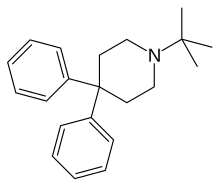
Pharmaceutical compound
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.055.494 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H27N |
| Molar mass | 293.454 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Budipine (brand name Parkinsan) is an antiparkinson agent marketed for the treatment of Parkinson's disease.
While its exact mechanism of action is not well characterized, it is believed to be an NMDA receptor antagonist, but also promoting the synthesis of dopamine.
Because it provides additional benefits relative to existing treatments, it probably does not precisely mimic the mechanism of an existing known treatment.
It is an hERG blocker and can produce long QT syndrome as a side effect.
Analogues include prodipine and medipine.
Synthesis
Budipine can be prepared from the 1-tert-butyl-4-piperidone directly by treatment with benzene in the presence triflic acid. This method of synthesis enables a 99% yield of product.

4-Phenyl-1-t-butyl-4-piperidinol, (1)
1-t-butyl-3-benzoyl-4-phenyl-4-piperidinol (3)
See also
- AD-1211
- Delucemine
- Diphenidine
- Ephenidine
- Fluorolintane
- Lanicemine
- Methoxphenidine (MXP)
- MT-45
- Remacemide
References
- Sweetman SC, ed. (2007). Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference (35th ed.). London: Pharmaceutical Press. ISBN 978-0-85369-687-2.
- ^ Reichmann H (October 2006). "Budipine in Parkinson's tremor". Journal of the Neurological Sciences. 248 (1–2): 53–55. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2006.05.039. PMID 16784759. S2CID 21540225.
- Przuntek H, Müller T (1999). "Clinical efficacy of budipine in Parkinson's disease". Diagnosis and Treatment of Parkinson's Disease — State of the Art. Journal of Neural Transmission. Supplementa. Vol. 56. pp. 75–82. doi:10.1007/978-3-7091-6360-3_3. ISBN 978-3-211-83275-2. PMID 10370903.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - "Budipine". AdisInsight. Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
- Kornhuber J, Herr B, Thome J, Riederer P (1995). "The antiparkinsonian drug budipine binds to NMDA and sigma receptors in postmortem human brain tissue". Journal of Neural Transmission. Supplementum. 46: 131–137. PMID 8821048.
- Palmer GC (September 2001). "Neuroprotection by NMDA receptor antagonists in a variety of neuropathologies". Current Drug Targets. 2 (3): 241–271. doi:10.2174/1389450013348335. PMID 11554551.
- ^ Przuntek H, Bittkau S, Bliesath H, Büttner U, Fuchs G, Glass J, et al. (May 2002). "Budipine provides additional benefit in patients with Parkinson disease receiving a stable optimum dopaminergic drug regimen". Archives of Neurology. 59 (5): 803–806. doi:10.1001/archneur.59.5.803. PMID 12020263.
- Owen JC, Whitton PS (October 2006). "Effects of amantadine and budipine on antidepressant drug-evoked changes in extracellular dopamine in the frontal cortex of freely moving rats". Brain Research. 1117 (1): 206–212. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2006.07.039. PMID 16996043. S2CID 29177107.
- Scholz EP, Zitron E, Kiesecker C, Lueck S, Kathöfer S, Thomas D, Weretka S, Peth S, Kreye VA, Schoels W, Katus HA, Kiehn J, Karle CA (November 2003). "Drug binding to aromatic residues in the HERG channel pore cavity as possible explanation for acquired Long QT syndrome by antiparkinsonian drug budipine". Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 368 (5): 404–414. doi:10.1007/s00210-003-0805-5. PMID 14557918.
- Russ H, Pindur U, Przuntek H (1986). "The interaction of 1-alkyl-4,4-diphenylpiperidines with the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine receptor binding site". J Neural Transm. 65 (3–4): 157–166. doi:10.1007/BF01249078. PMID 3011983.
Other representatives of this class of substances, the 1-alkyl-4,4-diphenylpiperidines, such as, e.g., the 1-isopropyl analogue (prodipine) or the 1-methyl analogue (medipine) have similar pharmacological properties including marked tremorin and reserpin antagonism (Schaefer et al., 1984). The mechanism of action of the 1-alkyl-4,4- diphenylpiperidines is not yet understood in detail.
- Fonne-Pfister R, Meyer UA (October 1988). "Xenobiotic and endobiotic inhibitors of cytochrome P-450dbl function, the target of the debrisoquine/sparteine type polymorphism". Biochem Pharmacol. 37 (20): 3829–3835. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(88)90063-9. PMID 2903741.
Budipine (1-t-butyl-4,4-diphenylpiperidine) (Parkinson's disease treatment); Prodipine (1-isopropyl-4,4-diphenylpiperidine); Medipine (1-methyl-4,4-diphenylpiperidine)
- Klumpp, D. A., Garza, M., Jones, A., Mendoza, S. (1 September 1999). "Synthesis of Aryl-Substituted Piperidines by Superacid Activation of Piperidones". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 64 (18): 6702–6705. doi:10.1021/jo990454i.
- Schaefer H, Hackmack G, Eistetter K, Krüger U, Menge HG, Klosa J (1984). "". Arzneimittel-Forschung (in German). 34 (3): 233–240. PMID 6539602.
- "4-Phenyl-1-t-butyl-4-piperidinol". PubChem. U.S. National Library of Medicine. CID:20536606.
| Antiparkinson agents (N04) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dopaminergics |
| ||||||||||
| Anticholinergics | |||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
This drug article relating to the nervous system is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |