.
- "phenyllithium (CHEBI:51470)". Chemical Entities of Biological Interest (ChEBI). Cambridge, UK: European Bioinformatics Institute. 2009-01-22. Main. Retrieved 2013-06-01.
- Wietelmann, U.; Bauer, R. J. "Lithium and Lithium Compounds". [[Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry]]. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a15_393. ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: URL–wikilink conflict (help) - Gilman, H.; Zoellner, E. A.; Selby, W. M. (1932). "An Improved Procedure for the Preparation of Organolithium Compounds". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 54 (5): 1957–1962. doi:10.1021/ja01344a033.
- Green, D. P.; Zuev, D. (2008). "Phenyllithium". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. Wiley and Sons. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rp076.pub2. ISBN 978-0471936237.
- Evans, J. C. W.; Allen, C. F. H. "2-Phenylpyridine" Organic Syntheses (1938), vol. 18, p. 70 doi:10.15227/orgsyn.018.0070
- Dinnebier, R. E.; Behrens, U.; Olbrich, F. (1998). "Lewis Base-Free Phenyllithium: Determination of the Solid-State Structure by Synchrotron Powder Diffraction". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 120 (7): 1430–1433. doi:10.1021/ja972816e.
- Hope, H.; Power, P. P. (1983). "Isolation and Crystal Structures of the Halide-Free and Halide-Rich Phenyllithium Etherate Complexes and ". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 105 (16): 5320–5324. doi:10.1021/ja00354a022.