| Troponin C | |
|---|---|
| Test of | Troponin |

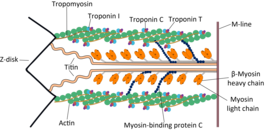
Troponin C is a protein which is part of the troponin complex. It contains four calcium-binding EF hands, although different isoforms may have fewer than four functional calcium-binding subdomains. It is a component of thin filaments, along with actin and tropomyosin. It contains an N lobe and a C lobe. The C lobe serves a structural purpose and binds to the N domain of troponin I (TnI). The C lobe can bind either Ca or Mg. The N lobe, which binds only Ca, is the regulatory lobe and binds to the C domain of troponin I after calcium binding.
Isoforms
| Troponin C, slow skeletal and cardiac muscles | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Symbol | TNNC1 | ||||||
| HGNC | 11943 | ||||||
| OMIM | 191040 | ||||||
| RefSeq | NM_003280 | ||||||
| UniProt | P63316 | ||||||
| Other data | |||||||
| Locus | Chr. 3 p21.1 | ||||||
| |||||||
| Troponin C, skeletal muscle | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Symbol | TNNC2 | ||||||
| HGNC | 11944 | ||||||
| OMIM | 191039 | ||||||
| RefSeq | NP_003270.1 | ||||||
| UniProt | P02585 | ||||||
| Other data | |||||||
| Locus | Chr. 20 q13.12 | ||||||
| |||||||
The tissue specific subtypes are:
- Slow troponin C, TNNC1 (3p21.1 Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): 191040)
- Fast troponin C, TNNC2 (20q12-q13.11, Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): 191039)
Mutations
Point mutations can occur in troponin C inducing alterations to Ca and Mg binding and protein structure, leading to abnormalities in muscle contraction. In cardiac muscle, they are related to dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM).
These known point mutations are:
See also
References
- Kalyva A, Parthenakis FI, Marketou ME, Kontaraki JE, Vardas PE (April 2014). "Biochemical characterisation of Troponin C mutations causing hypertrophic and dilated cardiomyopathies". Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility. 35 (2): 161–78. doi:10.1007/s10974-014-9382-0. PMID 24744096. S2CID 1726747.
- Cheng Y, Regnier M (July 2016). "Cardiac troponin structure-function and the influence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy associated mutations on modulation of contractility". Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. Special Issue: Myofilament Modulation of Contraction. 601: 11–21. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2016.02.004. PMC 4899195. PMID 26851561.
- Pinto JR, Parvatiyar MS, Jones MA, Liang J, Ackerman MJ, Potter JD (July 2009). "A functional and structural study of troponin C mutations related to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 284 (28): 19090–100. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.007021. PMC 2707221. PMID 19439414.
External links
- Troponin+C at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
| Muscle tissue | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smooth muscle | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Striated muscle |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Proteins of the cytoskeleton | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nonhuman | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| See also: cytoskeletal defects | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cell signaling: calcium signaling and calcium metabolism | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell membrane |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Intracellular signaling |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Extracellular chelators |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Calcium-binding domains | |||||||||||||||||